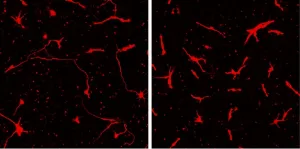
(Press-News.org) According to the U.S. Surgeon General, women should not drink alcoholic beverages during pregnancy because of the risk of birth defects in their unborn child. Now, research at Texas A&M University demonstrates that a father’s alcohol consumption before conception also links to growth defects that affect the development of his offspring’s brain, skull and face.
Research investigating fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) exclusively examines maternal alcohol exposure. However, because men drink more and are more likely to binge drink than women, Dr. Michael Golding, an associate professor in the School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences’ Department of Veterinary Physiology & Pharmacology, and his team set out to challenge the existing dogma, using a mouse model to examine what happens when the mother, father and both parents consume alcohol.
In a new article published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, Golding and his team found that male alcohol consumption before conception caused FAS brain and facial growth defects.
“We found that male exposures actually drive certain craniofacial differences much stronger than maternal exposures do, so this programming effect that's coming through sperm has a profound effect on the organization of the face and the growth and proportion of different facial features,” Golding said. “When it was the dad drinking, we saw a profound shift in the organization of the face.”
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), FAS is a fetal disorder caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy.
FAS is hard to diagnose, but when doing so, doctors currently look for abnormal facial features; lower-than-average weight, height or both; central nervous system problems such as a small head size, problems with attention and hyperactivity or poor coordination; and verification of maternal alcohol use during pregnancy.
“When doctors suspect a child has FAS, they sit down with the mother to confirm the diagnosis by discussing her drinking habits during pregnancy,” Golding said. “It’s not uncommon for the mother to deny consuming alcohol while pregnant. When they do, there's this stigma or this notion that women are lying about their alcohol use.”
Golding said this research, which was funded by a Medical Research Grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation and the NIH National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, reveals a potential blind spot in the current diagnostic criteria for FAS, the most severe form of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD), which requires documentation of maternal alcohol use during pregnancy.
“Our research proves there’s a plausible alternative explanation – the father’s contribution, which has never been examined before,” he said. “In this study, we call into question the dismissal of the mother’s denial and really examine the capacity of male alcohol use to induce FAS growth defects.”
Golding explained that findings from his holistic approach that examines both parents’ contributions to FAS reveal the need for two critical changes.
“First is the recognition of the importance of male health in pregnancy outcomes and fetal health,” he said.
Golding pointed out that paternal health before conception is a novel consideration in terms of pregnancy outcomes and fetal health; as a result, raising awareness of the role a father's health plays in his offspring's health is just as important as awareness of the mother's contributions from preconception and through gestation.
“Research examining fetal health is overwhelmingly focused on maternal health,” he said. “I'm not saying that this is not appropriate; I'm just saying it's not the complete picture and we need some balance.
“The second,” he said, “is the fact that both parents are responsible for preventing alcohol-related birth defects.”
FAS has significant, life-changing consequences for children.
Because their study identified FAS-related craniofacial differences in offspring born to fathers who regularly consumed alcohol at or more than the legal limit, Golding pointed out that both parents should commit to limiting or omitting their alcohol consumption before trying to become pregnant.
Ultimately, Golding emphasizes that the first step in this process is expanding messaging outreach about the reproductive dangers of alcohol use to both parents.
“Change the alcohol warning label to remove the maternal emphasis and put it on both parents to say, ‘The decision to consume this beverage can have significant, life-changing consequences to a future child,’” he said. “Right now, the warning label only conveys part of the story. We must get that message out into the world as quickly as possible.”
By Rachel Knight, Texas A&M University School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences
###
END
Father’s alcohol consumption before conception linked to brain and facial defects in offspring
Fetal alcohol syndrome-related craniofacial differences could be seen in offspring born to fathers who regularly consumed as little alcohol as the legal limit
2023-04-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New technique allows researchers to dig into molecular causes of pediatric bipolar disorder
2023-04-12
It’s extremely difficult to study the biological basis of psychiatric disorders, in part because researchers can’t easily collect brain cells from living people to study in the laboratory. Now, University of Utah Health scientists have developed a way around that.
The researchers grew three-dimensional structures, called “organoids”, derived from blood cells donated by a patient with pediatric bipolar disorder and by several family members. The approach identified significant molecular changes linked to the psychiatric condition.
The results, reported in Molecular Psychiatry, suggest that structural changes in the ...
COVID-19 pandemic will disrupt cancer reporting for years to come
2023-04-12
Key takeaways:
American College of Surgeons research published in JAMA Surgery reveals the complexities and variations that occurred in cancer reporting in the National Cancer Database (NCDB) because of the pandemic.
