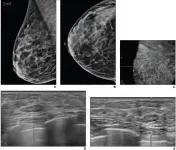
Routine screening for BI-RADS lesions on automated whole-breast ultrasound
Return to routine screening for BI-RADS 3 lesions on supplemental automated whole-breast ultrasound substantially reduces the recall rate, while being unlikely to result in adverse outcome
2021-07-15
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, July 15, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), return to routine screening for BI-RADS 3 lesions on supplemental automated whole-breast US (ABUS) substantially reduces the recall rate, while being unlikely to result in adverse outcome.
"This prospective study supports a recommendation for routine annual follow-up for BI-RADS 3 lesions at supplemental ABUS," wrote lead author Richard G. Barr of Northeastern Ohio Medical University in Rootstown.
From August 2013 to December 2016, Barr and colleagues' prospective study (NCT02650778) enrolled patients with BI-RADS 1 or 2 on screening mammography and breast density C or D to undergo supplemental ABUS, which was interpreted as BI-RADS 1, 2, 3, or 0. For ABUS BI-RADS 1, return to routine screening was recommended, whereas ABUS BI-RADS 0 lesions underwent targeted hand-held ultrasound.
In 2,257 women (mean age, 58 years), routine follow-up of BI-RADS 3 lesions detected on supplemental ABUS screening in women with dense breasts and any risk resulted in a recall rate of 3.8% (85/2,257), biopsy rate of 0.5% (12/2,257), and positive biopsy rate of 58.3% (7/12)--with no missed cancers (95% CI, 0.0-0.86%).
Noting that ABUS can help mitigate acquisition variability by standardizing the documentation, recording, and archiving of ultrasound images from the entire breast (excluding the axilla), Barr et al. reiterated that ABUS images of similar quality can be obtained from adequately trained ultrasonographers and mammographers.
"Avoiding earlier follow-up for these probably benign lesions can be associated with substantial cost savings," the authors of this AJR article added.
INFORMATION:
Founded in 1900, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is the first and oldest radiological society in North America, dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of radiology and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in medical imaging since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with an annual scientific meeting, monthly publication of the peer-reviewed American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), quarterly issues of InPractice magazine, AJR Live Webinars and Podcasts, topical symposia, print and online educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-15
Undeniably the shark movie to end all shark movies, the 1975 blockbuster, Jaws, not only smashed box office expectations, but forever changed the way we felt about going into the water - and how we think about sharks.
Now, more than 40 years (and 100+ shark movies) on, people's fear of sharks persists, with researchers at the University of South Australia concerned about the negative impact that shark movies are having on conservation efforts of this often-endangered animal.
In a world-first study, conservation psychology researchers, UniSA's Dr Briana Le Busque and Associate Professor Carla Litchfield ...
2021-07-15
About 70-80% of crop losses due to microbial diseases are caused by fungi. Fungicides are key weapons in agriculture's arsenal, but they pose environmental risks. Over time, fungi also develop a resistance to fungicides, leading growers on an endless quest for new and improved ways to combat fungal diseases.
The latest development takes advantage of a natural plant defense against fungus. In a paper published in Biotechnology and Bioengineering, engineers and plant pathologists at UC Riverside describe a way to engineer a protein that blocks fungi from breaking down cell walls, as well as a way to produce this protein in quantity for external application as a natural fungicide. The work could lead to a new way of controlling plant disease that reduces reliance on conventional ...
2021-07-15
What are the fundamental skills that young children need to develop at the start of school for future academic success? While a large body of research shows strong links between cognitive skills (attention, memory, etc.) and academic skills on the one hand, and emotional skills on the other, in students from primary school to university, few studies have explored these links in children aged 3 to 6 in a school context. Researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) and Valais University of Teacher Education, Switzerland (HEP-VS), in collaboration with teachers from Savoie in France and their pedagogical advisor, examined the links between emotion knowledge, cooperation, locomotor activity and numerical skills in 706 pupils aged 3 to 6. The results, to be read in the journal ...
2021-07-15
Contamination of urban lakes, rivers and surface water by human waste is creating pools of 'superbugs' in Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMIC) - but improving access to clean water, sanitation and sewerage infrastructure could help to protect people's health, a new study reveals.
