(Press-News.org) Researchers have achieved a breakthrough to enable ‘perfectly secure’ hidden communications for the first time.
The method uses new advances in information theory methods to conceal one piece of content inside another in a way that cannot be detected.
This may have strong implications for information security, besides further applications in data compression and storage.
A group of researchers has achieved a breakthrough in secure communications by developing an algorithm that conceals sensitive information so effectively that it is impossible to detect that anything has been hidden.
The team, led by the University of Oxford in close collaboration with Carnegie Mellon University, envisage that this method may soon be used widely in digital human communications, including social media and private messaging. In particular, the ability to send perfectly secure information may empower vulnerable groups, such as dissidents, investigative journalists, and humanitarian aid workers.
The algorithm applies to a setting called steganography: the practice of hiding sensitive information inside of innocuous content. Steganography differs from cryptography because the sensitive information is concealed in such a way that this obscures the fact that something has been hidden. An example could be hiding a Shakespeare poem inside an AI-generated image of a cat.
Despite having been studied for more than 25 years, existing steganography approaches generally have imperfect security, meaning that individuals who use these methods risk being detected. This is because previous steganography algorithms would subtly change the distribution of the innocuous content.
To overcome this, the research team used recent breakthroughs in information theory, specifically minimum entropy coupling, which allows one to join two distributions of data together such that their mutual information is maximised, but the individual distributions are preserved.
As a result, with the new algorithm, there is no statistical difference between the distribution of the innocuous content and the distribution of content that encodes sensitive information.
The algorithm was tested using several types of models that produce auto-generated content, such as GPT-2, an open-source language model, and WAVE-RNN, a text-to-speech converter. Besides being perfectly secure, the new algorithm showed up to 40% higher encoding efficiency than previous steganography methods across a variety of applications, enabling more information to be concealed within a given amount of data. This may make steganography an attractive method even if perfect security is not required, due to the benefits for data compression and storage.
The research team has filed a patent for the algorithm, but intend to issue it under a free licence to third parties for non-commercial responsible use. This includes academic and humanitarian use, and trusted third-party security audits. The researchers have published this work as a preprint paper on arXiv, as well as open-sourced an inefficient implementation of their method on Github. They will also present the new algorithm at the premier AI conference, the 2023 International Conference on Learning Representations in May.
AI-generated content is increasingly used in ordinary human communications, fuelled by products such as ChatGPT, Snapchat AI-stickers, and TikTok video filters. As a result, steganography may become more widespread as the mere presence of AI-generated content will cease to arouse suspicion.
Co-lead author Dr Christian Schroeder de Witt (Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford) said: ‘Our method can be applied to any software that automatically generates content, for instance probabilistic video filters, or meme generators. This could be very valuable, for instance, for journalists and aid workers in countries where the act of encryption is illegal. However, users still need to exercise precaution as any encryption technique may be vulnerable to side-channel attacks such as detecting a steganography app on the user’s phone.’
Co-lead author Samuel Sokota (Machine Learning Department, Carnegie Mellon University) said: ‘The main contribution of the work is showing a deep connection between a problem called minimum entropy coupling and perfectly secure steganography. By leveraging this connection, we introduce a new family of steganography algorithms that have perfect security guarantees.’
Contributing author Professor Jakob Foerster (Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford) said: ‘This paper is a great example of research into the foundations of machine learning that leads to breakthrough discoveries for crucial application areas. It's wonderful to see that Oxford, and our young lab in particular, is at the forefront of it all.’
Besides Dr Christian Schroeder de Witt, Samuel Sokota and Professor Jakob Foerster, the study involved Prof. Zico Kolter at Carnegie Mellon University, USA, and Dr Martin Strohmeier from armasuisse Science+Technology, Switzerland. The work was partially funded by a EPSRC IAA Doctoral Impact fund hosted by Professor Philip Torr, Torr Vision Group, at the University of Oxford.
