(Press-News.org) A global team of researchers has created an algorithmic tool that can identify existing drugs in order to combat future pandemics. The work, reported in the Cell Press journal Heliyon, offers the possibility of responding more quickly to public-health crises.
“There is no silver bullet to defeat the Covid pandemic as it takes us over a public-health roller-coaster of deaths and devastation,” explains Naomi Maria, an immunologist, a visiting scientist at New York University’s Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, and the paper’s lead author. “However, using this AI tool, coupled with in vitro data and other resources, we’ve been able to model the SARS-CoV-2 infection and identify several COVID-19 drugs currently available as potentially effective in battling the next outbreak.”
“Drug repurposing strategies provide an attractive and effective approach for quickly targeting potential new interventions,” adds Bud Mishra, a professor at NYU’s Courant and one of the paper’s senior authors. “Identifying and selecting ahead of time the best candidates, prior to costly and laborious in vitro and in vivo experiments and ensuing clinical trials, could significantly improve disease-specific drug development.”
COVID-19 has shown to be a daunting challenge over the past three years, even though vaccines and hygienic practices have, over time, lessened its severity. However, despite these tools to combat it, SARS-CoV-2—the virus that causes COVID-19—continues to spread and take lives. This is due, in part, to its ability to rapidly diversify in its target cell-types, immune-response pathways, and modes of transmission. These traits make traditional approaches to vaccine and drug design less effective than in the past—and especially when the virus co-infects with other pathogens, such as RSV and influenza.
Recognizing that current methods leave us chasing the virus, the team—which also included researchers from the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in New York, the Red Cross Blood Bank Foundation Curaçao, the Curaçao Biomedical Health and Research Institute, the Netherlands’ University Medical Center Groningen, and Catania University’s Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine in Sicily—conceived an approach aimed at closing the gap in future pandemics: repurposing existing drugs to fight back.
To do so, they developed a systems biology tool, the PHENotype SIMulator (PHENSIM). PHENSIM simulates tissue-specific infection of host cells of SARS-CoV-2 and then performs, through a series of computer—or in silico—experiments to identify drugs that would be candidates for repurposing. The algorithm computes, taking into account selected cells, cell lines, and tissues and under an array of contexts, by propagating the effects and alterations of biomolecules—such as differentially expressed genes, proteins, and microRNAs—and then calculates antiviral effects. The team confirmed the validity of the tool by comparing its results with recently published in vitro studies, demonstrating PHENSIM’s potential power in aiding effective drug repurposing.
The researchers are part of RxCovea—a multi-disciplinary group of immunologists, biologists, chemists, data scientists, game theorists, geneticists, mathematicians, and physicians, among others, that seeks to develop innovative strategies to address COVID-19.
END
The next pandemic: Researchers develop tool to identify existing drugs to use in a future outbreak
Algorithm calculates how to effectively “repurpose” present-day therapies for future use
2023-03-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cancer stage and receptor status indicate a breast cancer survivor’s risk of recurrence
2023-03-06
Study’s findings may lead to more personalized follow-up care for patients.
New research indicates that for patients with breast cancer, the cancer’s stage and receptor status can help clinicians predict whether and when cancer might recur after initial treatment. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, Heather Neuman, MD, MS, of the University of Wisconsin, and her colleagues analyzed data on 8,007 patients with stage I–III breast cancer who participated in nine clinical trials from 1997–2013 ...
Bees follow linear landmarks to find their way home, just like the first pilots
2023-03-06
In the earliest days of human flight, before the invention of the first radio beacons and ground-based electronic systems, and modern GPS, pilots commonly navigated by following roads and railways – striking linear landscape elements at ground level that guide towards a destination of interest.
Enter the honeybee. A century of research has shown that honeybees are navigators par excellence. They can navigate by their sense of smell, the sun, the sky’s pattern of polarized light, vertical landmarks that stand out from the panorama, and possibly the Earth’s magnetic field. They are also clever learners, able to recognize associations between disparate ...
Community strategy reduced opioid overdose deaths in Pennsylvania counties
2023-03-06
PITTSBURGH, March 6, 2023 — The monthly opioid overdose death (ODD) rate fell by 30% in Pennsylvania counties that implemented a novel community-focused strategy developed by University of Pittsburgh researchers, according to a new study published today in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
By analyzing counties that did or didn’t implement the Pennsylvania Opioid Overdose Reduction Technical Assistance Center (ORTAC) strategy over time, the researchers estimate that this cost-effective, community-led approach prevented 1,818 opioid-related deaths over two years.
