(Press-News.org) A comprehensive analysis of an archaeological site in Saudi Arabia sheds new light on mustatils—stone monuments from the Late Neolithic period thought to have been used for ritual purposes. Melissa Kennedy of the University of Western Australia, Perth, and colleagues, in conjunction with The Royal Commission for AlUla present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 15, 2023.
Built around 7,000 years ago, mustatils are rectangular, low-walled, stone structures that range from 20 to 600 meters in length. Researchers first discovered them in the 1970s, and more than 1,600 mustatils have now been discovered, primarily concentrated in northern Saudi Arabia.
Recent excavations in the city of AlUla suggest that mustatils were used for ritualistic purposes involving placement of animal offerings. Now, Kennedy and colleagues have conducted an extensive excavation at a mustatil located 55 east of AlUla. This mustatil is 140 meters long and is constructed from local sandstone.
The researchers’ analysis included identification of 260 fragments of animal skulls and horns, primarily from domestic cattle, as well as from domestic goats, gazelle, and small ruminants. Nearly all of these remains were clustered around a large upright stone interpreted to be a betyl. Radiocarbon dating suggested that the betyl is one of the oldest identified in the Arabian Peninsula, and the bones provide some of the earliest evidence for domestication of cattle in the northern Arabia.
This study also uncovered evidence for several phases of offerings at the mustatil, as well as interment of an adult male human, suggesting that the site may have been the destination of repeated pilgrimages.
Taking all the new data into consideration, the researchers suggest that ritualistic belief and economic factors were more closely intertwined for Neolithic people in northwest Arabia than previously thought, and that this entanglement was shared over a broad geographic area.
The authors add: “The ritual deposition of animal horns and upper cranial element within the mustatil suggests a profound intersection of belief and economic life-ways in the Late Neolithic of Northern Arabia. The incorporation of these two facets suggests a deeply rooted ideological entanglement, one which was shared over a vast geographic distance, indicating a far more interconnected landscape and culture than had previously been supposed for the Neolithic period in north-west Arabia.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281904
Citation: Kennedy M, Strolin L, McMahon J, Franklin D, Flavel A, Noble J, et al. (2023) Cult, herding, and ‘pilgrimage’ in the Late Neolithic of north-west Arabia: Excavations at a mustatil east of AlUla. PLoS ONE 18(3): e0281904. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0281904
Author Countries: Australia, Switzerland, Saudi Arabia
Funding: HT, MK This work was funded by the Royal Commission for AlUla. https://www.rcu.gov.sa/en/. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Uncovering the ritual past of an ancient stone monument in Saudi Arabia
Researchers conduct extensive excavation of one of more than 1600 monuments known as mustatils
2023-03-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The WWII shipwreck of the SS Thistlegorm, now a popular Red Sea dive site, has formed an artificial coral reef for a diverse community of fish, according to data gathered by volunteer divers
2023-03-15
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282239
Article Title: Eight years of community structure monitoring through recreational citizen science at the “SS Thistlegorm” wreck (Red Sea)
Author Countries: Italy
Funding: STE project was funded by Project AWARE Foundation, ASTOI Association, Ministry of Tourism of the Arab Republic of Egypt, Settemari S.p.A Tour Operator, Scuba Nitrox Safety International, Viaggio nel Blu Diving Center. The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
Analysis links specific skills taught by US undergraduate degree courses with graduate earnings
2023-03-15
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282323
Article Title: Connecting higher education to workplace activities and earnings
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This research is supported in part by the University of Pittsburgh Pitt Momentum Fund and the Center for Research Computing. This work has been supported (in part) by # 2109-33808 from the Russell Sage Foundation. Any opinions expressed are those of the principal investigator(s) alone and should not be construed as representing the opinions of the Foundation. The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
Estrogen possible risk factor in disturbed heart rhythm
2023-03-15
The sex hormone estrogen has a negative impact on heartbeat regulation, according to an experimental study from Linköping University, Sweden, published in Science Advances. Estrogen impact seems to interact with hereditary changes causing a heart disease disturbing the heart’s rhythm, while other endogenous substances may have a protecting effect.