Notes to editors:
For media enquiries and interview requests, contact Dr Christian Schroeder de Witt (cs@robots.ox.ac.uk).
The paper ‘Perfectly Secure Steganography using Minimum Entropy Coupling’ will be published on arXiv. The paper will be available at https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.14889. To view a copy of the paper before this, under embargo, contact Dr Christian Schroeder de Witt (cs@robots.ox.ac.uk).
About the University of Oxford
Oxford University has been placed number 1 in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings for the seventh year running, and number 2 in the QS World Rankings 2022. At the heart of this success are the twin-pillars of our ground-breaking research and innovation and our distinctive educational offer.
Oxford is world-famous for research and more and home to some of the most talented people from across the globe. Our work helps the lives of millions, solving real-world problems through a huge network of partnerships and collaborations. The breadth and interdisciplinary nature of our research alongside our personalised approach to teaching sparks imaginative and inventive insights and solutions.
Through its research commercialisation arm, Oxford University Innovation, Oxford is the highest university patent filer in the UK and is ranked first in the UK for university spinouts, having created more than 200 new companies since 1988. Over a third of these companies have been created in the past three years. The university is a catalyst for prosperity in Oxfordshire and the United Kingdom, contributing £15.7 billion to the UK economy in 2018/19, and supports more than 28,000 full time jobs.
About Carnegie Mellon University
A private, global research university, Carnegie Mellon stands among the world's most renowned educational institutions, and sets its own course. Start the journey here. Over the past 10 years, more than 400 startups linked to CMU have raised more than $7 billion in follow-on funding. Those investment numbers are especially high because of the sheer size of Pittsburgh’s growing autonomous vehicles cluster – including Uber, Aurora, Waymo and Motional – all of which are here because of their strong ties to CMU. With cutting-edge brain science, path-breaking performances, innovative startups, driverless cars, big data, big ambitions, Nobel and Turing prizes, hands-on learning, and a whole lot of robots, CMU doesn't imagine the future, it creates it.
END
New breakthrough enables perfectly secure digital communications
2023-03-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
CNIO researchers propose biomarkers to select breast cancer patients who could benefit from denosumab treatment
2023-03-07
The study supports the therapeutic benefit of this drug in postmenopausal patients with hormone-receptor negative breast tumours and RANK protein expression.
"These results revive the option of starting clinical trials of denosumab in breast cancer by selecting patients," says Eva González-Suarez, CNIO researcher and lead author.
The results are published today in the scientific journal EMBO Molecular Medicine.
The drug denosumab is currently used to treat osteoporosis and bone metastases. For more than a decade, its potential therapeutic benefit in the treatment of breast cancer has also been studied. However, due to conflicting clinical ...
The planet that could end life on Earth
2023-03-07
A terrestrial planet hovering between Mars and Jupiter would be able to push Earth out of the solar system and wipe out life on this planet, according to a UC Riverside experiment.
UCR astrophysicist Stephen Kane explained that his experiment was meant to address two notable gaps in planetary science.
The first is the gap in our solar system between the size of terrestrial and giant gas planets. The largest terrestrial planet is Earth, and the smallest gas giant is Neptune, which is four times wider and 17 times more massive than Earth. There is nothing in between.
“In other star ...
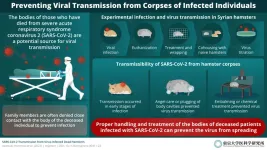
Scientists suggest guidelines to prevent SARS-CoV-2 transmission from deceased individuals
2023-03-07
Their findings highlight that embalming or "angel care" can effectively prevent virus transmission, to allow family members to say goodbye
During the pandemic, COVID-19 control measures in several countries prevented family members from coming into contact with loved ones who died from the infection. This had an impact on cremation practices and caused emotional distress. Researchers from Japan have now shown that, while deceased SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals may be a potential source of the ...