“I ...
A mixture of trees purifies urban air best
2023-03-06
Conifers are generally better than broadleaved trees at purifying air from pollutants. But deciduous tree may be better at capturing particle-bound pollution. A new study led by the University of Gothenburg shows that the best trees for air purification depend on the type of pollutant involved.
Trees and other greenery in cities provide many benefits that are important for the well-being of residents. Leaves and needles on trees filter air pollutants and reduce exposure to hazardous substances in the air. But which trees purify the air most effectively? Researchers from the University ...
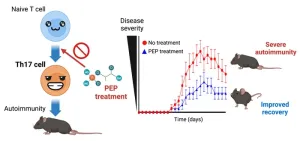
Potential treatment of autoimmune diseases revealed in new study
2023-03-06
Scientists in Japan have revealed a chemical compound that could be used for the treatment of various autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. These diseases occur when the body’s immune response goes wiry. The immune system, which normally attacks pathogens and infections, instead attacks healthy cells and tissues. For the millions of people who suffer from autoimmune diseases worldwide, the result can be debilitating—rheumatoid arthritis causes excessive joint pain, while multiple sclerosis can disable one’s brain and spinal cord function.
“The key to the development of autoimmune ...
Physical activity and tailored support fails to deliver lasting benefits for smokers not ready to quit
2023-03-06
Promoting physical activity and other behavioural support can help people wanting to reduce their smoking to quit in the short-term.
However, after nine months, physical activity delivers no noticeable benefits – compared with offering no additional support – in the rates of people stopping smoking, according to the findings of a major national study.
The Trial of physical Activity and Reduction of Smoking (TARS) study, led by the University of Plymouth with funding from the National Institute for Health and Care Research, took place across four cities – Plymouth, Nottingham, Oxford and ...
Death rates from lung cancer will fall overall in the EU and UK in 2023, but rise among women in France, Italy and Spain
2023-03-06
A total of 1,261,990 people will die from cancer in 2023 in the EU (EU-27). A further 172,314 people will die from the disease in the UK, according to new research published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Monday).
Researchers led by Carlo La Vecchia (MD), a professor at the University of Milan (Italy), estimate there will be a 6.5% fall in cancer death rates in men and a 3.7% fall in women between 2018 and 2023.
They predict that death rates from the ten most common cancers will continue to fall in most European countries in 2023, although the numbers of people dying will go up ...
As urban populations soar wastewater treatment struggles to find sustainable solutions
2023-03-06
Globally, activated sludge treats the majority of urban wastewaters; yet it is one of the most complex biological processes used. It is a sophisticated microbial process fraught with operational problems leading to occasional failures in achieving required effluent quality standards. With the increasing problem of partially treated and raw sewage entering rivers and estuaries, the pressure on the process to cope with ever increasing volumes of wastewater has never been so great.
With increasing volumes of dilute wastewater entering treatment plants the high variability in hydraulic and organic ...
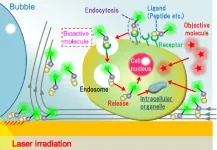
Light-induced acceleration of intracellular delivery
2023-03-06
Cell membranes are barriers that maintain cellular homeostasis, and the intracellular delivery of biologically functional molecules, including peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids to manipulate cellular functions. Conventional intracellular uptake processes require high concentrations of biofunctional molecules with low permeability to pass through the cell membrane. This results in low drug activity because the probability of the biofunctional molecules entering target cells and their organelles is low. In addition, many drugs damage healthy cells as well as the cells that are supposed to target due to poor selectivity, making ...
Physician workforce planning must adjust for aging population, changing practice patterns: New analysis
2023-03-06
Why are Canadians having problems accessing physicians despite historic highs in physician numbers? Factoring in changing demographics and physician work trends can help with physician workforce planning, according to a new analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221239.
"[T]he increasing [health care] needs of an aging population have been empirically important since around 2005, while the supply of physician service hours has simultaneously declined in a manner that is largely unrelated to the evolving age–sex composition of the physician workforce," writes Dr. Arthur Sweetman, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] The next pandemic: Researchers develop tool to identify existing drugs to use in a future outbreakAlgorithm calculates how to effectively “repurpose” present-day therapies for future use