(Press-News.org) As smoky air becomes more common during Washington's wildfire season, many wildlife enthusiasts wonder: What happens to the birds?
Few studies have looked at wildfire smoke impacts on animals, let alone birds. And as Washington and the larger West Coast continue to experience more massive wildfires and smoke-filled air, understanding how birds are affected by smoke -- and how air pollution may influence our ability to detect birds -- are important factors for bird conservation.
Researchers from the University of Washington now provide a first look at the probability of observing common birds as air pollution worsens during wildfire seasons. They found that smoke affected the ability to detect more than a third of the bird species studied in Washington state over a four-year period. Sometimes smoke made it harder to observe birds, while other species were actually easier to detect when smoke was present. The results were published June 29 in the journal Ornithological Applications.
"We want to know how wildfire smoke affects birds and other wildlife, and this study is a great place to start," said lead author Olivia Sanderfoot, a doctoral candidate in the UW School of Environmental and Forest Sciences. "Smoke clearly has an impact on detection of wildlife, and that hasn't been adequately explored in the literature to date. Now we know that smoke pollution specifically affects our observations of birds and our ability to detect them."
The researchers combined data from eBird, an online citizen-science program managed by the Cornell Lab of Ornithology, with publicly available data from an extensive network of air quality monitors across Washington state. They were able to analyze how fine particulate matter, known as PM2.5 and a marker of smoke pollution, affected the probability of observing 71 common bird species during the wildfire seasons of 2015 to 2018. Higher concentrations of smoke affected the chances of observing 37%, or 26, of the bird species included in the study.
Sixteen of the bird species were harder to observe with more wildfire smoke, the study found. These include turkey vultures, Canada geese, two gull species, bald eagles and several other birds of prey. Many of these birds are observed circling high above the ground, so it's not surprising that people would have a harder time detecting them on smoky days, the authors said. However, 10 additional species were easier to observe when smoke concentrations were higher. These include three types of warblers, cedar waxwing, spotted towhee and California quail.
The reasons for this aren't clear and are outside of the scope of this study, but the authors lay out some hypotheses for future exploration. It could be that reduced visibility due to smoke pushes some birds lower to the ground where they can be more easily seen and heard. Or, as smoke prompts birds of prey to relocate, that could alleviate pressure on some songbirds and cause them to be more active -- and thus more detectable by people.
"These behavioral changes are all hypotheticals, and we very much hope that researchers follow up on them because we have a lot to learn about how smoke affects wildlife," Sanderfoot said.
Conservation and management efforts rely on the ability to observe animals in the wild, and it's no different for birds. Air pollution clearly plays a role in detecting animals, and this paper makes the case that it should be considered alongside other factors like time of day, temperature and precipitation that all can influence observations of animals.
"If we see or hear birds more or less frequently because of smoke, that also impacts bigger inferences we make in terms of how certain bird populations are doing," said senior author Beth Gardner, an associate professor in the School of Environmental and Forest Sciences. "We want to get that part right, so we first need to understand the effect of air pollution on how we're seeing birds in the wild."
The researchers chose a four-year study period that included some summers where wildfire smoke was heavy in parts of the state, and other summers where smoke was negligible. All of the species included in the study had to have had at least 750 observations recorded for the first year (2015), and all observations used were within about 20 miles (32 kilometers) of an air quality monitor in Washington.
Data from the catastrophic 2020 wildfire season was not part of this analysis, although air quality during that period was worse than in any of the years in the study. As extreme wildfire seasons like 2020 become more common, it's important to consider the influence of events like these in future studies, the researchers said.
INFORMATION:
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation and the McIntire-Stennis Cooperative Forestry Research Program from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.
For more information, contact Sanderfoot at oliviavs@uw.edu and Gardner at bg43@uw.edu.
Interactive map: https://bit.ly/3dgBUNX
Interactive graph of affected birds: https://bit.ly/35Tfuyg
For the first time, researchers have confirmed the detection of a collision between a black hole and a neutron star. In fact, the scientists detected not one but two such events occurring just 10 days apart in January 2020. The extreme events made splashes in space that sent gravitational waves rippling across at least 900 million light-years to reach Earth. In each case, the neutron star was likely swallowed whole by its black hole partner.
Gravitational waves are disturbances in the curvature of space-time created by massive objects in motion. During the five years since the waves were first measured, a finding that led to the END ...
A long time ago, in two galaxies about 900 million light-years away, two black holes each gobbled up their neutron star companions, triggering gravitational waves that finally hit Earth in January 2020.
Discovered by an international team of astrophysicists including Northwestern University researchers, two events -- detected just 10 days apart -- mark the first-ever detection of a black hole merging with a neutron star. The findings will enable researchers to draw the first conclusions about the origins of these rare binary systems and how often they merge.
