EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, APRIL 19, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People with epilepsy living in disadvantaged neighborhoods—areas with higher poverty levels and fewer educational and employment opportunities— may be more likely to have memory, thinking, and mental health problems compared to people with epilepsy living in neighborhoods with fewer disadvantages, according to new research published in the April 19, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that living in disadvantaged neighborhoods causes memory and mental health problems. It only shows an association.
“Epilepsy research has arguably ignored the potential impact of the social determinants of health in neighborhoods on cognition—factors that have been hiding in plain sight for many years,” said study author Robyn Busch, PhD, of Cleveland Clinic in Ohio. “Our study shows that these neighborhood social factors are linked to epilepsy outcomes.”
For the study, researchers reviewed a registry of people with temporal lobe epilepsy, the most common adult form of epilepsy, which is associated with high risk for thinking problems and depressed mood. Researchers identified 800 people with an average age of 38 whose epilepsy was resistant to treatment and who were evaluated for potential epilepsy surgery.
Researchers compared the participants’ scores on measures of intelligence, attention, memory and other thinking skills, depression and anxiety.
Researchers used the home address of each participant and a measure called the Area Deprivation Index to determine if each participant lived in an advantaged or disadvantaged neighborhood. The index incorporates information on the socioeconomic conditions of each neighborhood and its residents, ranking neighborhoods based on 17 indicators including income, employment, education and housing quality. Neighborhoods in the index are determined by census areas of about 1,500 residents.
Researchers divided participants into five groups based on neighborhood advantage.
In a composite score of all attention tests, with scores ranging from 60 to 135, people in neighborhoods with the most disadvantage had an average score of 85 compared to those in neighborhoods with the least disadvantage who had an average score of 95. Higher scores indicate better attention. Similar results were seen on measures of intelligence, processing speed, language, visuospatial skills, and memory, with people in the most disadvantaged neighborhoods showing lower test scores than those in less disadvantaged neighborhoods.
When compared to people in neighborhoods with the least disadvantage, people in neighborhoods with the most disadvantage were more likely to have worse cognitive outcomes across tests of different thinking skills. People who self-identified as Black, Hispanic or from other non-white groups were overrepresented in the most disadvantaged neighborhood group and were nearly three times more likely to have reduced scores on multiple cognitive tests than non-Hispanic white people.
Based on their self-reported symptoms, people in neighborhoods with the most disadvantage reported mild symptoms of depression and anxiety compared to those in neighborhoods with the least disadvantage who reported minimal symptoms of depression and anxiety.
“These study findings elevate the need to consider the role of social and neighborhood issues in assessing the outcomes for people with epilepsy,” said editorial author Lidia M. V. R. Moura, MD, MPH, PhD of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston and Fellow of the American Academy of Neurology. “More research is needed to identify these social factors that may be modifiable that can help improve cognition and prevent further worsening. More community-based partnerships and the usage of screening and mapping tools may help reduce these disparities among people with epilepsy.”
A limitation of the study was that Area Deprivation Index scores were measured at only one point in adulthood. This does not include neighborhood information during critical periods of early development or changes throughout life.
The study was supported by the Cleveland Clinic Epilepsy Center.
Learn more about epilepsy at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
For people with epilepsy, neighborhood may be tied to memory, mental health
2023-04-19
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Surgery for sciatica reduces leg pain and disability for some people, but benefits are short-lived
2023-04-19
Surgery to relieve leg pain and disability in some people with sciatica may be better than other non-surgical treatments, but the benefits are short-lived, lasting only up to 12 months, finds an analysis of the latest evidence published by The BMJ today.
What’s more, the certainty of available evidence is low to very low, prompting the researchers to suggest that surgery might only be a worthwhile option for people who feel that the rapid relief outweighs the costs and potential risks associated with surgery.
Sciatica refers to pain that travels along the path of the sciatic nerve, from the lower back and down the leg. In some people, sciatica occurs ...
Scientists discover cause of sea urchin die-offs in the Caribbean: a protozoan parasite
2023-04-19
The long-spined sea urchin Diadema antillarum is a keystone species. Coral reefs rely on healthy sea urchins to eat algae so coral can thrive. Healthy coral means healthy fish, and their positive impacts continue up the food chain.
In early 2022, long-spined sea urchins in St. Thomas began to quickly die in large numbers. Scientists rushed in to find the cause and have discovered that a microscopic parasite swarms the body and spines of the urchins, eating them alive.
