(Press-News.org)
The results of the clinical trial of a new wrist device designed to help control the symptoms of Tourette syndrome have shown it significantly reduces the severity and frequency of tics.
The prototype wrist device, which was recently tried out by Lewis Capaldi, delivers electrical pulses to reduce the amount and severity of tics experienced by individuals with Tourette’s and was trialed by 121 people across the UK. The results have been announced in MedRxive.
The device has been developed by scientists at the University of Nottingham and spin-out company Neurotherapuetics Ltd who have recently secured £1m in additional funding to commercialise the ‘Neupulse’ device with the aim of having a device and App available within the next 3 years.
Tourette Syndrome (TS) is a neurodevelopmental condition that is usually diagnosed between the ages of eight and 12. It causes involuntary sounds and movements called tics. Tics are repetitive, stereotyped movements and vocalisations that occur in bouts, typically many times in a single day, and are often preceded by a strong urge-to-tic, referred to as a premonitory urge (PU).
Previous research by scientists from the University of Nottingham’s School of Psychology and School of Medicine used repetitive trains of electrical stimulation to the median nerve (MNS) at the wrist to entrain rhythmic electrical brain activity - known as brain oscillations - associated with the suppression of movements. They found that rhythmic MNS substantially reduces tic frequency and tic intensity, and remove the urge-to-tic, in individuals with TS.
Trial participants used the device at home at a similar time each day for 15 mins for a period of one month. A subset of people were also videoed each day. Each week participants gave feedback on their experience.
The results of the trial revealed that people who received active stimulation experienced a significant reduction in the severity and frequency of their tics. On average, they saw a reduction in tic frequency of more than 25% while they received stimulation.
After using the device for 4 weeks, people who received active stimulation experienced a reduction in their tic severity of more than 35%. In total, 59% of the people who received active stimulation experienced a reduction in tic severity of at least 25% compared to baseline.
13-year-old Mylo was one of the participants in the trial. His parents noticed unusual symptoms when he was a toddler, but he wasn’t diagnosed until he was 10 after his tics became more noticeable. He said: “The device was easy to use - you strap it on like a watch and press a button to start it. You have to make sure the pads are on the back properly otherwise it might hurt a tiny bit. When the stimulation occurs it feels a bit like a fizzing on my wrist and forearm, not painful just a bit different.
The device definitely helped my tics. I still did the occasional tic when it was on but the need to do it was a lot less. I definitely want this device when it is available. I think it can help people with Tourette's in different ways. For me, I would use it if I was going to the cinema or the theatre - places where you sometimes have to be quiet or still so you don't disturb people. Tourette's can be really exhausting sometimes, like when you have a tic attack and can't get a break from it - this device could really help with that. I think different people would benefit in different ways - because Tourette's can vary quite a lot. I don't think I would use it all day, just when I felt I especially needed it.”
Mylo’s mum Alex added: “I feel this device could be a great safety net for us. I don't know how Mylo's Tourette's will progress as he gets older, but knowing there is something out there that can help if he wants it makes me feel so much better. I would also say that the device might not be for everyone - if you are accepting of your tics and they don't impact your life you might not want or need it, but for those people that really struggle I believe it will make a significant impact with daily challenges. We feel really lucky to have taken part in the trial."
Professor Stephen Jackson from the University of Nottingham and Chief Scientific Officer at Neurotherapeutics Ltd said: “Though the Neupulse device is still early in development, the results of this UK-wide double-blind clinical trial have been extremely encouraging. This device has the potential to dramatically improve the lives of those with Tourette syndrome, who often face challenges managing their tics, by providing increased control over their tics on demand.”
Dr. Barbara Morera Maiquez, Chief Research Officer at Neurotherapeutics Ltd managed the trial, she commented: “The results of this trial mark an exciting step towards an effective, non-invasive treatment for Tourette syndrome that can be used at home. We are now focused on using the knowledge from the trial to develop a commercial device that can be made available to people with Tourette’s.”
The research has been funded by the charity Tourettes Action, NIHR Nottingham Biomedical Research Centreand Neurotherapeutics Ltd.
Emma McNally, Chief Executive Officer of Tourettes Action said: “The results of the trial are extremely promising. Many with Tourette’s suffer with pain caused by the repetitive nature of their tics and often find it hard to get any respite from this. The device could provide them with a useful self-managing treatment to help them better manage and control their tics, ultimately giving them a break from the tic pain cycle. It could potential improve the lives of so many people.”