"Gravitational ...
Gravitational wave detectors have observed a new type of cataclysmic event in the cosmos: the merger of a neutron star with a black hole.
The phenomenon was detected twice in January 2020.
Several hypotheses could explain the existence of such mixed pairs. Further observations will be needed in order to settle the question.
Another missing piece has just been added to our knowledge of cosmic phenomena. The LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA collaborations have announced the first detection of gravitational waves (1) resulting from the 'mixed' merger between a black hole and a neutron star (2). The discovery, published on June 29, 2021 in Astrophysical Journal Letters, involves CNRS researchers working within ...
LOUISVILLE, Ky. - Historically, most large-scale immunogenomic studies - those exploring the association between genes and disease - were conducted with a bias toward individuals of European ancestry. Corey T. Watson, Ph.D., assistant professor in the University of Louisville Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, is leading a call to actively diversify the genetic resources he and fellow immunogenomics researchers use in their work to advance genomic medicine more equitably.
Watson, along with UofL post-doctoral fellow Oscar Rodriguez, Ph.D., and visiting fellow Yana Safonova, Ph.D., are part of an international group of researchers ...
PHILADELPHIA -- (June 29, 2021) -- New biomarkers that predict HIV remission after antiretroviral therapy (ART) interruption are critical for the development of new therapeutic strategies that can achieve infection control without ART, a condition defined as functional cure. These biomarkers can also provide critical clues into the biological mechanisms that control HIV replication after stopping therapy, and can help design novel strategies to cure HIV. Scientists at The Wistar Institute have identified metabolic and glycomic signatures in the blood of a rare population of HIV-infected individuals who can naturally sustain viral suppression after ART cessation, known as post-treatment controllers. These findings were published in Nature ...
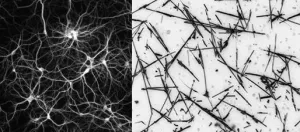
Scientists at the University of Sydney and Japan's National Institute for Material Science (NIMS) have discovered that an artificial network of nanowires can be tuned to respond in a brain-like way when electrically stimulated.
The international team, led by Joel Hochstetter with Professor Zdenka Kuncic and Professor Tomonobu Nakayama, found that by keeping the network of nanowires in a brain-like state "at the edge of chaos", it performed tasks at an optimal level.
This, they say, suggests the underlying nature of neural intelligence is physical, and their discovery opens an exciting avenue for the development of artificial intelligence.
The study is published today in Nature Communications.
"We used wires 10 micrometres long and no thicker than 500 nanometres ...
Researchers from Queen Mary University of London have identified a protein that could be used to aid in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Findings from the new study suggest that a protein called pentraxin 3 (PTX3) may be a specific diagnostic biomarker - or biological measure - for pancreatic cancer, with the ability to differentiate pancreatic cancer from other non-cancerous conditions of the pancreas.
The research was published today in npj Precision Oncology, and primarily funded by the Pancreatic Cancer Research Fund, Barts Charity and Cancer Research UK.
PTX3 levels elevated in patients with pancreatic ...
This press release is in support of a presentation by Dr Maria Cerrillo Martinez presented online at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
29 June 2021: Fertility patients who have a poor response to ovarian stimulation represent a stubborn challenge in IVF. Few eggs are collected, success rates are low, and several treatments are usually needed to achieve pregnancy (if at all). Clinical guidelines indicate that increasing the drug dose for stimulation or applying any of several adjunct therapies are of little benefit. Now, however, a study assessing two cycles of ovarian stimulation and two egg collections in the same menstrual cycle may yet provide ...
This press release is in support of a presentation by Dr Gulam Bahadur presented online at the 37th Annual Meeting of ESHRE.
29 June 2020: Studies indicate that the optimal and safe number of oocytes needed for achieving an ongoing pregnancy is between six and 15. However, the use of egg freezing, frozen embryo replacement (FER) cycles and aggressive stimulation regimes has increased this number in order to boost success rates in older women and in poor responders who produce fewer eggs. What is not known is the impact of numbers of eggs retrieved and of over-stimulation practices on the health of patients, and on their emotional and financial well-being.
Now, a retrospective observational ...
After centuries of human impact on the world's ecosystems, a new study from Flinders University details an example of how a common native bee species has flourished since the very first land clearances by humans on Fiji.
In a new paper in Molecular Ecology (DOI: 10.1111/mec.16034), research led by Flinders University explores a link between the expansion of Homalictus fijiensis, a common bee in the lowlands of Fiji, which has increased its spread on the main island Viti Levu alongside advancing land clearance and the introduction of new plants and weeds to the environment.
"Earlier research connected the relatively recent population expansion to warming climates, ...