(Press-News.org) Along their eight arms, octopuses have highly sensitive suckers that allow methodical explorations of the seafloor as they search for nourishment in a “taste by touch” approach. Squids, on the other hand, use a much different tactic to find their next meal: patiently hiding until they ambush their prey in swift bursts.
In a unique analysis that provides a glimpse into the origin stories of new animal traits, a pair of research studies led by University of California San Diego and Harvard University scientists has traced the evolutionary adaptations of octopus and squid sensing capabilities. The studies, featured on the cover of the April 13 issue of Nature, reveal evolutionary links to human brain receptors.
Researchers with Ryan Hibbs’ newly established laboratory in the School of Biological Sciences at UC San Diego (formerly based at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center) and Nicholas Bellono’s lab at Harvard analyzed octopuses and squids, animals known as cephalopods, through a comprehensive lens that spanned atomic-level protein structure to the entire functional organism. They focused on sensory receptors as a key site for evolutionary innovation at the crossroads of ecology, neural processing and behavior.
By looking at the way octopuses and squids sense their marine environments, the researchers discovered new sensory receptor families and determined how they drive distinct behaviors in the environment. With cryo-electron microscopy technology, which uses cryogenic temperatures to capture biological processes and structures in unique ways, they showed that adaptations can help propel new behaviors.
“Cephalopods are well known for their intricate sensory organs, elaborate nervous systems and sophisticated behaviors that are comparable to complex vertebrates, but with radically different organization,” said Hibbs, a professor in the Department of Neurobiology. Hibbs brings expertise on the structure of a family of proteins in humans that mediate communication between brain neurons and other areas such as between neurons and muscle cells. “Cephalopods provide striking examples of convergent and divergent evolution that can be leveraged to understand the molecular basis of novelty across levels of biological organization.”
In one Nature study, the research teams described for the first time the structure of an octopus chemotactile (meaning chemical and touch) receptor, which octopus arms use for taste-by-touch exploration. These chemotactile receptors are similar to human brain and muscle neurotransmitter receptors, but are adapted through evolution to help evaluate possible food sources in the marine environment.
“In octopus, we found that these chemotactile receptors physically contact surfaces to determine whether the animal should eat a potential food source or reject it,” said Hibbs. “Through its structure, we found that these receptors are activated by greasy molecules, including steroids similar to cholesterol. With evolutionary, biophysical and behavioral analyses, we showed how strikingly novel structural adaptations facilitate the receptor’s transition from an ancestral role in neurotransmission to a new function in contact-dependent chemosensation of greasy environmental chemicals.”
The second Nature study focused on squid and their wholly different ambush strategy for capturing food. The researchers combined genetics, physiology and behavioral experiments to discover a new class of ancient chemotactile receptors and determined one structure within the class. They also conducted an evolutionary analysis to link adaptations in squid receptors to more elaborate expansions in octopus. They were then able to place chemotactile and ancestral neurotransmitter receptors on an evolutionary timeline and described how evolutionary adaptations drove the development of new behaviors.
“We discovered a new family of cell surface receptors that offer a rare lens into the evolution of sensation because they represent the most recent and only functionally tractable transition from neurotransmitter to environmental receptors across the entire animal kingdom,” said Hibbs. “Our structures of these unique cephalopod receptors lay a foundation for the mechanistic understanding of major functional transitions in deep evolutionary time and the origin of biological novelty.”
Hibbs says the pair of new studies offers an excellent example of how curiosity in interesting creatures can lead to insights important for all of biology, namely how proteins—life’s building blocks—adapt to mediate new functions and behaviors.
“These studies are a great example of what being a scientist is all about—wonder, exploration and understanding how things work,” he said.
END
Tracking a new path to octopus and squid sensing capabilities
Research reveals that the octopus explores the marine environment with sensing features that are evolutionarily related to human brain receptors
2023-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Trees in savanna areas of Cerrado produce three times more bark than species in forest areas
2023-04-14
In tropical regions of the planet, savannas and forests often coexist in the same area and are exposed to the same climate. An example is the Cerrado, a Brazilian biome that includes several types of vegetation, from broad-leaved and sclerophyllous in dense woodland or shrubland (cerrado sensu stricto) to semi-evergreen in closed-canopy forest (cerradão), as well as grassland with scattered shrubs (campo sujo) and even semi-deciduous seasonal forest.
Areas of cerradão develop in the absence of fire, in both poor and moderately fertile soil (dystrophic to mesotrophic).
This coexistence intrigues botanists and ecologists ...
Wayne State researcher receives $1.95 million NIH grant to study impact of inositol homeostasis on essential cellular functions
2023-04-14
DETROIT – A researcher from Wayne State University’s Department of Biological Sciences has received a five-year, $1.95 million grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health to identify mechanisms that regulate inositol synthesis in mammalian cells and determine the cellular consequences of inositol depletion.
