(Press-News.org) Black men have a higher death rate within 30 days of surgery compared with any other subgroup of race and sex, finds a study of adults in the United States published in The BMJ.
This inequality in death rate was mainly observed for elective, or planned, surgeries, where the death rate for Black men was 50% higher than that of White men.
The researchers say further research is needed to understand better the “factors contributing to this higher mortality rate among Black men after elective surgery.”
In previous studies, racial inequities in surgical care and outcomes, including a higher death rate following surgery for Black patients, have been well documented.
However, less is known of how surgical outcomes differ by the race and sex of patients undergoing both elective or non-elective (urgent or emergency) surgeries.
To fill in this knowledge gap, the researchers used nationwide Medicare data on 1,868,036 adults with an average age of 75 years who underwent one of eight surgeries —abdominal aortic aneurysm repair, appendectomy, cholecystectomy, colectomy, coronary artery bypass surgery, hip replacement, knee replacement, and lung resection—between 2016–2018.
They analysed data for differences in death rates between subgroups of race and sex, following elective or urgent surgeries
Of the adults included in this study, 40.7% were White men, 53.4% were White women, 2.2% were Black men, and 3.7% were Black women. Just over 70% of the surgeries were elective.
After accounting for other potentially influential factors such as age, disability, and a range of underlying chronic conditions, the researchers found that Black men had a higher death rate (3.05%) within 30 days of both urgent and elective surgery than White men (2.69%), White women (2.38%), and Black women (2.18%).
A similar pattern was found for elective surgery: Black men had a higher death rate (1.3%) than White men (0.85%), White women (0.82%), and Black women (0.79%).
This 0.45 percentage point difference between Black and White men “implies that mortality after elective procedures was 50% higher in Black men compared with White men", say the researchers.
And much of this difference persisted even when patients operated on by the same surgeon were compared, they note.
The researchers did not find a statistically significant difference between Black and White men following urgent surgery, with death rates of 6.69% and 7.03%, respectively.
They did, however, find that deaths after urgent surgery were lower for both White and Black women, than men of either race, at 6.12% and 5.29%, respectively.
This is an observational study, so cannot establish cause, and the researchers acknowledge that their results were limited to Black and White Medicare patients undergoing certain procedures, so may not apply to other groups or types of surgery.
However, results remained largely unchanged after further sensitivity analyses, suggesting that they are robust.
The researchers suggest that structural racism within society, such as higher rates of poverty among Black patients, which can lead to poorer underlying health and challenges accessing care, may, at least partially, explain their findings, and say better standardisation of care is needed to help mitigate some of these factors and reduce inequities in surgical outcomes.
“Further research is needed to understand better the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative factors contributing to this higher mortality rate among Black men after elective surgery, ” they conclude.
END
Black men more likely to die after surgery than White men, or women of either race
Unequal post-surgery death rate mainly applies to planned surgeries. Findings highlight the need for better understanding of the challenges facing Black men requiring surgery in the US
2023-03-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US government catalyzed and substantially invested in mRNA covid-19 vaccine development over decades
2023-03-02
In the 35 years before the covid-19 pandemic, the US government invested at least $337 million into critical research that led to the mRNA covid-19 vaccines, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The US government also paid $31.6 billion during the pandemic to support vaccine research, production, and to purchase vaccines for all Americans and for global donation.
These public investments saved millions of lives - and mRNA vaccine technology also has the potential to address future pandemics and treat other diseases. But the researchers ...
Public investment in critical research contributed to the success of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines
2023-03-02
Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech have recently announced plans to increase the price of their respective mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, thrusting them into the spotlight of debates around drug price hikes. A new study, led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, analyzed the role of public funding in the development of mRNA vaccines. In a systematic assessment, the team found that over the last 35 years, three federal agencies—the National Institutes of Health, the Department ...
Only two in five British businesses have introduced support to help staff with the rising cost of living as many see operating costs rise
2023-03-02
New research from the Work Foundation at Lancaster University reveals that while two thirds of senior business leaders (66%) agree that employers have a ‘substantial role’ to play in supporting staff through the rising cost of living, only 40% have introduced new support measures since the start of 2022.
At the same time, four in ten business leaders (41%) also report increases in production costs in their organisation. Pressures that are likely to increase, the Work Foundation ...