An internal thermometer tells the seeds when to germinate
2023-03-07
Germination is a crucial stage in the life of a plant as it will leave the stage of seed resistant to various environmental constraints (climatic conditions, absence of nutritive elements, etc.) to become a seedling much more vulnerable. The survival of the young plant depends on the timing of this transition. It is therefore essential that this stage be finely controlled. A Swiss team, led by scientists from the University of Geneva (UNIGE), has discovered the internal thermometer of seeds that can delay or even block germination if temperatures are too high for the future seedling. This work could help optimize plant growth in a context of global warming. These results can be ...
Study reveals limitations in evaluating gene editing technology in human embryos
2023-03-07
A commonly used scientific method to analyze a tiny amount of DNA in early human embryos fails to accurately reflect gene edits, according to new research led by scientists at Oregon Health & Science University.
The study, published today in the journal Nature Communications, involved sequencing the genomes of early human embryos that had undergone genome editing using the gene-editing tool CRISPR. The work calls into question the accuracy of a DNA-reading procedure that relies on amplifying a small amount of DNA for purposes of genetic testing.
In addition, the study reveals that gene editing to correct disease-causing mutations in early human embryos can also lead to unintended ...
Keck Medicine of USC names Ikenna (Ike) Mmeje president and CEO of USC Arcadia Hospital
2023-03-07
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC has named Ikenna (Ike) Mmeje president and CEO of USC Arcadia Hospital (USC-AH), effective March 13.
In this position, Mmeje will further the health system’s mission to expand access to specialized health care and research to the San Gabriel Valley and beyond. He will oversee all management and operations of the hospital, including corporate compliance, strategic plan implementation and fundraising.
“Mmeje will utilize his wealth of knowledge and experience running complex, high-performing hospitals in his new role leading USC Arcadia Hospital,” said Rod Hanners, CEO of Keck Medicine.
Mmeje replaces current ...
What makes a neural network remember?
2023-03-07
Computer models are an important tool for studying how the brain makes and stores memories and other types of complex information. But creating such models is a tricky business. Somehow, a symphony of signals – both biochemical and electrical – and a tangle of connections between neurons and other cell types creates the hardware for memories to take hold. Yet because neuroscientists don’t fully understand the underlying biology of the brain, encoding the process into a computer model in order to study it further has been a challenge.
Now, ...
How do microbes live off light?
2023-03-07
Plants convert light into a form of energy that they can use – a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – through photosynthesis. This is a complex process that also produces sugar, which the plant can use for energy later, and oxygen. Some bacteria that live in the light-exposed layers of water sources can also convert light to ATP, but the process they use is simpler and less efficient than photosynthesis. Nonetheless, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology researchers now find this process isn’t as straightforward and limited as was previously thought.
Rhodopsins are the light-driven proton pumps ...
Commercial water purification system may have caused pathogen infection in 4 hospitalized patients
2023-03-07
1. Commercial water purification system may have caused pathogen infection in 4 hospitalized patients
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M22-3306
URL goes live when the embargo lifts
A study of 4 cardiac surgery patients in one hospital found that they developed Mycobacterium abscessus infections, a multidrug-resistant nontuberculous mycobacteria, potentially due to a commercial water purifier. The water purifier had been installed in the hospital to improve water palatability but was inadvertently removing chlorine from the supply lines feeding ice and water machines in the affected area of ...
Dr. B. Hadley Wilson is new American College of Cardiology President
2023-03-07
B. Hadley Wilson, MD, FACC, is the new president of the American College of Cardiology. Today marks the first day of his one-year term leading the global cardiovascular organization in its mission to transform cardiovascular care and improve heart health.
“Some of the best qualities of the ACC and its members are the commitment to patient care and the shared vision of a world where science, innovation and knowledge optimize and transform cardiovascular care and outcomes for all,” Wilson said. “I believe we all really practice what we preach. I am honored to lead an organization dedicated to innovating ...