The key role of astrocytes in cognitive development
2021-07-01
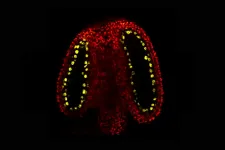
(Press-News.org) Astrocytes are cells in the brain which have long been considered only as mere support cells for neurons. In recent years, the study of astrocytes has grown, gradually revealing their importance in brain function. Researchers from Inserm, CNRS and Collège de France at the Center for Interdisciplinary Research in Biology have now uncovered their crucial role in closing the period of brain plasticity that follows birth, finding them to be key to the development of sensory and cognitive faculties. Over the longer term, these findings will make it possible to envisage new strategies for reintroducing brain plasticity in adults, thereby promoting rehabilitation following brain lesions or neurodevelopmental disorders. This research has been published in Science.
Brain plasticity is a transient key period after birth in which the brain remodels the "wiring" of the neurons according to the external stimulations it receives (environment, interactions, etc.). The end - or "closure" - of this period marks the stabilization of the neural circuits, associated with efficient information processing and normal cognitive development. Plasticity is still possible in the future, although at a much lower level than at the beginning of life.
Problems occurring during the brain plasticity period could have major long-term consequences. For example, in the event of an eye condition preventing an individual from seeing correctly, such as strabismus (crossed eyes), the corresponding brain wiring will be permanently altered if it is not treated in time.
To remedy this, the researchers aim to remodel this wiring by identifying a therapy that would reintroduce brain plasticity, even once closure has occurred. To achieve this, they also seek to better characterize the biological mechanisms that underlie this closure.
Pioneering studies from the 1980s showed that transplanting immature astrocytes into the brains of adult animals reintroduced a period of major plasticity. The team of Inserm researcher and study coordinator Nathalie Rouach at the Center for Interdisciplinary Research in Biology (Inserm/CNRS/Collège de France) took inspiration from this procedure to reveal the hitherto unknown cellular process responsible for the closure of plasticity.
Transplanting immature astrocytes to reintroduce brain plasticity
Through experiments on the mouse visual cortex, the researchers show that the presence of immature astrocytes is the key to brain plasticity. The astrocytes are then later involved in developing interneuron maturation during the plasticity period, ultimately leading to its closure. This maturation process occurs via a novel mechanism involving the protein Connexin 30, of which the researchers found high levels in mature astrocytes during closure.
Could transplanting astrocytes into adult mice reintroduce brain plasticity?
To find out, the researchers cultured immature astrocytes from the visual cortex of young mice (1 to 3 days' old). These immature astrocytes were transplanted into the primary visual cortex of adult mice, following which the activity of the visual cortex was evaluated after four days of monocular occlusion - a standard technique used to assess brain plasticity. They found that the mice transplanted with the immature astrocytes presented a high level of plasticity, unlike the control mice which did not receive the transplant.
"This study is a reminder that in the neurosciences we must not only focus on neurons. The glial cells, of which the astrocytes are a subtype, regulate most of the brain's functions. We realized that these cells have active roles. Glial cells are less fragile than neurons and so represent a more accessible means of acting on the brain, " emphasizes Rouach.
Glial cells account for over half of the brain's cells. They do not have the same cell lineage as neurons and their functions are very different. Until recently they were considered to be the brain's "cleaners", but the researchers realized that they also play an active role in releasing molecules. Compared with neurons, they occur at a later stage in the brain's development, do not communicate in the same way, and are predominant.
INFORMATION:
This research on astrocytes makes it possible to envisage novel cellular and molecular strategies aimed at reopening a period of increased plasticity in adults in order, for example, to promote rehabilitation following a brain lesion, or compensate sensorimotor or psychiatric dysfunction caused by neurodevelopmental disorders.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-01
Hereditary information is passed from parent to offspring in the genetic code, DNA, and epigenetically through chemically induced modifications around the DNA.
New research from the John Innes Centre has uncovered a mechanism which adjusts these modifications, altering the way information beyond the genetic code is passed down the generations.
DNA methylation, one example of these epigenetic modifications, happens when a methyl group or chemical cap is added to the DNA, switching a gene, or genes, on or off.
As germline (eggs and sperm) cells develop some of the methyl markers are reset, affecting the information passed onto the next generation.
How this process ...
