(Press-News.org) About The Study: Among adults with laboratory-confirmed Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) with one or more prior CDI episodes in the last six months and those with primary CDI at high risk for recurrence, high-dose VE303 (a novel oral microbiome-directed therapy composed of nonpathogenic, nontoxigenic, commensal strains of Clostridia) prevented recurrent CDI compared with placebo. A larger, phase 3 study is needed to confirm these findings.
Authors: Jeffrey L. Silber, M.D., of Vedanta Biosciences Inc., in Cambridge, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.4314)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: The study is being released to coincide with presentation at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2023.4314?guestAccessKey=78cc89bf-06db-4687-a463-da021a5f18dd&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=041523
END
Bacterial consortium therapy for prevention of recurrent c difficile infection
JAMA
2023-04-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
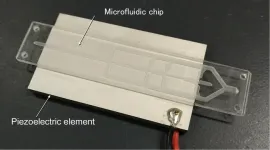
Filtering pollution: A microfluidic device for collecting microplastics via acoustic focusing
2023-04-15
Plastic debris particles smaller than 5 mm in size, known as microplastics (MPs), are a serious environmental concern. Formed by the breaking down of plastic waste due to wear and tear and sunlight or produced by fiber waste in laundry wastewater and as microbeads in beauty products, they adsorb and introduce harmful chemicals that pollute the environment. By 2050, MPs might outnumber the fish in the oceans. Under these circumstances, the collection and removal of MPs from water are crucial.
Conventionally, MPs are collected by filtering water through meshes. ...
Detailed guidance on natural pacemaker method published today
2023-04-15
Barcelona, Spain – 15 April 2023: An international consensus statement on the safest and most effective way to implant a pacing system that mimics the heart’s normal function is published today in EP Europace,1 a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). The document is being launched at the EHRA Conduction System Pacing (CSP) Summit2 and will be discussed during EHRA 2023, a scientific congress of the ESC.3
“It is estimated that 1.4 million patients worldwide will receive a pacemaker in 2023,” said first author ...
Clinical staff MRSA carriage and environmental contamination by other “superbugs” found in Portuguese veterinary practices
2023-04-15
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Examination tables, scales and other surfaces in small animal veterinary practices are frequently contaminated with multidrug-resistant “superbugs”, the results of a Portuguese study suggest.
The research, which is being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) ...
Multidrug-resistant bacteria found in 40% of supermarket meat samples
2023-04-15
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Multidrug-resistant E. coli were found in 40% of supermarket meat samples tested in a Spanish study. E. coli strains capable of causing severe infections in people were also highly prevalent, this year's European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April) will hear.
Antibiotic resistance is reaching dangerously high levels around the world. Drug-resistant infections kill ...
Major genetic study reveals how antibiotic resistance varies according to where you live, demographics, and diet
2023-04-15
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
A genetic study analysing the microbiome (bacteria in the gut) of a large nationally representative sample of the Finnish population finds that geographic, demographic, diet, and lifestyle factors are driving the spread of antibiotic resistance in the general population.
The most comprehensive study of its kind by Dr Katariina Pärnänen ...
UK-Portuguese study shows antibiotic-resistant “superbugs” are being passed between dogs and cats and their owners, study strongly suggests
2023-04-15
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Evidence that multidrug-resistant bacteria are being passed between pet cats and dogs and their owners will be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
Six pets in Portugal and one in the UK were carrying antibiotic-resistant bacteria similar to those found in their owners, a Portuguese study found.
The finding underlines the importance ...
Study of cerebral blood vessels uncovers potential new drug targets for treating stroke
2023-04-14
Strokes cause numerous changes in gene activity in affected small blood vessels in the brain, and these changes are potentially targetable with existing or future drugs to mitigate brain injury or improve stroke recovery, according to a study led by Weill Cornell Medicine scientists.
In the study, which appears Apr. 14 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers performed a comprehensive survey, in a preclinical model, of gene activity changes in small blood vessels in the brain following stroke. Comparing these changes to those that have been recorded in stroke patients, they catalogued hundreds ...
Tracking a new path to octopus and squid sensing capabilities
2023-04-14
Along their eight arms, octopuses have highly sensitive suckers that allow methodical explorations of the seafloor as they search for nourishment in a “taste by touch” approach. Squids, on the other hand, use a much different tactic to find their next meal: patiently hiding until they ambush their prey in swift bursts.
In a unique analysis that provides a glimpse into the origin stories of new animal traits, a pair of research studies led by University of California San Diego and Harvard University scientists has traced the evolutionary adaptations of octopus and squid sensing capabilities. The studies, featured on ...
Trees in savanna areas of Cerrado produce three times more bark than species in forest areas
2023-04-14
In tropical regions of the planet, savannas and forests often coexist in the same area and are exposed to the same climate. An example is the Cerrado, a Brazilian biome that includes several types of vegetation, from broad-leaved and sclerophyllous in dense woodland or shrubland (cerrado sensu stricto) to semi-evergreen in closed-canopy forest (cerradão), as well as grassland with scattered shrubs (campo sujo) and even semi-deciduous seasonal forest.
Areas of cerradão develop in the absence of fire, in both poor and moderately fertile soil (dystrophic to mesotrophic).
This coexistence intrigues botanists and ecologists ...
Wayne State researcher receives $1.95 million NIH grant to study impact of inositol homeostasis on essential cellular functions
2023-04-14
DETROIT – A researcher from Wayne State University’s Department of Biological Sciences has received a five-year, $1.95 million grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health to identify mechanisms that regulate inositol synthesis in mammalian cells and determine the cellular consequences of inositol depletion.
Inositol is a type of sugar that is essential for the viability of eukaryotic cells. Myo-inositol is the precursor of all inositol compounds, which play pivotal roles in cell signaling and metabolism. Consistent with its importance, a disturbance of inositol homeostasis ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] Bacterial consortium therapy for prevention of recurrent c difficile infectionJAMA