In a lifetime, the heart beats around 2.5 billion times. Each heartbeat is triggered by an electrical impulse that causes the heart muscle to contract in a very well-coordinated movement. ...
Radar images record potential volcanic activity on Venus
2023-03-15
Researchers have identified evidence they interpret as active volcanism on the surface of Venus, according to a new analysis of radar images from the Magellan spacecraft. The images reveal a vent that changed shape on Venus, which they believe points to ongoing volcanic activity there. Many volcanoes have been identified on the surface of Venus, but evidence of recent volcanic activity on the planet has been lacking. As a result, it was unknown whether the prominent volcanic features of Venus’ geologically young surface are a product of ongoing active volcanism ...
AJR on a decade of lung cancer screening in American newspapers
2023-03-15
Leesburg, VA, March 15, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), sentiment of U.S. newspaper articles covering lung cancer screening (LCS) from 2010 to 2022 was overall positive; however, certain key elements of LCS were infrequently mentioned.
“The findings highlight areas for potential improvement of LCS media coverage; radiologists have an opportunity to take a more active role in this coverage,” concluded first author Brent P. Little, MD, of Mayo Clinic Florida in Jacksonville.
Little et al. searched the ProQuest U.S. Newsstream ...
Resilient bug-sized robots keep flying even after wing damage
2023-03-15
Bumblebees are clumsy fliers. It is estimated that a foraging bee bumps into a flower about once per second, which damages its wings over time. Yet despite having many tiny rips or holes in their wings, bumblebees can still fly.
Aerial robots, on the other hand, are not so resilient. Poke holes in the robot’s wing motors or chop off part of its propellor, and odds are pretty good it will be grounded.
Inspired by the hardiness of bumblebees, MIT researchers have developed repair techniques that enable a bug-sized aerial robot to sustain severe damage to the actuators, or artificial muscles, that power its wings — but to still fly effectively.
They optimized these artificial muscles ...
Psychological intervention reduced stress during COVID lockdown
2023-03-15
Resilience and well-being in difficult times can be developed via online interventions in the workplace. An international team of researchers from France, the UK and Russia (with the participation of researchers from the HSE International Laboratory of Positive Psychology of Personality and Motivation) studied the effectiveness of SPARK Resilience, a programme for developing resilience, at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. The results of the study were published in the PLOS One journal.
By creating the SPARK Resilience programme, psychologists focused on helping people gain ...
Biotechnologies harnessing microbes might enable us to extract rare elements and minerals, chemicals and fuels from wastewater
2023-03-15
Biotechnologies harnessing microbes might enable us to extract rare elements and minerals, chemicals and fuels from wastewater.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000105
Article Title: Environmental biotechnologies can make water pollutants part of the path to mitigating climate change
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The author received no specific funding for this work.
END ...
Vitamin A may reduce pancreatitis risk during ALL treatment
2023-03-15
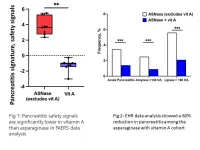
Consuming a diet rich in vitamin A or its analogs may help prevent children and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) reduce their risk of developing painful pancreas inflammation during chemotherapy treatment.
Details about this potential dietary solution to prevent a potentially life-threatening adverse event were published March 15, 2023, in Science Translational Medicine. The research team was led by Sohail Husain, MD, chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition at Stanford University and Anil Goud Jegga, DVM, MRes, a computational ...
UAF scientist offers evidence that Venus is volcanically active
2023-03-15
Embargoed: Not for release until 2 p.m. U.S. Eastern time Wednesday, March 15, 2023
Venus appears to have volcanic activity, according to a new research paper that offers strong evidence to answer the lingering question about whether Earth’s sister planet currently has eruptions and lava flows.
Venus, although similar to Earth in size and mass, differs markedly in that it does not have plate tectonics. The boundaries of Earth’s moving surface plates are the primary locations of volcanic activity.
New research by University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute research professor Robert Herrick revealed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Uncovering the ritual past of an ancient stone monument in Saudi ArabiaResearchers conduct extensive excavation of one of more than 1600 monuments known as mustatils