INFORMATION:
Massive exome-wide association study in humans identifies rare variants that protect against obesity
2021-07-01
(Press-News.org) Through the sequencing of more than 640,000 human exomes, researchers identify rare gene coding variants strongly associated with body mass index (BMI) - including the variant GPR75, which conferred protection from obesity in mouse models. Not only do the findings provide potential therapeutic targets for treating obesity, but they also demonstrate the power and versatility of massive-scale exome sequencing in discovering rare coding variants that could offer new and potentially translatable biological functions. Body fat is a highly heritable trait and the obesity to which body fat contributes is linked to a variety of human diseases, including diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. While it's known that genetic factors play an essential role in energy balance and body fat regulation, how genes and rare coding variants can predispose or protect individuals from obesity is not fully understood. Understanding this could provide a pathway to developing safe and effective therapeutic strategies for treating obesity. Parsa Akbari et al. sequenced the exomes of 645,626 individuals from the United Kingdom, United States and Mexico and discovered a set of 16 genes in which rare coding variants exhibited an exome-wide significant association with BMI. One of these, GPR75 - a brain-expressed G protein-coupled receptor - was observed in roughly 4 out of every 10,000 sequenced individuals and associated with lower BMI. Knock-out of this gene in mice resulted in resistance to weight gain and improved glycemic control in a high-fat diet. "The principles of discovery exemplified in the study of Akbari et al. go beyond that of body weight control and obesity," write Giles Yeo and Stephan O'Rahilly in a related Perspective. "It is likely that human exome sequencing at scale will become an increasingly important entry point for the discovery of mechanistic insights into mammalian biology."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In full-shell semiconductor-superconductor nanowires, zero-bias peaks induced by Andreev states, not Majorana modes
2021-07-01
Researchers could not confirm that a feature that supposedly signals the presence of Majorana bound states - the unusual quasiparticles that may become the cornerstone of topological quantum computing - was in fact due to elusive Majorana particles, in full-shell semiconductor/superconductor nanowires. Rather, this feature, known as zero bias conductance peak, can arise from another quantum phenomenon in these hybrid nanowire structures, the authors say. In recent years, intense research has been conducted on nanowire-based semiconductor-superconductor hybrid systems because predictions suggest that a topological superconductor state with Majorana zero modes (MZMs) can be engineered from them. Even though several experiments in such platforms have reported ...
Introducing 'sci-Space,' a new method for embryo-scale, single-cell spatial transcriptomics
2021-07-01
Researchers introduce "sci-Space," a new approach to spatial transcriptomics that can retain single-cell resolution and spatial heterogeneity at scales much larger than previous methods. They used their approach to build single-cell atlases of whole sections of mouse embryos at 14 days of development. Single-cell RNA sequencing methods have led to great advances in understanding how organisms and complex tissues develop. Although cells' spatial organization is central to normal development, homeostasis, and pathophysiology, many single-cell RNA sequencing methods lose valuable contextual spatial information. Those that preserve spatial context between cells can be limited to a specific set of genes and/or ...
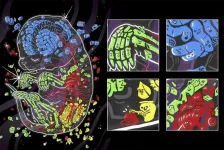
Spatial patterns of gene transcripts captured across single cells of mouse embryo
2021-07-01
A new technique called sci-Space, combined with data from other technologies, could lead to four-dimensional atlases of gene expression across diverse cells during embryonic development of mammals.
Such atlases would map how the gene transcripts in individual cells reflect the passage of time, cell lineages, cell migration, and location on the developing embryo. They would also help illuminate the spatial regulation of gene expression.
Mammalian embryonic development is a remarkable phenomenon: a fertilized egg divides repeatedly and turns, in a matter of weeks or months, into a complex organism capable of a myriad of physiological processes and composed of a variety ...
Unfinding a split electron
2021-07-01
Quantum computers promise great advances in many fields - from cryptography to the simulation of protein folding. Yet, which physical system works best to build the underlying quantum bits is still an open question. Unlike regular bits in your computer, these so-called qubits cannot only take the values 0 and 1, but also mixtures of the two. While this potentially makes them very useful, they also become very unstable.