The culprit, a microscopic organism called a scuticociliate, appears most similar to Philaster apodigitiformis, a type of protozoan parasite. It began decimating sea urchin populations around the Caribbean, ...
How opioid drugs get into our cells
2023-04-19
The human body naturally produces opioid-like substances, such as endorphins, which block the perception of pain and increase the feeling of well-being. Similarly, opioid drugs, including morphine or fentanyl, are widely used for alleviating severe pain. However, their use is associated with a high risk of dependence and addiction, and their excessive misuse causes over 350,000 annual deaths worldwide. Researchers from the University of Geneva (UNIGE) have compared the action of natural and therapeutic opioids. The latter penetrate inside the cells ...
Grambank shows the diversity of the world's languages
2023-04-19
Linguists have long been interested in language variation. What are common or universal patterns across languages? What limits the possible variation between them? Grambank, the world's largest and most comprehensive database of language structure, enables researchers to answer some of these questions.
Grambank was constructed in an international collaboration between the Max Planck institutes in Leipzig and Nijmegen, the Australian National University, the University of Auckland, Harvard University, ...
Nanoparticles provoke immune response against tumors but avoid side effects
2023-04-19
CAMBRIDGE, MA — Cancer drugs that stimulate the body’s immune system to attack tumors are a promising way to treat many types of cancer. However, some of these drugs produce too much systemic inflammation when delivered intravenously, making them harmful to use in patients.
MIT researchers have now come up with a possible way to get around that obstacle. In a new study, they showed that when immunostimulatory prodrugs — inactive drugs that require activation in the body — are tuned for optimal activation timing, the drugs provoke the immune system to attack tumors without the side effects that occur when the ...
Informed by mechanics and computation, flexible bioelectronics can better conform to a curvy body
2023-04-19
MADISON – Today, foldable phones are ubiquitous. Now, using models that predict how well a flexible electronic device will conform to spherical surfaces, University of Wisconsin–Madison and University of Texas at Austin engineers could usher in a new era in which these bendy devices can integrate seamlessly with parts of the human body.
In the future, for example, a flexible bioelectronic artificial retina implanted in a person’s eyeball could help restore vision, or a smart contact lens could continuously sense glucose levels in ...
Killer heatwaves endanger India’s development
2023-04-19
Deadly heatwaves fuelled by climate change in 2022 made almost 90 percent of Indians more vulnerable to public health issues, food shortages and increased risks of death, a new study from researchers at the University of Cambridge reported in PLOS Climate.
India currently uses a national Climate Vulnerability Indicator (CVI) to measure climate vulnerability and make plans for adaptation. The CVI includes many different socioeconomic, biophysical, institutional, and infrastructural factors. But it doesn't ...
Newfound link between Alzheimer’s and iron could lead to new medical interventions
2023-04-19
There is a growing body of evidence that iron in the brain may play a role in Alzheimer’s disease. Lending weight to that idea, a new imaging probe has for the first time shown that in the same regions of the brain where the amyloid beta plaques associated with Alzheimer’s occur, there is also an increase in iron redox, meaning the iron in these regions is more reactive in the presence of oxygen. Their imaging probe could yield even more details about the causes of Alzheimer’s and help in the search for new drugs to treat it.
A ...
Scientists identify 2022 sea urchin killer
2023-04-19
TAMPA, Fla. (APRIL 19, 2023) – The search for the 2022 killer that decimated the long-spined sea urchin population in the Caribbean and along Florida’s east coast is over. A team of researchers organized by Mya Breitbart, Distinguished University Professor at the University of South Florida’s College of Marine Science, identified a single-celled organism called a ciliate as the cause of a massive die-off event to a marine animal vital to coral reef health.
Their findings were reported in Science Advances.
“We’re beyond ...
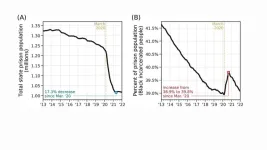
How the pandemic exacerbated racial inequalities in the US criminal legal system
2023-04-19
APRIL 19, 2023
As Covid roared through prisons in 2020, the U.S. prison population fell by as much as 30 percent, creating the largest, fastest reduction in prison population in American history. But this decarceration disproportionately benefited white incarcerated people, sharply increasing the fraction of incarcerated Black and Latino people. A new study in Nature shows that this increased racial disparity in U.S. prisons stems in large part from a long-standing problem with the justice system: Non-white people tend ...