'Zombie cells' hold clues to spinal cord injury repair
2021-07-06
(Press-News.org) Mammals have a poor ability to recover after a spinal cord injury which can result in paralysis. A main reason for this is the formation of a complex scar associated with chronic inflammation that produces a cellular microenvironment that blocks tissue repair. Now, a research team led by Leonor Saude, group leader at Instituto de Medicina Molecular Joao Lobo Antunes (iMM; Portugal) and Professor at Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de Lisboa, have shown that the administration of drugs that target specific cellular components of this scar, improve functional recovery after injury. The results now published in the scientific journal Cell Reports* set the basis for a new promising therapeutic strategy not only for spinal cord injuries, but potentially for other organs that lack regenerative competence.
This study was performed at iMM with collaboration from researchers at CEDOC NOVA Medical School and was funded by "la Caixa" Foundation - CaixaResearch Call and Fundacao para a Ciencia e a Tecnologia (Portugal).
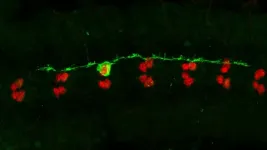
Leonor Saude and her team have been studying spinal cord injury using two different models: the zebrafish, where there is spinal injury recovery, and mammals that show poor recovery. The dense scar that forms at the lesion site has been of particular interest. In mammals, upon spinal cord injury, researchers observed that cells start to accumulate at the lesion periphery. But not any cells: "These cells are known as senescent cells. They have specific features and markers and are what we can call "zombie cells", where growth and division is interrupted, but where the normal cell death program is not activated", explains Leonor Saude.
"While in zebrafish, the accumulation of these cells at the injury periphery is cleared out over time, in mammals, these cells persist and are important components of the dense scar observed. Because senescent cells have specific molecular markers, there are specific drugs that could be tested in this context", says Diogo Paramos-de-Carvalho, first author of the study. "With the administration of different senolytic drugs, that specifically target these senescent cells, we have observed a progressive decrease of these cells, a decrease in the scar extension and lower levels of inflammation due to a decreased secretion of pro-fibrotic and pro-inflammatory factors. The observed changes at the molecular level underlie the improved locomotor, sensory and bladder functions that we have also found", explains Isaura Martins, also first author of the study.
"Although we are still far from healing spinal cord injuries in humans, we are learning more about the molecular signatures of these lesions and these new promising results can open new therapeutic strategies that can be applied not only to spinal cord injuries but in other conditions that lack regenerative competence", says Leonor Saude.
INFORMATION:
*Diogo Paramos-de-Carvalho*, Isaura Martins*, Ana Margarida Cristóvão, Ana Filipa Dias, Dalila Neves-Silva, Telmo Pereira, Diana Chapela, Ana Farinho, António Jacinto, Leonor Saude. (2021) Targeting senescent cells improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Cell Reports.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-06
From the bark of a puppy to the patter of rain against the window, our brains receive countless signals every second. Most of the time, we tune out inconsequential cues--the buzz of a fly, the soft rustle of leaves in the tree--and pay attention to important ones--the sound of a car horn, a bang on the door. This allows us to function, navigate and, indeed, survive in the world around us.
The brain's remarkable ability to sift through this ceaseless flow of information is enabled by an intricate neural network made up of billions of synapses, specialized junctions that regulate signal transmission between and ...
2021-07-06
PITTSBURGH, July 6, 2021 - Scientists from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine described a new phenomenon in which the deletion of a single gene involved in liver embryogenesis completely wipes out bile ducts of newborn mice. But despite a major defect in their bile excretion system, those animals don't die immediately after birth. Rather, they survive for up to eight months and remain physically active, if small and yellow-tinted.
Published today in the journal Cell Reports, the finding offers clues as to why some patients with cholestasis--or impaired ...
2021-07-06
What The Study Did: Rates at which patients with type 2 diabetes received diabetes-related health services prior to and during the COVID-19 pandemic are compared in this study.
Authors: Ateev Mehrotra, M.D., M.P.H., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3047)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
2021-07-06
What The Study Did: COVID-19 vaccine-associated messenger RNA (mRNA) wasn't detected in 13 human milk samples collected after vaccination from seven breastfeeding mothers.
Authors: Stephanie L. Gaw, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.1929)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict ...
2021-07-06
What The Study Did: This study in the Lombardy region of Italy examined the association of different health care professional categories and operational units, including in-hospital wards and outpatient facilities, with the seroprevalence of positive IgG antibody tests for SARS-CoV-2 and the likelihood of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Authors: Piero Poletti, Ph.D., of the Bruno Kessler Foundation in Trento, Italy, and Marcello Tirani, M.D., Directorate General for Health, Lombardy region, in Milan, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.15699)
Editor's Note: The article includes ...
2021-07-06
What The Study Did: This national analysis examined the association between the travel distance to the nearest abortion care facility and abortion rate and the effect of reduced travel distance.
Authors: Kirsten M. J. Thompson, M.P.H., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.15530)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
2021-07-06
What The Study Did: The amount Medicare pays for common generic prescriptions in Part D was compared with prices available to patients without insurance at Costco.
Authors: Erin Trish, Ph.D., of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3366)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked ...
2021-07-06
Melbourne researchers have identified a way to improve the immune response in the face of severe viral infections.
It is widely known that severe viral infections and cancer cause impairments to the immune system, including to T cells, a process called immune 'exhaustion'. Overcoming immune exhaustion is a major goal for the development of new therapies for cancer or severe viral infections.
A team from the Peter Doherty Institute of Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) led by University of Melbourne's Dr Sarah Gabriel, Dr Daniel Utzschneider and Professor Axel Kallies has been able to identify why immune exhaustion occurs and how this may be overcome.
The team had previously identified that while some T cells ...
2021-07-06
Most human cells are able to repair damage by dividing at wounds.
But mature nerve cells (neurons) in our brain are different. If they attempt division, they will likely die - and this is what happens during brain injury, or in conditions such as Alzheimer's Disease (AD). Now new research led by the University of Plymouth has uncovered a pathway that has shed new light on how these divisions may be triggered.
The research, published today in Cell Reports, has focused on intracellular structures called microtubules - which are found in most animal cells, and can be damaged by a build-up of a protein called Tau in the brain during AD.
The study was conducted in fruit flies, with comparison to postmortem brain samples ...
2021-07-06
Can you remember the smell of flowers in your grandmother's garden or the tune your grandpa always used to whistle? Some childhood memories are seemingly engrained into your brain. In fact, there are critical periods in which the brain learns and saves profound cognitive routines and memories. The structure responsible for saving them is called the perineuronal net.
This extracellular structure envelops certain neurons, thereby stabilizes existing connections - the synapses - between them and prevents new ones from forming. But what if we could remove the perineuronal net and restore the adaptability of a young brain? The neuroscientist Sandra Siegert and her research group at IST Austria now ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Zombie cells' hold clues to spinal cord injury repair