INFORMATION:
Triple-negative breast cancer metastases in lungs contain more diverse cells than those in liver
The site of breast cancer metastases dictates their clonal composition and reversible transcriptomic profile
2021-07-07
(Press-News.org) Metastatic tumors originating from notoriously aggressive triple-negative breast cancer that emerge in the lungs contain a more diverse array of cancer cells than those that arise in the liver, according to a new study in mice and organs from deceased cancer patients. The study also identified a set of genes that distinguish lung and liver metastases; together, the findings may inform future research on how targeted therapies impact tumors across various microenvironments. While scientists have known that the presence of distinct tumor cell populations within the same tumor drives breast cancer progression, it has not been fully understood why this dangerous cellular diversity develops within some tumors and not others. To investigate how metastases vary based on host tissue type, Jean Berthelet and colleagues optimized a new optical barcoding strategy and analyzed 31 triple-negative breast cancer subclones (subpopulations of cells descended from cancer cells). The researchers injected fluorescently labeled cells into the mammary fat pads of mice with cancer and mapped the clonal composition of thousands of metastases in the lungs and liver, where triple-negative breast cancer cells tend to spread. They found that the inflammatory tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-? ) pathway was particularly upregulated in metastases in the lungs compared with those in the liver, with some genes in this pathway potentially responsible for the success of lung metastases. Berthelet et al. also collected 4 lung and 7 liver metastases from autopsies of 3 patients with breast cancer, confirming that the genes they identified were also expressed differently between the lungs and liver in humans.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA space lasers map meltwater lakes in Antarctica with striking precision
2021-07-07
From above, the Antarctic Ice Sheet might look like a calm, perpetual ice blanket that has covered Antarctica for millions of years. But the ice sheet can be thousands of meters deep at its thickest, and it hides hundreds of meltwater lakes where its base meets the continent's bedrock. Deep below the surface, some of these lakes fill and drain continuously through a system of waterways that eventually drain into the ocean.
Now, with the most advanced Earth-observing laser instrument NASA has ever flown in space, scientists have improved their maps of these hidden lake systems under the West Antarctic ice sheet--and ...
How plants compensate symbiotic microbes
2021-07-07
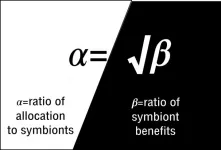
"Equal pay for equal work," a motto touted by many people, turns out to be relevant to the plant world as well. According to new research by Stanford University ecologists, plants allocate resources to their microbial partners in proportion to how much they benefit from that partnership.
"The vast majority of plants rely on microbes to provide them with the nutrients they need to grow and reproduce," explained Brian Steidinger, a former postdoctoral researcher in the lab of Stanford ecologist, Kabir Peay. "The problem is that these microbes differ in how well they do the job. We wanted to see how the plants reward their microbial employees."
In a new study, published July 6 in the journal American Naturalist, the researchers investigated ...
Quantum particles: Pulled and compressed
2021-07-07
Very recently, researchers led by Markus Aspelmeyer at the University of Vienna and Lukas Novotny at ETH Zurich cooled a glass nanoparticle into the quantum regime for the first time. To do this, the particle is deprived of its kinetic energy with the help of lasers. What remains are movements, so-called quantum fluctuations, which no longer follow the laws of classical physics but those of quantum physics. The glass sphere with which this has been achieved is significantly smaller than a grain of sand, but still consists of several hundred million atoms. In contrast to ...
When taste and healthfulness compete, taste has a hidden advantage
2021-07-07
DURHAM, N.C. -- You dash into a convenience store for a quick snack, spot an apple and reach for a candy bar instead. Poor self-control may not be the only factor behind your choice, new research suggests. That's because our brains process taste information first, before factoring in health information, according to new research from Duke University.
"We spend billions of dollars every year on diet products, yet most people fail when they attempt to diet," said study co-author Scott Huettel, a professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke. "Taste seems to have an advantage that sets us up for failure."
"For many individuals, health information enters the decision process ...
Reducing the melting of the Greenland ice cap using solar geoengineering?