END
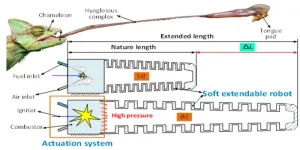
A research paper by scientists at the Beijing Institute of Technology and University of Lancaster displayed a recent advancement of using fuel explosion as the power of source to achieve the rapid and powerful motion for the medium-size robots.
The new research paper, published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, provided a new kind of actuation system for the robotic system, providing a promising patentability to largely improve the working length of the conventional medium-size robotic systems.
“Achieving the rapid and fast motion of the medium-size robot has been a challenging task for many years, …” ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Most of what scientists know about viruses in animals is the list of nucleotides that compose their genomic sequence – which, while valuable, offers very few hints about a virus’s ability to infect humans.
Rather than let the next outbreak take the world by surprise, two virologists say in a Science Perspective article published today (March 10, 2023) that the scientific community should invest in a four-part research framework to proactively identify animal viruses that might infect humans.
“A lot of financial investment has gone into sequencing viruses in nature and thinking that from sequence alone we’ll be ...
EAST LANSING, MI – The International Research Network for Nuclear Astrophysics (IReNA), supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and headquartered at Michigan State University (MSU), brings together nuclear physicists, astronomers, and computational scientists to try to answer a long-standing question in science: Where do the elements that make up our world come from?
Founded in 2019, IReNA continues to expand its global reach for cooperation to advance knowledge in nuclear astrophysics, and now welcomes a new network partner: the Ibero-American Network of Nuclear ...
“[...] there is a need to explore brain mechanisms through which psychological processes may exert their protective or deleterious effects.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 10, 2023 – Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) published a new editorial paper in Volume 15, Issue 4, entitled, “Cognitive aging and dementia prevention: the time for psychology?”
Modifiable risk and protective factors (e.g. engaging in active lifestyles ...
Inflammatory neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), can arise when cell-to-cell communication between cells in the central nervous system (CNS) goes awry. But exactly how this cellular crosstalk leads to the molecular changes that drive disease remain unknown. To address this, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, developed a platform that allows them to perform genetic screens of cell-cell interactions to identify genes that control biologic processes. ...
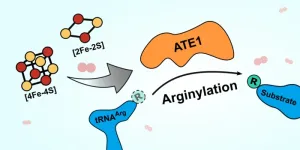
A new paper in Nature Communications illuminates how a previously poorly understood enzyme works in the cell. Many diseases are tied to chronic cellular stress, and UMBC’s Aaron T. Smith and colleagues discovered that this enzyme plays an important role in the cellular stress response. Better understanding how this enzyme functions and is controlled could lead to the discovery of new therapeutic targets for these diseases.
The enzyme is named ATE1, and it belongs to a family of enzymes called arginyl-tRNA transferases. These enzymes add arginine (an amino acid) to proteins, which often flags the proteins for destruction in the cell. Destroying ...
Physicists are learning more about the bizarre behavior of “strange metals,” which operate outside the normal rules of electricity.
Theoretical physicist Yashar Komijani, an assistant professor at the University of Cincinnati, contributed to an international experiment using a strange metal made from an alloy of ytterbium, a rare earth metal. Physicists in a lab in Hyogo, Japan, fired radioactive gamma rays at the strange metal to observe its unusual electrical behavior.
Led by Hisao Kobayashi with the University of Hyogo and RIKEN, the study was published in the journal Science. The experiment revealed unusual fluctuations in the strange metal’s electrical charge.
“The ...
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [March 10, 2023] — New research in the March 2023 issue of JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network highlights how the lack of genomic research for people with African ancestry, particularly those from the Sub-Saharan region, is hampering efforts to reduce disparities for people with cancer. In a first-of-its-kind study, the researchers evaluated molecular genetic results for 113 Black South African men diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer to find evidence for ...
Individuals with Type 1 diabetes have a smaller pancreas than people without diabetes. This is surprising because insulin-producing beta cells account for just a small fraction of the pancreas, so the loss of beta cells in Type 1 diabetes would not be expected to reduce pancreas size.
Now, a study of one family from Alabama has led Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers to discover that insulin deficiency, independent of the autoimmunity associated with Type 1 diabetes, is the principal factor leading to a markedly smaller pancreas.
Four ...
Urology involves some of the most intimate medical conditions, yet patients don’t necessarily always prefer to be treated by a urologist of their own gender, new research has found.
In some situations, male and female patients would prefer a male urologist but in others – if they have a painful condition, for example – both men and women would choose to be treated by a female doctor.
The study, by researchers from University Hospital Munich, is being presented today at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Congress ...