INFORMATION:
Protein-based vaccine candidate combined with potent adjuvant yields effective SARS-CoV-2 protection
2021-07-15
(Press-News.org) A new protein-based vaccine candidate combined with a potent adjuvant provided effective protection against SARS-CoV-2 when tested in animals, suggesting that the combination could add one more promising COVID-19 vaccine to the list of candidates for human use. The protein antigen, based on the receptor binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2, was expressed in yeast instead of mammalian cells - which the authors say could enable a scalable, temperature-stable, low-cost production process well suited for deployment in the developing world. In a study by Maria Pino and colleagues, the adjuvant - a TLR7/TLR8 agonist named 3M-052, formulated with alum - substantially improved performance of the vaccine compared with vaccine adjuvanted with alum alone, inducing stronger antibody and T cell responses in vaccinated rhesus macaques. The vaccine and adjuvant combination also significantly reduced the quantity of virus in the respiratory tracts of macaques challenged by infection with SARS-CoV-2, and reduced lung inflammation as well. Pino et al. vaccinated 5 macaques with the RBD protein and the 3M-052/alum adjuvant and another 5 with the RBD protein and alum alone, each at 0, 4, and 9 weeks; they also included 5 unvaccinated macaques as controls. The vaccine and adjuvant combination induced more neutralizing antibodies with higher binding affinity for the virus RBD and also enhanced CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses compared with the alum-only formulation. About one month after the third round of vaccinations, the researchers then infected the macaques with SARS-CoV-2, and noted the macaques vaccinated with the novel adjuvant formulation showed a reduced viral load in their nasal mucus and lung fluid, as well as fewer inflammatory cytokines in their plasma.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: Incarcerated people placed in solitary confinement differ significantly from others in prison population
2021-07-15
Concern has grown about prison systems' use of extended solitary confinement as a way to manage violent and disruptive incarcerated people. A new study identified groups that are more likely to be placed in extended solitary management (ESM). The study found that individuals sent to ESM differed considerably from the rest of the prison population in terms of mental health, education, language, race/ethnicity, and age.
The study, by researchers at Florida State University and the University of Cincinnati, appears in Justice Quarterly, a publication of the Academy of Criminal Justice Sciences.
"Many ...
Kelp for corn? Illinois scientists demystify natural products for crops
2021-07-15
URBANA, Ill. - Corn growers can choose from a wide array of products to make the most of their crop, but the latest could bring seaweed extract to a field near you. The marine product is just one class in a growing market of crop biostimulants marketed for corn.
Biostimulants benefit crops and soil, but the dizzying array of products has farmers confused, according to Fred Below, corn and soybean researcher at the University of Illinois.
"Farmers hear the term 'plant biostimulant' and think they all do the same thing, and can be used in the same way at the same time. But that's not the case. There's huge confusion ...
Climate regulation changed with the proliferation of marine animals and terrestrial plants
2021-07-15
Earth's climate was relatively stable for a long period of time. For three billion years, temperatures were mostly warm and carbon dioxide levels high - until a shift occurred about 400 million years ago. A new study suggests that the change at this time was accompanied by a fundamental alteration to the carbon-silicon cycle. "This transformation of what was a consistent status quo in the Precambrian era into the more unstable climate we see today was likely due to the emergence and spread of new life forms," said Professor Philip Pogge von Strandmann, a geoscientist at Johannes ...
When fawns perceive constant danger from many sources, they almost seem to relax
2021-07-15
Burnout. It is a syndrome that is said to afflict humans who feel chronic stress. But after conducting a novel study using trail cameras showing the interactions between white-tailed deer fawns and predators, a Penn State researcher suggests that prey animals feel it, too.
"And you can understand why they do," said Asia Murphy, who recently graduated with a doctorate from Penn State's Intercollege Graduate Degree Program in Ecology. "Less than half of whitetail fawns live to see their first birthday, and many are killed by predators, such as coyotes, black ...
Learning aids: Skoltech method helps train computer vision algorithms on limited data
2021-07-15
Researchers from Skoltech have found a way to help computer vision algorithms process satellite images of the Earth more accurately even with very limited data for training. This will make various remote sensing tasks easier for machines and ultimately the people who use their data. The paper outlining the new results was published in the journal Remote Sensing.
Researchers have been using computer vision and machine learning techniques to help with environmental monitoring for a while now. Tasks that may seem tedious and prone to human error are normally a piece of cake for algorithms. But before a neural network can successfully, say, discriminate between the kinds of trees in a forested area, it needs to be trained, ...
High daily screen time linked to cognitive, behavioral problems in children born extremely preterm
2021-07-15
WHAT:
Among 6- and 7-year-olds who were born extremely preterm--before the 28th week of pregnancy--those who had more than two hours of screen time a day were more likely to have deficits in overall IQ, executive functioning (problem solving skills), impulse control and attention, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. Similarly, those who had a television or computer in their bedrooms were more likely to have problems with impulse control and paying attention. The findings suggest that high amounts of screen time may ...
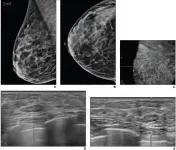
Routine screening for BI-RADS lesions on automated whole-breast ultrasound
2021-07-15
Leesburg, VA, July 15, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), return to routine screening for BI-RADS 3 lesions on supplemental automated whole-breast US (ABUS) substantially reduces the recall rate, while being unlikely to result in adverse outcome.
"This prospective study supports a recommendation for routine annual follow-up for BI-RADS 3 lesions at supplemental ABUS," wrote lead author Richard G. Barr of Northeastern Ohio Medical University in Rootstown.
From August 2013 to December 2016, Barr and colleagues' prospective study (NCT02650778) ...
"Get out of the water!" Monster shark movies massacre shark conservation
2021-07-15
Undeniably the shark movie to end all shark movies, the 1975 blockbuster, Jaws, not only smashed box office expectations, but forever changed the way we felt about going into the water - and how we think about sharks.
Now, more than 40 years (and 100+ shark movies) on, people's fear of sharks persists, with researchers at the University of South Australia concerned about the negative impact that shark movies are having on conservation efforts of this often-endangered animal.
In a world-first study, conservation psychology researchers, UniSA's Dr Briana Le Busque and Associate Professor Carla Litchfield ...
Modified yeast inhibits fungal growth in plants
2021-07-15
About 70-80% of crop losses due to microbial diseases are caused by fungi. Fungicides are key weapons in agriculture's arsenal, but they pose environmental risks. Over time, fungi also develop a resistance to fungicides, leading growers on an endless quest for new and improved ways to combat fungal diseases.
The latest development takes advantage of a natural plant defense against fungus. In a paper published in Biotechnology and Bioengineering, engineers and plant pathologists at UC Riverside describe a way to engineer a protein that blocks fungi from breaking down cell walls, as well as a way to produce this protein in quantity for external application as a natural fungicide. The work could lead to a new way of controlling plant disease that reduces reliance on conventional ...
Emotion, cooperation and locomotion crucial from an early age
2021-07-15
What are the fundamental skills that young children need to develop at the start of school for future academic success? While a large body of research shows strong links between cognitive skills (attention, memory, etc.) and academic skills on the one hand, and emotional skills on the other, in students from primary school to university, few studies have explored these links in children aged 3 to 6 in a school context. Researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and Valais University of Teacher Education, Switzerland (HEP-VS), in collaboration with teachers from Savoie in France and their pedagogical advisor, examined the links between emotion knowledge, cooperation, locomotor activity and numerical skills in 706 pupils aged 3 to 6. The results, to be read in the journal ...