(Press-News.org) A hitherto unknown mechanism for DNA folding is described in a study in Nature published by researchers from Karolinska Institutet and the Max Planck Institute for Biophysics. Their findings provide new insights into chromosomal processes that are vital to both normal development and to prevent disease.
The DNA in our cells is organised into chromosomes, which are highly dynamic structures that are altered when genes are transcribed, when DNA damage is repaired or when chromosomes are compacte in preparation for cell division. These processes are affected by so called SMC protein complexes (SMC, Structural Maintenance of Chromosomes), which by mediating chromosomal interactions ensure correct spatial organization of the genome.
In humans and other eukaryotes, i.e., organisms whose cells contain a nucleus, there are three such protein complexes. Scientists have already revealed the mechanism of function for two of them. In the present study, the researchers investigated the third, the Smc5/6 complex, the function of which has remained mostly unknown.
“These results reveal the Smc5/6 complex as a new regulator of DNA folding, which can tell us more about how chromosomes are organised,” says Camilla Björkegren, professor at the Department of Cell and Molecular Biology at Karolinska Institutet, who led the study together with Eugene Kim, research group leader at the Max Planck Institute for Biophysics in Frankfurt am Main. “The discovery is also medically relevant, since DNA folding is important for normal chromosome function and for avoiding chromosomal alterations that could lead to disease.”
The researchers have purified the Smc5/6 complex from yeast and, using high-resolution microscopy of individual molecules, have studied how it binds and affects individual DNA molecules. The principles of chromosomal organisation are believed to be generally identical in yeast and humans, which are both eukaryotic organisms. For their experiments, the researchers both protein complex and DNA were labeled with differently coloured fluorescing molecules to make them traceable through a microscope.
Their results show that the Smc5/6 complex operates by extruding an increasingly larger DNA loop, a property it shares with the other known eukaryotic SMC complexes.
The researchers have also examined how the process is regulated and found, amongst other things, that two Smc5/6 complexes are needed to form a loop, while single protein complexes only translocates along the DNA molecule.
Previous research indicates that Smc5/6 inhibits certain viruses and suggests that it also protects against certain types of cancer, and is important to normal fetal development. The KI researchers now want to study how these properties are related to the newly discovered mechanism.
“The next step of our research is to find out how the Smc5/6 complex’s ability to make DNA loops affects their function in cells, which can increase our understanding of how Smc5/6 can function as a virus blocker, protect against cancer and contribute to fetal development,” says Professor Björkegren.
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Cancer Society, CIMED (the Centre for Innovative Medicine) and the Max Planck Institute for Biophysics. There are no declared potential conflicts of interest.
Publication: “The Smc5/6 complex is a DNA loop extruding motor”, Biswajit Pradhan, Takaharu Kanno, Miki Umeda Igarashi, Mun Siong Loke, Martin Dieter Baaske, Jan Siu Kei Wong, Kristian Jeppsson, Camilla Björkegren and Eugene Kim, Nature, online April 19 2023, doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05963-3
END
Nature-study reveals new mechanism for DNA folding
2023-04-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New findings pave the way for stable organic solar cells that may enable cheap and renewable electricity generation
2023-04-19
Due to the recent improvements in the efficiency with which solar cells made from organic (carbon-based) semiconductors can convert sunlight into electricity, improving the long-term stability of these photovoltaic devices is becoming an increasingly important topic. Real-world applications of the technology demand that the efficiency of the photovoltaic device be maintained for many years. To address this key problem, researchers have studied the degradation mechanisms for the two components used in the light-absorbing layer of organic solar cells: the ‘electron donor’ and ‘electron ...
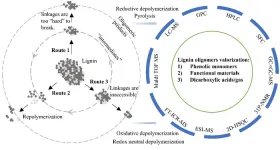
Perspective on oligomeric products from lignin depolymerization: their generation, identification, and further valorization
2023-04-19
Lignin depolymerization is playing a pivotal role in transforming the second most abundant biopolymers in nature into many valuable chemicals/fuels. This route could directly replace their petrol-based equivalents and therefore a great pathway to fight climate change and contribute to future sustainability. Interpretation of the reaction pathways is always desired to gain an insightful mechanic view in understanding the depolymerization chemistry and also paving new paths for lignin valorization at the industrial scale. However, such interpretation heavily relies on the state-of-art analytical capability since ...
