(Press-News.org) Chemical elements make up pretty much everything in the physical world. As of 2016, we know of 118 elements, all of which can be found categorized in the famous periodic table that hangs in every chemistry lab and classroom.
Each element in the periodic table appears as a one-, two-letter abbreviation (e.g. O for oxygen, Al for aluminum) along with its atomic number, which shows how many protons there are in the element's nucleus. The number of protons is enormously important, as it also determines how many electrons orbit the nucleus, which essentially makes the element what it is and gives it its chemical properties. In short, the atomic number is an element's ID card.
The periodic table should include oxidation states
Publishing in Nature Chemistry, chemical engineers at EPFL's School of Basic Sciences investigate another number that must be reported for each element in the periodic table: the element's oxidation state, also known as oxidation number. Simply put, the oxidation state describes how many electrons an atom must gain or lose in order to form a chemical bond with another atom.
"In chemistry, the oxidation state is always reported in the chemical name of a compound," says Professor Berend Smit who led the research. "Oxidation states play such an important role in the fundamentals of chemistry that some have argued that they should be represented as the third dimension of the periodic table." A good example is chromium: in oxidation state III it is essential to the human body; in oxidation state IV, it is extremely toxic.
Complex materials complicate things
But although figuring out the oxidation state of a single element is pretty straightforward, when it comes to compounds made up of multiple elements, things become complicated. "For complex materials, it is in practice impossible to predict the oxidation state from first principles," says Smit. "In fact, most quantum programs require the oxidation state of the metal as input."
The current state-of-the-art in predicting oxidation states is still based on a something called "bond valence theory" developed in the early 20th century, which estimates the oxidation state of a compound based on the distances between the atoms of its constituent elements. But this doesn't always work, especially in materials with crystal structures. "It is well known that it is not only the distance that matters but also the geometry of a metal complex," says Smit. "But attempts to take this into account have not been very successful."
A machine-learning solution
Until now, that is. In the study, the researchers were able to train a machine-learning algorithm to categorize a famous group of materials, the metal-organic frameworks, by oxidation state.
The team used the Cambridge structural database, a repository of crystal structures in which the oxidation state in given in the name of the materials. "The database is very messy, with many errors and a mixture of experiments, expert guesses, and different variations of the bond valence theory are used to assign oxidation states," says Smit. "We assume that chemistry is self-correcting," he adds. "So while there are many errors on individual accounts, the community as a whole will get it right."
"We basically made a machine-learning model that has captured the collective knowledge of the chemistry community," says Kevin Jablonka, a PhD student in Smit's group at EPFL. "Our machine learning is nothing more than the television game "Who Wants to Be a Millionaire?" If a chemist does not know the oxidation state, one of the lifelines is to ask the audience of chemistry what they think the oxidation state should be. By uploading a crystal structure and our machine-learned model is the audience of chemists that will tell them what the most likely oxidation state is."
INFORMATION:
Reference
Kevin Maik Jablonka, Daniele Ongari, Seyed Mohamad Moosavi, and Berend Smit. Using collective knowledge to assign oxidation states of metal-cations in metal-organic frameworks. Nature Chemistry 05 July 2021. DOI: 10.1038/s41557-021-00717-y
A new organic (carbon-based) semiconducting material has been developed that outperforms existing options for building the next generation of biosensors. An international research team led by KAUST is the first to overcome some critical challenges in developing this polymer.
Much research effort is currently expended into novel types of biosensors that interact directly with the body to detect key biochemicals and serve as indicators of health and disease.
"For a sensor to be compatible with the body, we need to use soft organic materials with ...
Networks of ground-based sensors paired with airborne drones could give firefighters a critical edge when battling wildfires, KAUST researchers have found. The sensor/unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) network could significantly shorten the time taken to detect a wildfire, giving firefighters a better chance to contain the fire before it grows too large to control.
Wildfire detection is currently performed mainly by satellite imaging and remote cameras, but these technologies can be impeded by cloudy weather and fires can grow to a considerable size before they are spotted. With the recent significant global ...