Researchers studied bodies of water in urban and rural sites in three areas of Bangladesh - Mymensingh, Shariatpur and Dhaka. They found more antibiotic resistant faecal coliforms in urban surface water compared to rural settings, consistent with reports of such bacteria in rivers across Asia.
Publishing their findings in mSystems today, researchers from the University of Birmingham and the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh call for further research to quantify the drivers ...
2021-07-15
COVID-19 NEWS: CAN DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS HELP THE IMMUNE SYSTEM FIGHT CORONAVIRUS INFECTION?
Media Contact: Patrick Smith, pjsmith88@jhmi.edu
Johns Hopkins Medicine gastroenterologist Gerard Mullin, M.D., and a team of co-authors published an article May 11, 2021, in Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology that details the scientific rationale and possible benefits -- as well as possible drawbacks -- of several dietary supplements currently in clinical trials related to COVID-19 treatment.
According to business analysts, the U.S. nutritional supplement industry grew as much as 14.5% in 2020, due in large part to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mullin, associate professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University ...
2021-07-15
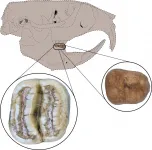
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Two fossil teeth from a distant relative of North American gophers have scientists rethinking how some mammals reached the Caribbean Islands.
The teeth, excavated in northwest Puerto Rico, belong to a previously unknown rodent genus and species, now named Caribeomys merzeraudi. About the size of a mouse, C. merzeraudi is the Caribbean's smallest known rodent and one of the region's oldest, dating back about 29 million years.
It also represents the first discovery of a Caribbean rodent from a North American lineage, a finding that complicates an idea ...
2021-07-15
A new study by the University of Malta and Staffordshire University highlights an urgent need for change in the curriculum and demonstrates how introducing longer, more frequent and more physically intense PE lessons can significantly improve children's weight and overall health.
Malta currently has one of the highest rates of obesity worldwide with 40% of primary and 42.6% of secondary school children being overweight or obese.
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that children engage in at least 60 minutes of age-appropriate moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) daily, however ...
2021-07-15
New Rochelle, NY, July 14, 2021-Firsthand reports from nurses in correctional facilities detail the challenges they faced during the COVID-19 pandemic. These firsthand accounts are reported in a special issue on correctional nursing in the Journal of Correctional Health Care. Click here (https://www.liebertpub.com/toc/jchc/27/2) to read the issue now.
Karen Monsen, PhD, RN, School of Nursing, University of Minnesota, and colleagues present the Omaha System COVID-19 Response Guidelines, which provide evidence-based pandemic response interventions used in correctional ...
2021-07-15
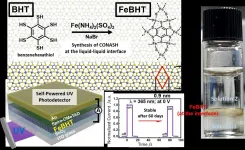
Converting light to electricity effectively has been one of the persistent goals of scientists in the field of optoelectronics. While improving the conversion efficiency is a challenge, several other requirements also need to be met. For instance, the material must conduct electricity well, have a short response time to changes in input (light intensity), and, most importantly, be stable under long-term exposure.
Lately, scientists have been fascinated with "coordination nanosheets" (CONASHs), that are organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials in which organic molecules are bonded to metal atoms in a 2D network. The interest in CONASHs stems mainly from their ability to absorb light at multiple wavelength ranges and convert ...
2021-07-15
Indiana Jones hates snakes. And he's certainly not alone. The fear of snakes is so common it even has its own name: ophidiophobia.
Kibret Mequanint doesn't particularly like the slithery reptiles either (he actually hates them too) but the Western University bioengineer and his international collaborators have found a novel use for snake venom: a body tissue 'super glue' that can stop life-threatening bleeding in seconds.
Over the past 20 years, Mequanint has developed a number of biomaterials-based medical devices and therapeutic technologies - some of which are either licensed to medical companies or are in the advanced stage of preclinical testing.
His latest collaborative research discovery ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Routine screening for BI-RADS lesions on automated whole-breast ultrasound
Return to routine screening for BI-RADS 3 lesions on supplemental automated whole-breast ultrasound substantially reduces the recall rate, while being unlikely to result in adverse outcome