Fishing for proteins: Scientists use new optical tweezer technology to study DNA repair
2023-03-02
Tucked away in a small, dark room at UPMC Hillman Cancer Center, Brittani Schnable is on a fishing expedition.
Wielding a joystick similar to those used by video gamers, she casts microscopic beads into an ocean of molecules, pushing and pulling the beads apart until they eventually catch a strand of DNA. After a few taps of the keyboard, a lightshow begins. A burst of colors flashes across the black screen like fireworks exploding in the night sky.
Although these colors seem random at first, a pattern starts to emerge. Lines of blue and red light streak across the screen: A DNA repair protein has bound to the site of damage.
Schnable, a Ph.D. student in Dr. Bennett ...
Can’t exercise a particular muscle? Strengthening the opposite side of your body can stop it wasting away
2023-03-02
Loss of muscle strength can be one of the most damaging outcomes when someone is unable to move a part of their body for a long period of time.
But a new Edith Cowan University (ECU) study may have found a way to offset or even protect against this — and it doesn’t even involve the affected body part at all.
Injury or illness may see a part of the body incapacitated for weeks or even months, causing unused muscles to weaken and lose their mass and strength, which can have ...
Physical activity can help mental health in pre-teen years
2023-03-02
Regular physical activity can improve adolescents’ mental health and help with behavioural difficulties, research suggests.
Engaging in regular moderate to vigorous physical activity at age 11 was associated with better mental health between the ages of 11 and 13, the study found.
Physical activity was also associated with reduced hyperactivity and behavioural problems, such as loss of temper, fighting with other children, lying, and stealing, in young people.
Researchers from the Universities of Edinburgh, Strathclyde, Bristol, and Georgia in the United States explored data from the Children of the 90s study (also known as the Avon Longitudinal Study of ...
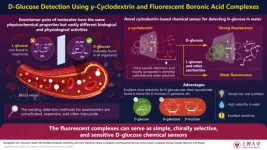
New fluorescent chiral-selective receptor system represents a breakthrough in molecular detection with potential for applications in diabetes management
2023-03-02
Diabetes mellitus, simply called diabetes, is a metabolic disorder characterized by the presence of abnormally high concentrations of glucose in blood. Existing methods for the diagnosis of diabetes rely on traditional techniques of detecting glucose in blood serum samples—a process that is typically tedious and expensive.
Molecular recognition is the science of accurately detecting specific compounds by exploiting their binding properties. Here, a receptor molecule–a kind of sensor–selectively binds to a target molecule. This process triggers some reaction, say, a change ...
Sleep too much or too little and you might get sick more, scientists find
2023-03-02
A good night’s sleep can solve all sorts of problems – but scientists have now discovered new evidence that sleeping well may make you less vulnerable to infection. Scientists at the University of Bergen recruited medical students working in doctors’ surgeries to hand out short questionnaires to patients, asking about sleep quality and recent infections. They found that patients who reported sleeping too little or too much were more likely also to report a recent infection, and patients ...
Study suggests EHR-focused interventions can significantly reduce unnecessary urine cultures among hospital patients
2023-03-02
Study Suggests EHR-Focused Interventions Can Significantly Reduce Unnecessary Urine Cultures Among Hospital Patients
Initiative highlighted in AJIC provides model for resource-limited institutions to decrease overdiagnosis and overtreatment of asymptomatic bacterial infections
Arlington, Va., March 2, 2023 – Physicians in the largest safety-net hospital system in the United States used two electronic health record (EHR)-focused interventions to significantly reduce inappropriate urine cultures among hospitalized patients. Findings from their study, published in the ...
Edible electronics: How a seaweed second skin could transform health and fitness sensor tech
2023-03-02
Scientists at the University of Sussex have successfully trialed new biodegradable health sensors that could change the way we experience personal healthcare and fitness monitoring technology.
The team at Sussex have developed the new health sensors – such as those worn by runners or patients to monitor heart rate and temperature – using natural elements like rock salt, water and seaweed, combined with graphene. Because they are solely made with ingredients found in nature, the sensors are fully biodegradable, making them more environmentally friendly than commonly used rubber and plastic-based alternatives. Their natural ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Black men more likely to die after surgery than White men, or women of either raceUnequal post-surgery death rate mainly applies to planned surgeries. Findings highlight the need for better understanding of the challenges facing Black men requiring surgery in the US