The number of reported cancer cases in NCDB declined by 14.4% compared with prior years, representing more than 200,000 cancer cases that were not diagnosed and/or treated at accredited facilities.
Research offers guidance to centers across the country on how to interpret data from 2020 and onwards.
CHICAGO: New research from the American College of Surgeons (ACS) outlines significant ways that the COVID-19 pandemic destabilized usual patterns of cancer care as reported ...
Is the language you speak tied to outcome after stroke?
2023-04-12
MINNEAPOLIS – Studies have shown that Mexican Americans have worse outcomes after a stroke than non-Hispanic white Americans. A new study looks at whether the language Mexican American people speak is linked to how well they recover after a stroke. The study is published in the April 12, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our study found that Mexican American people who spoke only Spanish had worse neurologic outcomes three months after having a stroke than Mexican American people who spoke only English or were bilingual,” said study author ...
Archaeological sites at risk from coastal erosion on the Cyrenaican coast, Libya
2023-04-12
Archaeological sites along the Libyan shoreline are at risk of being damaged or lost due to increasing coastal erosion, according to a study published April 12, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Kieran Westley and Julia Nikolaus of Ulster University, UK and colleagues.
The Cyrenaican coast of Eastern Libya, stretching from the Gulf of Sirte to the current Egypt-Libya border, has a long history of human occupation back to the Palaeolithic era, and it therefore hosts numerous important and often ...
Poor family cohesion is associated with long-term psychological impacts in bereaved teenagers
2023-04-12
The death of a parent can affect the health and well-being of children and adolescents, including higher risk of depression. A study published in PLOS ONE by Dröfn Birgisdóttir at Lund University, Lund, Sweden and colleagues suggests poor family cohesion is associated with long-term psychological symptoms among bereaved youth.
Parentally bereaved children are at increased risk for mental illness including depression, anxiety, suicide attempts, and self-injurious behaviors. However, the relationship ...
The stripes of the Lesser Pacific Striped Octopus are as unique as our own fingerprints, enabling scientists to track individuals as they grow
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0265292
Article Title: Individually unique, fixed stripe configurations of Octopus chierchiae allow for photoidentification in long-term studies
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Most retail cannabis may be less potent than claimed, with THC being at least 15% less potent than reported on the label in around 70% of products sampled in Colorado
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282396
Article Title: Uncomfortably high: Testing reveals inflated THC potency on retail Cannabis labels
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Headspace Sensory LLC provided funding for purchase of 13 of the 23 Cannabis samples that were included as part of another study [47], but had no other involvement in this study. All other funding was provided by the McGlaughlin Lab at the University of Northern Colorado and by the first author. Mile High Labs provided support for this study in the form of salaries for VJ and JH. The specific roles of these authors are articulated in the ‘author contributions’ ...
New 52 million-year-old bat species discovered in Wyoming, US, is the oldest bat skeleton known
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283505
Article Title: The oldest known bat skeletons and their implications for Eocene chiropteran diversification
Author Countries: The Netherlands, USA
Funding: 1) Theodore Roosevelt Memorial Fund of the American Museum of Natural History (TBR) https://www.amnh.org/research/richard-gilder-graduate-school/academics-and-research/fellowship-and-grant-opportunities/research-grants-and-graduate-student-exchange-fellowships/roosevelt-memorial-fund 2) ...
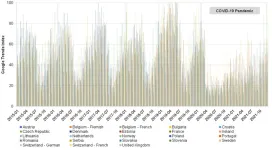
Google Trends reveal how the spread of chickenpox may have been suppressed during the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-04-12
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283465
Article Title: Impact assessment of immunization and the COVID-19 pandemic on varicella across Europe using digital epidemiology methods: A descriptive study
Author Countries: Sweden, Lithuania, Ireland, USA, Spain
Funding: Funding for this research was provided by Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA (MSD). We confirm that the funder provided support in the form of salaries for Ugne Sabale, Ligita Jarmale, Janice Murtagh, Manjiri Pawaskar, and Goran Bencina, but did not have any additional ...
Got milk? The ancient Tibetans did, according to study
2023-04-12
New research into ancient populations that resided on the Tibetan Plateau has found that dairy pastoralism was being practiced far earlier than previously thought and may have been key to long-term settlement of the region’s extreme environment.
Professor Michael Petraglia, Director of Griffith’s Australian Research Centre for Human Evolution, was part of the international research team that set out to understand how prehistoric populations adapted to the vast, agriculturally poor highlands of the Tibetan Plateau.
The research, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
[Press-News.org] Father’s alcohol consumption before conception linked to brain and facial defects in offspringFetal alcohol syndrome-related craniofacial differences could be seen in offspring born to fathers who regularly consumed as little alcohol as the legal limit