UVA launches ambitious effort to reduce health disparities
2023-04-19
The University of Virginia School of Medicine has launched a new Center for Health Equity and Precision Public Health to improve the health and well-being of rural residents, the economically challenged and minority groups across Virginia and beyond.
The center will bring to bear expertise from across UVA to tackle many of today’s greatest public health issues. The goal: reduce health disparities and promote health equity to help people live longer, healthier lives.
“The pandemic has really taught us that, one, our public health infrastructure is not nearly as strong as it should be. And, two, we can't ...
Wonder drug-capsule may one day replace insulin injection for diabetics
2023-04-19
Scientists in Melbourne have designed a new type of oral capsule that could mean pain-free delivery of insulin and other protein drugs.
Co-lead researcher Professor Charlotte Conn, a biophysical chemist from RMIT University, said protein drugs had proven challenging to deliver orally as the drugs degrade very quickly in the stomach – until now.
“These types of drugs are typically administered with an injection – thousands of diabetics in Australia need insulin injections up to several times a day, which can be unpleasant for the patient and results in high healthcare costs,” said Conn, from RMIT’s School of Science.
She said the new technology could also be ...
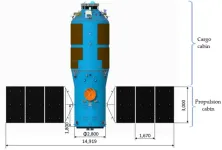
Scientists reviewed the research and development of Tianzhou cargo spacecraft
2023-04-19
Cargo spacecraft is robotic spacecraft designed to support space station operation by transporting food, propellant and other supplies. Tianzhou cargo spacecraft (The abbreviation is TZ) is a Chinese automated cargo spacecraft developed by the China Academy of Space Technology, as part of China's manned space Station program. The China Academy of Space Technology began to design TZ in 2010. Its main tasks are transporting and storing supplies for the space station, storing and descending waste materials for the space ...
SwRI launches the Global Decarbonized Mobility Summit Nov. 13-17
2023-04-19
SAN ANTONIO – 4.19.23 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) will host the inaugural Global Decarbonized Mobility Summit (GDMS) on Nov. 13-17. The multi-day summit will bring together key stakeholders in the transportation industry to discuss technology challenges associated with sustainable decarbonized mobility solutions for on-and-off-road applications.
The GDMS will assemble industry members from SwRI’s many automotive-related consortia and joint industry projects at its San Antonio headquarters. Throughout the summit, SwRI staff experts will hold sessions on the latest research and development advancements, pathways ...
Nebraska-led study first to define anxiety spiraling from national election
2023-04-19
Researchers are beginning to better understand the toll of polarized politics on mental and physical health, and a new study suggests that Americans’ political anxiety crescendos before a major election.
Led by University of Nebraska–Lincoln political scientist Kevin Smith, with Aaron Weinschenk of the University of Wisconsin–Green Bay and Costas Panagopoulos of Northeastern University, the study is the first to examine anxiety tethered to a specific political event — the 2020 presidential election, touted by both sides as the ...
A second chance for a healthy heart
2023-04-19
A recent study using mice has revealed a way to turn back the clock after heart attack. The researchers behind the work used RNAs to instruct cells in an injured heart to eliminate scar tissue and recreate cardiac muscle, allowing the heart to function like new again.
Cardiovascular disease, including heart attack, is the leading cause of death worldwide.
“Adult human hearts are not very good at repairing themselves,” said Conrad Hodgkinson, an associate professor of medicine and pathology at Duke University School of Medicine who oversaw the study. “Once they have a heart attack or any type of damage, ...
Study explores prosocial behavior within, between religious groups
2023-04-19
Does a commitment to one’s God facilitate altruistic behavior that benefits only members of the same religious group? Or does it extend to helping members of a different religion?
University of Illinois Chicago social psychologist Michael Pasek and colleagues examined this question through field and online experiments involving more than 4,700 people from diverse ethnoreligious populations in three political and cultural contexts.
Christians, Muslims, Hindus and Jews in the Middle East, Fiji and the United ...
Bad medical news causes patients to choose brand name drugs over generics, costing billions
2023-04-19
Researchers from Johns Hopkins University published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines how receiving negative medical results might affect how people choose between generic and brand name drugs.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Does Bad Medical News Reduce Preferences for Generic Drugs?” and is authored by Manuel Hermosilla and Andrew T. Ching.
At the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, Manuel Hermosilla received a call from a family friend in Chile who had been recently diagnosed with cancer. The friend needed help tracking down Hydroxychloroquine to treat ...