(Press-News.org) **Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Multidrug-resistant E. coli were found in 40% of supermarket meat samples tested in a Spanish study. E. coli strains capable of causing severe infections in people were also highly prevalent, this year's European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April) will hear.
Antibiotic resistance is reaching dangerously high levels around the world. Drug-resistant infections kill an estimated 700,000 people a year globally and, with the figure projected to rise to 10 million by 2050 if no action is taken, the World Health Organization (WHO) classes antibiotic resistance as one of the greatest public health threats facing humanity.
Multidrug-resistant bacteria can spread from animals to humans through the food chain but, due to commercial sensitivities, data on levels of antibiotic-resistant bugs in food is not made widely available.
To find out more, Dr Azucena Mora Gutiérrez and Dr Vanesa García Menéndez, of the University of Santiago de Compostela-Lugo, Lugo, Spain, together with colleagues from other research centres, designed a series of experiments to assess the levels of multidrug-resistant and extraintestinal pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae (Klebsiella pneumoniae, E. coli and other bacteria that can cause multidrug-resistant infections such as sepsis or urinary tract infections) in meat on sale in Spanish supermarkets.
They analysed 100 meat products (25 each of chicken, turkey, beef and pork) chosen at random from supermarkets in Oviedo during 2020.
The majority (73%) of the meat products contained levels of E. coli that were within food safety limits.
Despite this, almost half (49%) contained multidrug-resistant and/or potentially pathogenic E. coli. From those, 82 E. coli isolates were recovered and characterised. In addition, 12 K. pneumoniae isolates were recovered from 10 of the 100 meat products (7 chicken, 2 turkey and 1 pork).
Forty of the 100 meat products contained multidrug-resistant E. coli (56 of the 82 E. coli characterised). These included E. coli that produced extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), enzymes that confer resistance to most beta-lactam antibiotics, including penicillins, cephalosporins and the monobactam aztreonam.
The percentage of positive samples for the carriage of ESBL-producing E. coli per meat type was: 68% turkey, 56% chicken, 16% beef and 12% pork. This higher presence of ESBL-producing E. coli strains in poultry compared to other types of meat is likely due to differences in production and slaughter.
Twenty-seven per cent of the meat products contained potentially pathogenic extraintestinal E. coli (ExPEC). ExPEC possess genes that allow them to cause disease outside the gastrointestinal tract. ExPEC causes the vast majority of urinary tract infections (UTIs), is a leading cause of adult bacteraemia (sepsis) and is the second most common cause of neonatal meningitis.
Six per cent of the meat products contained uropathogenic (UPEC) E. coli – UPEC is part of the ExPEC group; these possess specific virulence traits that allow them to cause UTIs.
One per cent of the meat products contained E. coli harbouring the mcr-1 gene. This gene confers resistance to colistin, an antibiotic of last resort used to treat infections caused by bacteria resistant to all other antibiotics.
The study’s authors, who in a previous study reported high levels of bacteria that were potentially capable of causing severe human infections and/or multidrug resistant in chicken and turkey1, say that their latest research shows that consumers may also be exposed to these bacteria through beef and pork.
They are calling for regular assessment of levels of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, including ExPEC E. coli, in meat products.
Dr Mora adds: “Farm-to-fork interventions must be a priority to protect the consumer. For example, implementation of surveillance lab methods to allow further study of high-risk bacteria (in farm animals and meat) and their evolution due to the latest EU restriction programmes on antibiotic use in veterinary medicine.
“Strategies at farm level, such as vaccines, to reduce the presence of specific multidrug-resistant and pathogenic bacteria in food-producing animals, which would reduce the meat carriage and consumer risk.
“The consumer plays a key role in food safety through proper food handling. Advice to consumers includes not breaking the cold chain from the supermarket to home, cooking meat thoroughly, storing it properly in the refrigerator and disinfecting knives, chopping boards and other cooking utensils used to prepare raw meat appropriately to avoid cross-contamination. With these measures, eating meat becomes a pleasure and zero risk.”
Dr Azucena Mora Gutiérrez, University of Santiago de Compostela-Lugo, Lugo, Spain T) +34 630613742 E) azucena.mora@usc.es
Dr Vanesa García Menéndez, University of Santiago de Compostela-Lugo, Lugo, Spain. E) vanesag.menendez@usc.es
Alternative contact: Tony Kirby in the ECCMID Media Centre. T) +44 7834 385827 E) tony@tonykirby.com
Notes to editors:
References:
1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107713
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
This press release is based on abstract 3827 at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) annual meeting. The material has been peer reviewed by the congress selection committee. There is no full paper at this stage.
For full abstract click here
For full poster click here
END
Multidrug-resistant bacteria found in 40% of supermarket meat samples
“Superbugs” present in chicken, turkey, beef and pork, Spanish study finds
2023-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Major genetic study reveals how antibiotic resistance varies according to where you live, demographics, and diet
2023-04-15
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
A genetic study analysing the microbiome (bacteria in the gut) of a large nationally representative sample of the Finnish population finds that geographic, demographic, diet, and lifestyle factors are driving the spread of antibiotic resistance in the general population.
The most comprehensive study of its kind by Dr Katariina Pärnänen ...
