Evidence of sustained benefits of pimavanserin for dementia-related psychosis
2021-07-22
(Press-News.org) Evidence of the sustained benefits of an investigational antipsychotic treatment for people with dementia-related psychosis has been published.
Up to half of the 45 million people worldwide who are living with Alzheimer's disease will experience psychotic episodes, a figure that is even higher in some other forms of dementia. Psychosis is linked to a faster deterioration in dementia.
Despite this, there is no approved safe and effective treatment for these particularly distressing symptoms. In people with dementia, widely-used antipsychotics lead to sedation, falls and increased risk of deaths.
Pimavanserin works by blocking serotonin 5HT2A receptors, and doesn't interact with the dopamine receptors. It is licensed in the US to treat hallucinations and delusions in people with Parkinson's disease psychosis.
A new paper published in the New England Journal of Medicine outlines a clinical trial, conducted in 392 people with psychosis associated with Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Lewy body, frontotemporal, or vascular dementia. All participants were given pimavanserin for 12 weeks. Those who met a threshold of symptom improvement were then assigned to pimavanserin or placebo for up to 26 weeks.
The trial was stopped early for positive efficacy results. Of the 351 participants, 217 (61.8%) had a sustained initial treatment benefit, of whom 112 were assigned to placebo and 105 to pimavanserin. Relapse occurred in 28/99 (28.3%) of the placebo group, compared to 12/95 (12.6%) of the pimvanserin group, with pimvanserin more than halving the relapse rate and significantly improving the sustained benefit.
Professor Clive Ballard, Executive Dean of the University of Exeter Medical School, said: "Psychosis affects up to half of all people with dementia, and it's a particularly distressing symptom - yet there's currently no safe and effective treatment. Currently used antipsychotics are known to cause harms, and best practice guidelines recommend prescribing for no longer than 12 weeks for people with dementia as a result. We urgently need alternatives. It's exciting that the relapse rate in the pimavanserin group was lower than the placebo group, indicating that the treatment benefits may be sustained over time. We now need longer and larger scale trials to explore this further."
The trial found headache, urinary tract infection and constipation occurred more frequently in the pimavanserin group, but there was no increase in mortality or the other serious events, such as stroke, which are known to increase with other antipsychotics.
INFORMATION:
The full paper is entitled 'Trial of Pimavanserin in Dementia-related psychosis', published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-07-22
EAST LANSING, Mich. - In the wild, inheriting advantageous physical traits may be the difference between a long life and a short one. But for the spotted hyena, another kind of inheritance, one that has nothing to do with genetics, turns out to be extremely important for health and longevity -- social networks inherited from their mothers.
A new study, based on 27 years of observational data from Michigan State University Distinguished Professor Kay Holekamp, expands a previously established theoretical model of spotted hyena social networking to show how these networks emerge, how long they last and how they affect a hyena's life trajectory.
The paper is featured as the front cover for the journal Science.
"There ...
2021-07-22
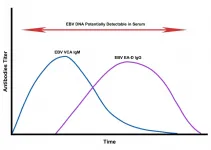
Two recently published studies available on the National Institutes of Health (NIH) website indicate Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation may play a role both in the development of long COVID symptoms, as well as severe COVID-19 cases.
The first evidence linking EBV reactivation to long COVID symptoms was discovered by Gold et al. (2021) and published in Pathogens. This study can be viewed on the NIH website here: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8233978/
"We ran Epstein-Barr virus serological tests on COVID-19 patients at least 90 days after testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, comparing EBV ...
2021-07-21
Alexandria, Va., USA - Walter Siqueira, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada, presented the poster "Self-collected Saliva and Courier Service - A Feasible Diagnostic Strategy for COVID-19" at the virtual 99th General Session & Exhibition of the International Association for Dental Research (IADR), held in conjunction with the 50th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Dental Research (AADR) and the 45th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), on July 21-24, 2021.