One approach to solve this problem bets on topological qubits that encode the information in their spatial arrangement. That could provide a more stable ...
Is global plastic pollution nearing an irreversible tipping point?
2021-07-01
Current rates of plastic emissions globally may trigger effects that we will not be able to reverse, argues a new study by researchers from Sweden, Norway and Germany published on July 2nd in Science. According to the authors, plastic pollution is a global threat, and actions to drastically reduce emissions of plastic to the environment are "the rational policy response".
Plastic is found everywhere on the planet: from deserts and mountaintops to deep oceans and Arctic snow. As of 2016, estimates of global emissions of plastic to the world's lakes, rivers and ...
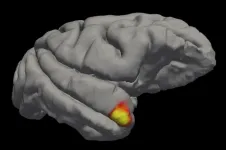
Scientists discover a new class of memory cells in the brain
2021-07-01
Scientists have long searched in vain for a class of brain cells that could explain the visceral flash of recognition that we feel when we see a very familiar face, like that of our grandmothers. But the proposed "grandmother neuron"--a single cell at the crossroads of sensory perception and memory, capable of prioritizing an important face over the rabble--remained elusive.
Now, new research reveals a class of neurons in the brain's temporal pole region that links face perception to long-term memory. It's not quite the apocryphal grandmother neuron--rather than a single ...
COVID-19 aggravates antibiotic misuse in India
2021-07-01
The COVID-19 catastrophe in India has resulted in more than 30 million people infected with the virus and nearly 400,000 deaths, though experts are concerned that the figures most likely are much higher. Meanwhile, another public health crisis has emerged along with COVID-19: the widespread misuse of antibiotics.
During India's first surge of COVID-19, antibiotic sales soared, suggesting the drugs were used to treat mild and moderate cases of COVID-19, according to research led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such use is considered inappropriate because antibiotics are only effective against bacterial infections, not viral infections such as COVID-19, and overuse increases the risk ...
The first commercially scalable integrated laser and microcomb on a single chip
2021-07-01
Fifteen years ago, UC Santa Barbara electrical and materials professor John Bowers pioneered a method for integrating a laser onto a silicon wafer. The technology has since been widely deployed in combination with other silicon photonics devices to replace the copper-wire interconnects that formerly linked servers at data centers, dramatically increasing energy efficiency -- an important endeavor at a time when data traffic is growing by roughly 25% per year.
For several years, the Bowers group has collaborated with the group of Tobias J. Kippenberg at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (EPFL), within the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) Direct On-Chip Digital Optical ...
Scalable manufacturing of integrated optical frequency combs
2021-07-01
Optical frequency combs consist of light frequencies made of equidistant laser lines. They have already revolutionized the fields of frequency metrology, timing and spectroscopy. The discovery of ''soliton microcombs'' by Professor Tobias Kippenberg's lab at EPFL in the past decade has enabled frequency combs to be generated on chip. In this scheme, a single-frequency laser is converted into ultra-short pulses called dissipative Kerr solitons.
Soliton microcombs are chip-scale frequency combs that are compact, consume low power, and exhibit broad bandwidth. Combined with large spacing of comb "teeth", microcombs are uniquely ...
Using computation to improve words: Novel tool could improve serious illness conversations
2021-07-01
Conversations between seriously ill people, their families and palliative care specialists lead to better quality-of-life. Understanding what happens during these conversations - and particularly how they vary by cultural, clinical, and situational contexts - is essential to guide healthcare communication improvement efforts. To gain true understanding, new methods to study conversations in large, inclusive, and multi-site epidemiological studies are required. A new computer model offers an automated and valid tool for such large-scale scientific analyses.
Research results on this model were published today in PLOS ONE.
Developed by a team of computer scientists, clinicians and engineers at the University of Vermont, the approach - called CODYM ...