UK-Portuguese study shows antibiotic-resistant “superbugs” are being passed between dogs and cats and their owners, study strongly suggests
2023-04-15
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Evidence that multidrug-resistant bacteria are being passed between pet cats and dogs and their owners will be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
Six pets in Portugal and one in the UK were carrying antibiotic-resistant bacteria similar to those found in their owners, a Portuguese study found.
The finding underlines the importance ...
Study of cerebral blood vessels uncovers potential new drug targets for treating stroke
2023-04-14
Strokes cause numerous changes in gene activity in affected small blood vessels in the brain, and these changes are potentially targetable with existing or future drugs to mitigate brain injury or improve stroke recovery, according to a study led by Weill Cornell Medicine scientists.
In the study, which appears Apr. 14 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers performed a comprehensive survey, in a preclinical model, of gene activity changes in small blood vessels in the brain following stroke. Comparing these changes to those that have been recorded in stroke patients, they catalogued hundreds ...
Tracking a new path to octopus and squid sensing capabilities
2023-04-14
Along their eight arms, octopuses have highly sensitive suckers that allow methodical explorations of the seafloor as they search for nourishment in a “taste by touch” approach. Squids, on the other hand, use a much different tactic to find their next meal: patiently hiding until they ambush their prey in swift bursts.
In a unique analysis that provides a glimpse into the origin stories of new animal traits, a pair of research studies led by University of California San Diego and Harvard University scientists has traced the evolutionary adaptations of octopus and squid sensing capabilities. The studies, featured on ...
Trees in savanna areas of Cerrado produce three times more bark than species in forest areas
2023-04-14
In tropical regions of the planet, savannas and forests often coexist in the same area and are exposed to the same climate. An example is the Cerrado, a Brazilian biome that includes several types of vegetation, from broad-leaved and sclerophyllous in dense woodland or shrubland (cerrado sensu stricto) to semi-evergreen in closed-canopy forest (cerradão), as well as grassland with scattered shrubs (campo sujo) and even semi-deciduous seasonal forest.
Areas of cerradão develop in the absence of fire, in both poor and moderately fertile soil (dystrophic to mesotrophic).
This coexistence intrigues botanists and ecologists ...
Wayne State researcher receives $1.95 million NIH grant to study impact of inositol homeostasis on essential cellular functions
2023-04-14
DETROIT – A researcher from Wayne State University’s Department of Biological Sciences has received a five-year, $1.95 million grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health to identify mechanisms that regulate inositol synthesis in mammalian cells and determine the cellular consequences of inositol depletion.
Inositol is a type of sugar that is essential for the viability of eukaryotic cells. Myo-inositol is the precursor of all inositol compounds, which play pivotal roles in cell signaling and metabolism. Consistent with its importance, a disturbance of inositol homeostasis ...
Head and neck, breast cancer research highlights University of Cincinnati AACR abstracts
2023-04-14
University of Cincinnati Cancer Center researchers will present more than a dozen abstracts at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2023, held in Orlando, Florida, April 14-19, including findings that could advance treatments for head and neck and breast cancers.
Enzyme shows promise as target to treat HPV negative head and neck cancer
Vinita Takiar’s lab in UC’s Department of Radiation Oncology studies how to improve radiation therapy for head and neck cancer patients.
Julianna Korns, a doctoral student working in Takiar’s lab, and her colleagues study an enzyme called Plk1 that allows healthy cells to divide ...
Scientists develop new way to measure wind
2023-04-14
Wind speed and direction provide clues for forecasting weather patterns. In fact, wind influences cloud formation by bringing water vapor together. Atmospheric scientists have now found a novel way of measuring wind – by developing an algorithm that uses data from water vapor movements. This could help predict extreme events like hurricanes and storms.
A study published by University of Arizona researchers in the journal Geophysical Research Letters provides, for the first time, data on the vertical distribution of horizontal winds ...
Ancient DNA reveals the multiethnic structure of Mongolia’s first nomadic empire
2023-04-14
Long obscured in the shadows of history, the world’s first nomadic empire - the Xiongnu - is at last coming into view thanks to painstaking archaeological excavations and new ancient DNA evidence. Arising on the Mongolian steppe 1,500 years before the Mongols, the Xiongnu empire grew to be one of Iron Age Asia’s most powerful political forces - ultimately stretching its reach and influence from Egypt to Rome to Imperial China. Economically grounded in animal husbandry and dairying, the Xiongnu were famously nomadic, building their empire on the backs of horses. ...
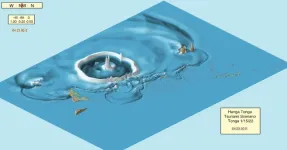
2022 Tongan volcanic explosion was largest natural explosion in over a century, new study finds
2023-04-14
The 2022 eruption of a submarine volcano in Tonga was more powerful than the largest U.S. nuclear explosion, according to a new study led by scientists at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science and the Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation.
The 15-megaton volcanic explosion from Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai, one of the largest natural explosions in more than a century, generated a mega-tsunami with waves up to 45-meters high (148 feet) along the coast of Tonga’s Tofua Island and waves up to 17 meters (56 feet) on Tongatapu, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
[Press-News.org] Multidrug-resistant bacteria found in 40% of supermarket meat samples“Superbugs” present in chicken, turkey, beef and pork, Spanish study finds