(Press-News.org) The time has come and gone for universal masking in healthcare settings, according to healthcare epidemiologists and infectious diseases experts from healthcare systems throughout Boston and beyond. In a commentary published in Annals of Internal Medicine and co-authored by experts from Mass General Brigham, Beth Israel Lahey Health, Tufts Medicine, the VA Healthcare System Boston, and other healthcare systems across the country, the authors describe the changing context and conditions of the pandemic and outline why universal masking should no longer be required in healthcare settings.
“While critically important in the earlier phases of the pandemic, we’ve entered a more stable phase, with substantial population-level immunity, durable protection against severe disease, a series of less virulent variants, and other important and favorable changes,” said corresponding author Erica S. Shenoy, MD, PhD, medical director of Infection Control for Mass General Brigham and an infectious diseases physician at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH). “As conditions change, we need to re-evaluate our infection prevention policies, including masking requirements in healthcare settings, and adapt.”
In the commentary, the authors emphasize different phases of the pandemic and describe that while universal masking was justifiable before medical countermeasures were available, advancements and population immunity have changed the appropriateness of the policy. Highlighting a theme of constant and ongoing change, they review the rationale for initially expanding mask use in healthcare settings, the reasons why de-escalation is needed, and conditions that could prompt reconsideration of use of masks more widely again.
“After three years of universal masking in healthcare, the risk-benefit calculation has shifted,” said Shira Doron, MD, chief infection control officer for Tufts Medicine health system and hospital epidemiologist at Tufts Medical Center. “Masks do have downsides, such as impaired communication and disrupted human connection. We are at a stage of the pandemic where it now makes sense to end mandatory masking.”
Given advancements, the authors advocate for managing SARS-CoV-2 in a similar way to how other respiratory viruses are managed in healthcare settings. This includes ensuring healthcare personnel use masks (and eye protection) when engaging in activities that could generate splashes or sprays and having patients mask if they have respiratory symptoms.
“As the pandemic moves into an endemic phase, we need to transition prevention efforts to incorporate all respiratory viruses. Performing risk assessments and applying lessons learned from COVID-19, including about how to apply masking, will permit a more flexible, durable response now and in future seasons,” said co-author Sharon Wright, MD, MPH, chief infection prevention officer at Beth Israel Lahey Health in Cambridge.
“The best evidence-based policy making is dynamic, and adapts to changing conditions, evidence, and contexts. As all these factors change, even policy goals may need to be updated,” said senior author Westyn Branch-Elliman, MD, MMSc, an infectious diseases specialist and clinical investigator at VA Boston Healthcare System. Since 2020, she explained, society has been living in a constant state of change during which we have achieved major preventative and therapeutic advancements and the infection fatality rate has fallen dramatically. She continued: “At the same time, we know universal masking is not without costs, even in healthcare. Given these realities, it is time to update policies once again, recognizing this is unlikely to be the last update. Change and adaptation are expected. That does not mean ‘the science has changed’, but almost everything around it has.”
Disclosures: None of the authors have relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. The views expressed are those of the authors. They do not necessarily represent those of the US Department of Veterans Affairs or the US Federal government.
Funding: No funding.
Paper cited: Shenoy ES et al. “Universal Masking in Healthcare Settings: A Pandemic Strategy Whose Time Has Come, and Gone, For Now.” Annals of Internal Medicine DOI: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-0793
END
Healthcare epidemiologists and infectious diseases experts review changing context for masking in healthcare settings
In a commentary, experts advocate for adapting policy to changing conditions
2023-04-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cardiac arrest in hospital: survival a matter of resources
2023-04-18
Hospital inpatients have better prospects of surviving a cardiac arrest in large hospitals and well-resourced wards, and daytime cardiac arrests are also associated with better chances of survival, a University of Gothenburg thesis shows.
Cardiac arrest means that the heart stops pumping blood. Within seconds, unconsciousness occurs; within minutes, brain cells start dying, causing irreparable damage.
The key to enhancing the patients’ chances of survival is restoring the circulation of oxygenated blood in the body. ...
Early study - faecal transplant to help slow early-stage motor neuron disease progression
2023-04-18
A randomised clinical trial is looking at whether faecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from healthy donors into adults with early-stage amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS – one of the most common forms of motor neurone disease) can modulate the immune reaction during inflammation responses that characterise disease progression, and aims to investigate the relationship between specific gut bacteria and their action on immune system cells.
The preliminary findings by Dr Alessandra Guarnaccia from Columbus-Gemelli University Hospital IRCCS, Rome, Italy and ...
Preventing a measles outbreak: steps taken by London hospital to protect patients and staff potentially exposed to the virus
2023-04-18
The steps taken by a London hospital to prevent an outbreak of measles will be detailed at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
Measles, which is highly contagious, can cause serious and potentially life-threating illness and complications including blindness, encephalitis (swelling of the brain) and pneumonia. Pregnant women, infants and severely immunocompromised individuals are at highest risk.
Contracted when pregnant, it can cause low birth weight babies, premature birth, miscarriage or stillbirth.
It usually starts with cold-like symptoms, followed by a rash a few days later. ...
AI software at least as good as radiologists at detecting TB from chest X-rays
2023-04-18
AI software can accurately detect TB from chest X-rays, a study being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark, (15-18 April), shows.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a major cause of death and disease worldwide. It causes 1.6 million deaths a year, making it is the 13th leading cause of death globally and the second biggest infectious killer, after COVID-19.
In low-resource settings, chest X-rays play an important role in the diagnosis of patients ...