Inositol is a type of sugar that is essential for the viability of eukaryotic cells. Myo-inositol is the precursor of all inositol compounds, which play pivotal roles in cell signaling and metabolism. Consistent with its importance, a disturbance of inositol homeostasis ...
Head and neck, breast cancer research highlights University of Cincinnati AACR abstracts
2023-04-14
University of Cincinnati Cancer Center researchers will present more than a dozen abstracts at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2023, held in Orlando, Florida, April 14-19, including findings that could advance treatments for head and neck and breast cancers.
Enzyme shows promise as target to treat HPV negative head and neck cancer
Vinita Takiar’s lab in UC’s Department of Radiation Oncology studies how to improve radiation therapy for head and neck cancer patients.
Julianna Korns, a doctoral student working in Takiar’s lab, and her colleagues study an enzyme called Plk1 that allows healthy cells to divide ...
Scientists develop new way to measure wind
2023-04-14
Wind speed and direction provide clues for forecasting weather patterns. In fact, wind influences cloud formation by bringing water vapor together. Atmospheric scientists have now found a novel way of measuring wind – by developing an algorithm that uses data from water vapor movements. This could help predict extreme events like hurricanes and storms.
A study published by University of Arizona researchers in the journal Geophysical Research Letters provides, for the first time, data on the vertical distribution of horizontal winds ...
Ancient DNA reveals the multiethnic structure of Mongolia’s first nomadic empire
2023-04-14
Long obscured in the shadows of history, the world’s first nomadic empire - the Xiongnu - is at last coming into view thanks to painstaking archaeological excavations and new ancient DNA evidence. Arising on the Mongolian steppe 1,500 years before the Mongols, the Xiongnu empire grew to be one of Iron Age Asia’s most powerful political forces - ultimately stretching its reach and influence from Egypt to Rome to Imperial China. Economically grounded in animal husbandry and dairying, the Xiongnu were famously nomadic, building their empire on the backs of horses. ...
2022 Tongan volcanic explosion was largest natural explosion in over a century, new study finds
2023-04-14
The 2022 eruption of a submarine volcano in Tonga was more powerful than the largest U.S. nuclear explosion, according to a new study led by scientists at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science and the Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation.
The 15-megaton volcanic explosion from Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai, one of the largest natural explosions in more than a century, generated a mega-tsunami with waves up to 45-meters high (148 feet) along the coast of Tonga’s Tofua Island and waves up to 17 meters (56 feet) on Tongatapu, ...
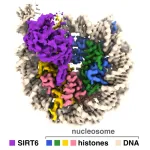
How does an aging-associated enzyme access our genetic material?
2023-04-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — New research provides insight into how an enzyme that helps regulate aging and other metabolic processes accesses our genetic material to modulate gene expression within the cell. A team led by Penn State researchers have produced images of a sirtuin enzyme bound to a nucleosome—a tightly packed complex of DNA and proteins called histones—showing how the enzyme navigates the nucleosome complex to access both DNA and histone proteins and clarifying how it functions in humans and other animals.
A paper describing the results appears April 14 in the journal ...
Aston University develops software to untangle genetic factors linked to shared characteristics among different species
2023-04-14
Has potential to help geneticists investigate vital issues such as antibacterial resistance
Will untangle the genetic components shared due to common ancestry from the ones shared due to evolution
The work is result of a four-year international collaboration.
Aston University has worked with international partners to develop a software package to help scientists answer key questions about genetic factors associated with shared characteristics among different species.
Called CALANGO (comparative analysis with annotation-based genomic ...
Single-use surgical items contribute two-thirds of carbon footprint of products used in common operations
2023-04-14
A new analysis of the carbon footprint of products used in the five most common surgical operations carried out in the NHS in England shows that 68% of carbon contributions come from single-use items, such as single-use gowns, patient drapes and instrument table drapes. Published by the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, the analysis highlights significant carbon contributors were the production of single use items and their waste disposal, together with processes for decontaminating reusable products.
Researchers ...
Study: Anti-obesity medications could be sold for lower prices
2023-04-14
ROCKVILLE, Md.—New research shows that several anti-obesity medications could be manufactured and profitability sold worldwide at far lower estimated lower prices compared to their high costs, according to a new study in Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
“Access to medicine is a fundamental element of the human right to health. While the obesity pandemic grows, especially amongst low-income communities, effective medical treatments remain inaccessible for millions in need. Our study highlights the inequality in pricing that exists for effective anti-obesity medications, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
[Press-News.org] Tracking a new path to octopus and squid sensing capabilitiesResearch reveals that the octopus explores the marine environment with sensing features that are evolutionarily related to human brain receptors