2021-07-01
Although plastics have become an essential material, permeating almost all aspects of modern living, many of the inherent properties that make them useful in such a wide variety of applications also make them a serious environmental threat. In a special issue of Science, "Our Plastics Dilemma," four Reviews, two Perspectives, a Policy Forum, an associated Report and two News features examine a wide range of topics related to plastics and the problems they present. "As for much new technology, their development and proliferation occurred with little consideration for their impacts, but now it's impossible to deny their dark side as we confront a rapidly ...
2021-07-01
Through the sequencing of more than 640,000 human exomes, researchers identify rare gene coding variants strongly associated with body mass index (BMI) - including the variant GPR75, which conferred protection from obesity in mouse models. Not only do the findings provide potential therapeutic targets for treating obesity, but they also demonstrate the power and versatility of massive-scale exome sequencing in discovering rare coding variants that could offer new and potentially translatable biological functions. Body fat is a highly heritable trait and the obesity to which body ...
2021-07-01
Researchers could not confirm that a feature that supposedly signals the presence of Majorana bound states - the unusual quasiparticles that may become the cornerstone of topological quantum computing - was in fact due to elusive Majorana particles, in full-shell semiconductor/superconductor nanowires. Rather, this feature, known as zero bias conductance peak, can arise from another quantum phenomenon in these hybrid nanowire structures, the authors say. In recent years, intense research has been conducted on nanowire-based semiconductor-superconductor hybrid systems because predictions suggest that a topological superconductor state with Majorana zero modes (MZMs) can be engineered from them. Even though several experiments in such platforms have reported ...
2021-07-01
Researchers introduce "sci-Space," a new approach to spatial transcriptomics that can retain single-cell resolution and spatial heterogeneity at scales much larger than previous methods. They used their approach to build single-cell atlases of whole sections of mouse embryos at 14 days of development. Single-cell RNA sequencing methods have led to great advances in understanding how organisms and complex tissues develop. Although cells' spatial organization is central to normal development, homeostasis, and pathophysiology, many single-cell RNA sequencing methods lose valuable contextual spatial information. Those that preserve spatial context between cells can be limited to a specific set of genes and/or ...
2021-07-01
A new technique called sci-Space, combined with data from other technologies, could lead to four-dimensional atlases of gene expression across diverse cells during embryonic development of mammals.
Such atlases would map how the gene transcripts in individual cells reflect the passage of time, cell lineages, cell migration, and location on the developing embryo. They would also help illuminate the spatial regulation of gene expression.
Mammalian embryonic development is a remarkable phenomenon: a fertilized egg divides repeatedly and turns, in a matter of weeks or months, into a complex organism capable of a myriad of physiological processes and composed of a variety ...
2021-07-01
Quantum computers promise great advances in many fields - from cryptography to the simulation of protein folding. Yet, which physical system works best to build the underlying quantum bits is still an open question. Unlike regular bits in your computer, these so-called qubits cannot only take the values 0 and 1, but also mixtures of the two. While this potentially makes them very useful, they also become very unstable.
One approach to solve this problem bets on topological qubits that encode the information in their spatial arrangement. That could provide a more stable ...
2021-07-01
Current rates of plastic emissions globally may trigger effects that we will not be able to reverse, argues a new study by researchers from Sweden, Norway and Germany published on July 2nd in Science. According to the authors, plastic pollution is a global threat, and actions to drastically reduce emissions of plastic to the environment are "the rational policy response".
Plastic is found everywhere on the planet: from deserts and mountaintops to deep oceans and Arctic snow. As of 2016, estimates of global emissions of plastic to the world's lakes, rivers and ...
2021-07-01
Scientists have long searched in vain for a class of brain cells that could explain the visceral flash of recognition that we feel when we see a very familiar face, like that of our grandmothers. But the proposed "grandmother neuron"--a single cell at the crossroads of sensory perception and memory, capable of prioritizing an important face over the rabble--remained elusive.
Now, new research reveals a class of neurons in the brain's temporal pole region that links face perception to long-term memory. It's not quite the apocryphal grandmother neuron--rather than a single ...
2021-07-01
The COVID-19 catastrophe in India has resulted in more than 30 million people infected with the virus and nearly 400,000 deaths, though experts are concerned that the figures most likely are much higher. Meanwhile, another public health crisis has emerged along with COVID-19: the widespread misuse of antibiotics.
During India's first surge of COVID-19, antibiotic sales soared, suggesting the drugs were used to treat mild and moderate cases of COVID-19, according to research led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such use is considered inappropriate because antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, not viral infections such as COVID-19, and overuse increases the risk ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The key role of astrocytes in cognitive development