Saliva has been proposed as a convenient and cost-effective biofluid for diagnostic purposes and in vitro studies have shown that the addition of stabilizers to saliva preserves it for up to 7-10 days at room temperature, but its translational application ...
2021-07-21
Although Enterococcus faecalis is usually an innocuous member of the bacterial community in the human gut, it can also cause several infections, including liver disorders. The bacteria produce cytolysins, which are molecules that destroy cells. In a new study, researchers have uncovered how they do so.
"Your chances of dying increase by 5-fold when you get infected by E. faecalis that can make cytolysin compared to those that cannot," said Wilfred van der Donk (MMG), a professor of chemistry and investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. "Cytolysin is an important molecule and it has been known since the 1930s, our lab determined the ...
2021-07-21
Researchers from the University of Southern California (USC) Department of Computer Science and NVIDIA have unveiled a new simulator for robotic cutting that can accurately reproduce the forces acting on a knife as it slices through common foodstuffs, such as fruit and vegetables. The system could also simulate cutting through human tissue, offering potential applications in surgical robotics. The paper was presented at the Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS) Conference 2021 on July 16, where it received the Best Student Paper Award.
In the past, researchers have had trouble creating intelligent ...
2021-07-21
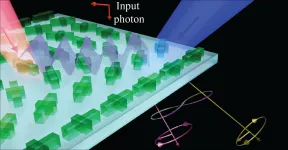
Los Alamos, N.M., July 21, 2021--A team of scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory propose that modulated quantum metasurfaces can control all properties of photonic qubits, a breakthrough that could impact the fields of quantum information, communications, sensing and imaging, as well as energy and momentum harvesting. The results of their study were released yesterday in the journal Physical Review Letters, published by the American Physical Society.
"People have studied classical metasurfaces for a long time," says Diego Dalvit, who works in the Condensed Matter and Complex Systems group at the Laboratory's Theoretical Division. "But we came up with this new idea, which was to modulate in time and space the optical properties of ...
2021-07-21
Northwestern University researchers have developed a new framework using machine learning that improves the accuracy of interatomic potentials -- the guiding rules describing how atoms interact -- in new materials design. The findings could lead to more accurate predictions of how new materials transfer heat, deform, and fail at the atomic scale.
Designing new nanomaterials is an important aspect of developing next-generation devices used in electronics, sensors, energy harvesting and storage, optical detectors, and structural materials. To design these materials, researchers create interatomic potentials through atomistic modeling, a computational approach that predicts how these materials behave by accounting for their ...
2021-07-21
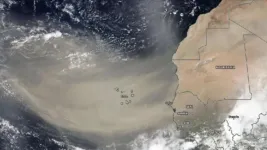
In a recently published paper, a research team, led by University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science Professor Emeritus Joseph M. Prospero, chronicles the history of African dust transport, including three independent "first" discoveries of African dust in the Caribbean Basin in the 1950s and 1960s.
Every year, mineral-rich dust from North Africa's Sahara Desert is lifted into the atmosphere by winds and carried on a 5,000-mile journey across the North Atlantic to the Americas. African dust contains iron, phosphorus and other important nutrients that are essential for life in marine and terrestrial ...
2021-07-21
BROOKLYN, New York, Weekday, Month xx, 2021 - The remarkable structural properties of the Venus' flower basket sponge (E. aspergillum) might seem fathoms removed from human-engineered structures. However, insights into how the organism's latticework of holes and ridges influences the hydrodynamics of seawater in its vicinity could lead to advanced designs for buildings, bridges, marine vehicles and aircraft, and anything that must respond safely to forces imposed by the flow of air or water.
While past research has investigated the structure of the sponge, there have been few studies of the hydrodynamic fields surrounding and penetrating the organism, and whether, besides improving its mechanical ...
2021-07-21
BROOKLYN, New York, Wednesday, July 21, 2021 - This week, at the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 21), researchers at the END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Evidence of sustained benefits of pimavanserin for dementia-related psychosis