2021-07-07
Injecting sulphur into the stratosphere to reduce solar radiation and stop the Greenland ice cap from melting. An interesting scenario, but not without risks. Climatologists from the University of Liège have looked into the matter and have tested one of the scenarios put forward using the MAR climate model developed at the University of Liège. The results are mixed and have been published in the journal The Cryosphere.
The Greenland ice sheet will lose mass at an accelerated rate throughout the 21st century, with a direct link between anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions and the extent of Greenland's mass loss. To combat this phenomenon, and therefore global warming, it is essential to reduce ...
Machine learning tool sorts the nuances of quantum data
2021-07-07
ITHACA, N.Y. - An interdisciplinary team of Cornell and Harvard University researchers developed a machine learning tool to parse quantum matter and make crucial distinctions in the data, an approach that will help scientists unravel the most confounding phenomena in the subatomic realm.
The Cornell-led project's paper, "Correlator Convolutional Neural Networks as an Interpretable Architecture for Image-like Quantum Matter Data," published June 23 in Nature Communications. The lead author is doctoral student Cole Miles.
The Cornell team was led by Eun-Ah Kim, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences, who partnered with Kilian Weinberger, associate professor of computing and information science in the Cornell Ann S. ...
Why insisting you're not racist may backfire
2021-07-07
When you insist you're not racist, you may unwittingly be sending the opposite message.
That's the conclusion of a new study* by three Berkeley Haas researchers who conducted experiments with white participants claiming to hold egalitarian views. After asking them to write statements explaining why they weren't prejudiced against Black people, they found that other white people could nevertheless gauge the writers' underlying prejudice.
"Americans almost universally espouse egalitarianism and wish to see themselves as non-biased, yet racial prejudice persists," says Berkeley ...
New generation anti-cancer drug shows promise for children with brain tumors
2021-07-07
A genetic map of an aggressive childhood brain tumour called medulloblastoma has helped researchers identify a new generation anti-cancer drug that can be repurposed as an effective treatment for the disease.
This international collaboration, led by researchers from The University of Queensland's (UQ) Diamantina Institute and WEHI in Melbourne, could give parents hope in the fight against the most common and fatal brain cancer in children.
UQ lead researcher Dr Laura Genovesi said the team had mapped the genetics of these aggressive brain tumours for five years to find new pathways that existing drugs could potentially target.
"These are drugs already approved for other diseases or cancers but have never been tested in paediatric brain tumours," Dr Genovesi ...
For many students, double-dose algebra leads to college attainment
2021-07-07
ST. LOUIS -- In the United States, low-income and minority students are completing college at low rates compared to higher-income and majority peers -- a detriment to reducing economic inequality. Double-dose algebra could be a solution, according to a new study published in roceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
The paper, "Effects of Double-Dose Algebra on College Persistence and Degree Attainment," is the culmination of a series of studies that followed two cohorts of ninth-grade students over a period of 12 years in the Chicago Public Schools (CPS) where double-dose algebra ...
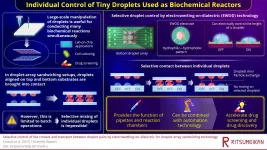
Tiny tools: Controlling individual water droplets as biochemical reactors
2021-07-07
Miniaturization is rapidly reshaping the field of biochemistry, with emerging technologies such as microfluidics and "lab-on-a-chip" devices taking the world by storm. Chemical reactions that were normally conducted in flasks and tubes can now be carried out within tiny water droplets not larger than a few millionths of a liter. Particularly, in droplet-array sandwiching techniques, such tiny droplets are orderly laid out on two parallel flat surfaces opposite to each other. By bringing the top surface close enough to the bottom one, each top droplet makes contact with the opposite bottom droplet, exchanging chemicals and transferring particles or even cells. In quite a literal way, these droplets can act as small reaction ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
[Press-News.org] Triple-negative breast cancer metastases in lungs contain more diverse cells than those in liverThe site of breast cancer metastases dictates their clonal composition and reversible transcriptomic profile