The surprising results of a decade-long investigation by Alessandro Vezzosi and Agnese Sabato provide a strong basis for advancing a project researching Leonardo da Vinci's DNA.
Their extensive study, published by the journal "Human Evolution" (Pontecorboli Editore, Florence), documents with new certainty the continuous male line, from father to son, of the Da Vinci family (later Vinci), from progenitor Michele (born 1331) to grandson Leonardo (6th generation, born 1452) through to today -- 21 generations in all, including five family branches -- and identifies 14 living descendants.
The work fills gaps and corrects errors in previous genealogical research into Leonardo's family, while ...
A new study shows how urbanisation has influenced anthropogenic CO2 and air pollutant emissions across all world regions, by making use of the latest developments in the Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR, https://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu/) developed by the Joint Research Centre of the European Commission. The results show that by 2015 urban centres were the source of a third of global anthropogenic greenhouse gases, and the majority of air pollutant emissions.
The authors, from institutions in France and Italy, used the EDGAR database to provide a country-to-global ...
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden publish new findings in the journal Cancer Discovery showing how pharmacological activation of the protein p53 boosts the immune response against tumours. The results can be of significance to the development of new combination therapies that will give more cancer patients access to immunotherapy.
Given its ability to react to damage to cellular DNA and the key part it is thought to play in preventing tumour growth, the protein p53 has been dubbed the "guardian of the genome". Half of all tumours have mutations in the gene that codes for the protein, and in many other tumours, p53 is disabled by another protein, MDM2.
It has long been known ...
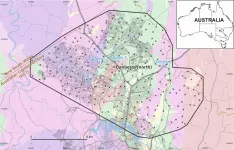
Scientists have taken the first steps in developing a new method of identifying the movements of criminals using chemical analysis of soil and dust found on equipment, clothing and cars. The locating system allows police or security services to match soil remnants found on personal items to regional soil samples, to either implicate or eliminate presence at a crime scene. The work is presented as a Keynote Lecture at the Goldschmidt Geochemistry Conference, after recent publication.
Dr Patrice de Caritat, Principal Research Scientist at Geoscience Australia, Australia's public sector geoscience organisation, said:
"We've ...
A unique study of ancient diamonds has shown that the basic chemical composition of the Earth's atmosphere which makes it suitable for life's explosion of diversity was laid down at least 2.7 billion years ago. Volatile gases conserved in diamonds found in ancient rocks were present in similar proportions to those found in today's mantle, which in turn indicates that there has been no fundamental change in the proportions of volatiles in the atmosphere over the last few billion years. This shows that one of the basic conditions necessary to support life, the presence of life-giving elements in sufficient quantity, appeared soon after Earth formed, and has remained fairly constant ever since.
Presenting the work at the Goldschmidt ...
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. Infusion centers associated with substantially better outcomes than the ER for patients with acute pain events and sickle cell disease
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-7171
Editorial: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M21-2650
Summary: ...
LAWRENCE -- A new paper from a lead author based at the University of Kansas finds wetlands constructed along waterways are the most cost-effective way to reduce nitrate and sediment loads in large streams and rivers. Rather than focusing on individual farms, the research suggests conservation efforts using wetlands should be implemented at the watershed scale.
The paper, just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, relied on computer modeling to examine the Le Sueur River Basin in southern Minnesota, a watershed subject to runoff from intense agricultural production of corn and soybeans -- crops characteristic of the entire ...
In the movie "A Fish Called Wanda", the villain Otto effortlessly gobbles up all the occupants of Ken`s fish tank. Reality, however, is more daunting. At least one unfortunate fan who re-enacted this scene was hospitalized with a fish stuck in the throat. At the same time this also was a painful lesson in ichthyology (the scientific study of fishes), namely that the defense of some fishes consists of needle-sharp fin spines.
Two types of fin elements
Indeed, many fish species possess two types of fin elements, "ordinary" soft fin rays, which are blunt and flexible and primarily serve locomotion, and fin spines, which are sharp and heavily ossified. As fin spines serve the ...