(Press-News.org)
Genetic markers such as fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP), simple sequence repeat (SSR), and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) provide unique identifiers for individual organisms. This aids the identification of significant genetic variations in plants, allowing modern plant breeding to select superior crop varieties. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has enhanced marker-assisted selection or backcross breeding of crops, which is the transfer a desired trait such into the favored genetic background of another.
However, due to its expensive nature and extensive data processing requirements, NGS is not practical for screening large populations of crop plants, especially among small and medium breeders. A more cost-effective and efficient solution to assess desirable genetic traits in these populations is SNP arrays. These chips have embedded DNA probes that interact with a genetic sample, enabling the detection of hundreds of thousands of variations amongst two or more plant samples.
Tapping the potential of this approach, Associate Professor Wensheng Wang from the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and his research team have created a SNP array containing over 56,606 genetic markers for rice.
“Globally, more than 2.6 billion people rely on rice as a staple in their diet. The gene chip developed in our study can be an effective tool for breeders in selecting superior, new, high-quality rice varieties that are more flavorful, better tasting, salt tolerant, and resistant to diseases and insects,” shared Wang. “Moreover, the gene chip can be used for various genetic studies.”
The researchers developed the custom SNP array by collecting and sequencing genetic samples belonging to 3,024 rice samples from around the world. From over 18.9 million high-quality SNPs from this sample, approximately 2.5 million polymorphic SNPs were identified and retained in the array design. These SNPs were then printed on a genotyping chip platform (Affymetrix) with four designs.
The effectiveness of the array was tested by using a representative set of 192 rice varieties, and the results were impressive. On average, it correctly identified 99.6 % of the relevant genome, while also demonstrating high density and uniform coverage with an average distance of 6.7-kb between two adjacent SNPs. Furthermore, the data obtained from this platform offered more genetic variability information than other previously developed arrays.
The team reported their findings in KeAi’s The Crop Journal.
“Rice3K56 can help small and medium-sized companies select for superior rice varieties in a manner that is less subjective and low-effort,” said Wang. “Our work makes genotyping more mechanized and streamlined, resulting in higher efficiency and accuracy. In the long run, this can ensure not only food security but also a diversification of rice flavors.”
###
Contact the corresponding author: Wensheng Wang
The publisher KeAi was established by Elsevier and China Science Publishing & Media Ltd to unfold quality research globally. In 2013, our focus shifted to open access publishing. We now proudly publish more than 100 world-class, open access, English language journals, spanning all scientific disciplines. Many of these are titles we publish in partnership with prestigious societies and academic institutions, such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC).
END
Recently,Prof. LIU Lei's group from Peking University,the user of the Steady-state High Magnetic Field Experimental Facility (SHMFF), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with Prof. WANG Zhaosheng from High Magnetic Field Center, HFIPS of CAS and other co-authors revealed the structure-property relationship in 2D amorphous materials for the first time by the study of amorphous monolayer carbon (AMC).
The relevant research was published in ...
Recently, Professor WU Dayu of Changzhou University, the user of China's Steady High Magnetic Field Facility (SHMFF), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with his collaborators proposed a facile mechanical strategy to optimize the electronic structures of the catalytic center by mechanically induced spin transition, and realized a new method for designing efficient biomimetic catalysts.
The results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
In recent years, the synthesis of transition-metal catalysts has received extensive attention. ...
Organic peroxy radicals (RO2) are important intermediates in the degradation of atmospheric volatile organic compounds (VOCs). RO2 not only participates in the chain cycles of atmospheric radicals and influences oxidizing capacity of the atmosphere, but also controls the formation of secondary pollutants. Under low NOx conditions, peroxy radicals react mainly with HO2 radicals, as well as with themselves, and their products tend to have low volatility easily entering the particulate phase. However, the associated double radical ...
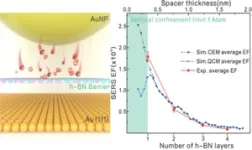
A research team led by Prof. YANG Liangbao from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences found that hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) could effectively block electron tunneling and extend the ultimate plasmonic enhancement limits in a single-atom-layer gap, providing deep insights into quantum mechanical effects in plasmonic systems and enabling potential novel applications based on quantum plasmonics.
The results were published in Nano Letters.
The team have been working on developing surface-enhanced ...
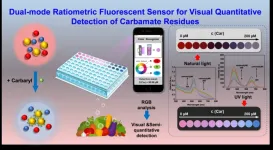
A team of researchers led by Prof. JIANG Changlong from Institute of Solid State Physics (ISSP), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of of Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a new sensing system for detecting carbaryl residues.
The research findings have been published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Carbaryl is a widely used insecticide that can easily enter the body through respiratory intake and dermal contact, resulting in serious health hazards, including carcinogenicity and reproductive abnormalities. Therefore, it is crucial to detect carbaryl residues in environmental and food samples. However, ...
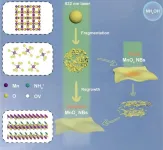
A recent study published in Sensors and Actuators: B. Chemical highlights the development of highly active oxidase mimics using MnOx nanobelts (NBs) generated through laser irradiation in liquid (LIL) techniques by researchers from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institute of Physical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Although nanozymes with oxidase mimic activity have shown promise for biomarker sensing, their lower activity compared to natural enzymes has constrained their wider application.
In this research, the team identified that MnOx NBs with an ultrathin layered structure ...
AUGUSTA, Ga. (April 25, 2023) – The first in-human-study of a new immunotherapy that blocks a natural enzyme tumors commandeer for their protection was well tolerated by children with relapsed brain tumors and enabled many to have unexpected months of a more normal life, researchers say.
“Our kids were by and large out of the hospital and going about their daily activities. They were in school, we had young adults who were in college living in a dorm on their own, taking their medicine on their own and coming to see us once a month,” says Theodore S. Johnson, MD/PhD, pediatric hematologist/oncologist ...
In the United States, depression and anxiety are on the rise in African Americans and the evidence suggests that racism is a contributing factor, creating a ripple effect on mental health.
Janeé M. Steele Ph.D. and Charmeka S. Newton, Ph.D. are licensed mental health professionals and scholars who specialize in culturally responsive therapy. They say: “In the Black community there can be a real resistance to our own trauma – for example, if I wasn’t exposed to physical abuse, is it really that bad?
“But this kind of systemic, permeating racism that exists all ...
It’s a dangerous world out there. From bacteria and viruses to accidents and injuries, threats surround us all the time. And nothing protects us more steadfastly than our skin. The barrier between inside and out, the body’s largest organ is also its most seamless defense.
And yet the skin is not invincible. It suffers daily the slings and arrows of outrageous fortune, and it tries to keep us safe by sensing and responding to these harms. A primary method is the detection of a pathogen, which kicks the immune system into action. But new research from the lab of Rockefeller’s Elaine Fuchs, published in Cell, reveals an alternative protective ...
The promise of superconductivity for electrical power transmission and transportation has long been held back by high costs. Now researchers from the University of Houston and Germany have demonstrated a way to cut the cost and upend both the transit and energy transport sectors by using superconductors to move people, cargo and energy along existing highway infrastructure.
The combined system would not only lower the cost of operating each system but would also provide a way to store and transport liquified hydrogen, an important ...