Targeting nurse and patient ‘supercontactors’ in hospitals and long-term care facilities can help minimize spread of infectious diseases
2023-04-18
New research presented at this week’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (Copenhagen, 15-18 April) shows how interventions focused on so called ‘supercontactors’ in hospitals and other long term care facilities (LTCF) can optimise infection control and reduce the spread of infectious diseases. The study is by Dr Quentin Leclerc and colleagues at Institut Pasteur and the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers (Paris, France).
Hospitals and ...
Using machine learning to find reliable and low-cost solar cells
2023-04-18
Researchers at the University of California, Davis College of Engineering are using machine learning to identify new materials for high-efficiency solar cells. Using high-throughput experiments and machine learning-based algorithms, they have found it is possible to forecast the materials’ dynamic behavior with very high accuracy, without the need to perform as many experiments.
The work is featured on the cover of the April issue of ACS Energy Letters.
Hybrid perovskites are organic-inorganic molecules that have received a lot of attention ...
Resident T-cells key to salmonella immunity
2023-04-18
Salmonella infections cause about a million deaths a year worldwide, and there is an urgent need for better vaccines for both typhoid fever and non-typhoidal Salmonella disease. New work from researchers at the UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine shows how memory T cells, crucial for a vaccine that induces a powerful immune response, can be recruited into the liver in a mouse model of Salmonella.
The work was published April 11 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Understanding the immunology is key to developing a better vaccine,” said Professor Stephen McSorley, ...
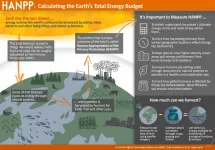
Counting the cost of sunshine: Finding a better metric to measure human ecological footprints
2023-04-18
This planet of 8 billion people is bumping up against its ecological limits, and researchers are trying to quantify the effect of human activity on these finite resources. Some keep tallies of how much carbon they contribute to the atmosphere, others measure direct and indirect water consumption or keep tabs on the amount of land that our food habits demand.
Each of these “footprints” offers an estimate of the impacts individuals and institutions have on the wider world, and are useful — but are flawed, according to geographer Chris ...
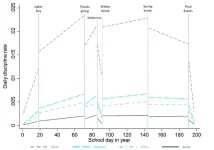
School discipline can be predicted, new research says. Is it preventable?
2023-04-18
Berkeley — Rates of school discipline fluctuate widely and predictably throughout a school year and increase significantly faster for Black students than for their white counterparts, University of California, Berkeley, researchers have found.
A new study published today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences documents for the first time the “dynamic” nature of student discipline during an academic year. Daily rates of punishment across all schools in the study ratchet up in the weeks before Thanksgiving break, decline immediately ...
How electricity can heal wounds three times as fast
2023-04-18
Chronic wounds are a major health problem for diabetic patients and the elderly – in extreme cases they can even lead to amputation. Using electric stimulation, researchers in a project at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, and the University of Freiburg, Germany, have developed a method that speeds up the healing process, making wounds heal three times faster.
There is an old Swedish saying that one should never neglect a small wound or a friend in need. For most people, a small wound does not lead to any serious complications, but many common diagnoses ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
CU Anschutz School of Medicine receives best ranking in NIH funding in 20 years
Mayo Clinic opens patient information office in Cayman Islands
Phonon lasers unlock ultrabroadband acoustic frequency combs
Babies with an increased likelihood of autism may struggle to settle into deep, restorative sleep, according to a new study from the University of East Anglia.
National Reactor Innovation Center opens Molten Salt Thermophysical Examination Capability at INL
International Progressive MS Alliance awards €6.9 million to three studies researching therapies to address common symptoms of progressive MS
Can your soil’s color predict its health?
Biochar nanomaterials could transform medicine, energy, and climate solutions
Turning waste into power: scientists convert discarded phone batteries and industrial lignin into high-performance sodium battery materials
PhD student maps mysterious upper atmosphere of Uranus for the first time
Idaho National Laboratory to accelerate nuclear energy deployment with NVIDIA AI through the Genesis Mission
Blood test could help guide treatment decisions in germ cell tumors
New ‘scimitar-crested’ Spinosaurus species discovered in the central Sahara
“Cyborg” pancreatic organoids can monitor the maturation of islet cells
Technique to extract concepts from AI models can help steer and monitor model outputs
Study clarifies the cancer genome in domestic cats
Crested Spinosaurus fossil was aquatic, but lived 1,000 kilometers from the Tethys Sea
MULTI-evolve: Rapid evolution of complex multi-mutant proteins
A new method to steer AI output uncovers vulnerabilities and potential improvements
Why some objects in space look like snowmen
Flickering glacial climate may have shaped early human evolution
First AHA/ACC acute pulmonary embolism guideline: prompt diagnosis and treatment are key
Could “cyborg” transplants replace pancreatic tissue damaged by diabetes?
Hearing a molecule’s solo performance
Justice after trauma? Race, red tape keep sexual assault victims from compensation
Columbia researchers awarded ARPA-H funding to speed diagnosis of lymphatic disorders
James R. Downing, MD, to step down as president and CEO of St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital in late 2026
A remote-controlled CAR-T for safer immunotherapy
UT College of Veterinary Medicine dean elected Fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology
AERA selects 34 exemplary scholars as 2026 Fellows
[Press-News.org] Healthcare epidemiologists and infectious diseases experts review changing context for masking in healthcare settingsIn a commentary, experts advocate for adapting policy to changing conditions