Investment in education in shrinking cities
Effectiveness of increasing the investment in educational support for children in shrinking cities
2023-04-25
(Press-News.org)
In Japan, many municipalities have suffered from population decline due to low birth rates and an aging population. In 2022, the Japanese population over the age of 65 was 36.21 million, accounting for 28.9% of the total population. In addition, approximately 1,300 shrinking cities are within the 1,700 municipalities in Japan. Moreover, the large number of shrinking cities in Japan is unprecedented on a global scale. As a response to the low birthrate, the Japanese government is discussing “unprecedented” measures to reverse the decline, such as providing financial assistance for education to families with young children.
Assistant Professor Haruka Kato, at the Graduate School of Human Life and Ecology, Osaka Metropolitan University, clarified the effectiveness of increasing educational support for children in preventing population decline. In detail, the study employed Bayesian network analysis, a technique for machine learning, using a dataset of economic, social, and educational indicators. The dataset consists of cross-sectional data from 259 indicators of approximately 1,300 shrinking cities, representing the majority of city-level government statistics in Japan.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates that social and educational indicators strongly affect the population decline rate. This implies that municipalities that invest more in education for children tend to have lower population decline rates. Surprisingly, educational indicators exert a greater influence than economic indicators, such as the financial strength index. The indicators include the “number of children per teacher in elementary school” and the “number of students per educational computer in schools.”
According to Professor Kato, “This relevance of educational indicators might be unique to Japan, which has experienced a declining population due to its low birthrates. Education accounts for a low percentage of national and administrative fiscal expenditures in Japan, primarily because social welfare expenditures for older adults are a heavy burden. However, among the fiscal expenditure limitations in Japan, the suggestion is that increasing investment in education for children might help solve the problem of shrinking cities. In addition, the conclusion would be effective in some Asian countries, such as South Korea and China, which will decline in population due to low birth rates and aging populations.”
The results were published in PLOS ONE.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established by a merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in April 2022. For more science news, see https://www.upc-osaka.ac.jp/new-univ/en-research/, and follow @OsakaMetUniv_en and #OMUScience.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-25
A new Cochrane Review led by an Upstate Medical University professor has found that, compared with standard antibiotic treatment, stool transplantation can increase the number of people recovering from Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection, a condition which causes potentially life-threatening diarrhea. 77 percent of people who received a stool transplant did not experience reinfection within eight weeks, compared to 40 percent of those who received antibiotics alone.
C. diff is a bacterium that can cause life-threatening diarrheal illness in individuals ...
2023-04-25
Poor air quality linked to cognitive problems in babies
Poor air quality could be causing cognitive deficits in babies and toddlers, according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today reveals an association between poor air quality in India and impaired cognition in infants under two.
Without action, the negative impact on children’s long-term brain development could have consequences for life.
Lead researcher Prof John Spencer, from UEA’s School of Psychology, said: “Prior work has shown that poor air quality is linked ...
2023-04-25
During the peak of the Covid-19 pandemic, a constant public fear was the rise of a new variant of the disease. Among the countless possibilities of a SARS-CoV-2 viral mutation, some were really alarming, such as Omicron, Delta, and Gamma. The strains with greater virulence and ability to invade the immune system are defined as variants of concern (VOCs), since they also have the potential to overwhelm the health system, increasing the number of admissions to intensive care units (UTIs). Recently published in the Intensive ...
2023-04-25
Genetic markers such as fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP), simple sequence repeat (SSR), and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) provide unique identifiers for individual organisms. This aids the identification of significant genetic variations in plants, allowing modern plant breeding to select superior crop varieties. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has enhanced marker-assisted selection or backcross breeding of crops, which is the transfer a desired trait such into the favored genetic background of another.
However, due to its expensive nature and extensive data processing requirements, NGS is not practical for screening large populations ...
2023-04-25
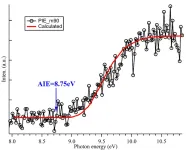
Recently,Prof. LIU Lei's group from Peking University,the user of the Steady-state High Magnetic Field Experimental Facility (SHMFF), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with Prof. WANG Zhaosheng from High Magnetic Field Center, HFIPS of CAS and other co-authors revealed the structure-property relationship in 2D amorphous materials for the first time by the study of amorphous monolayer carbon (AMC).
The relevant research was published in ...
2023-04-25
Recently, Professor WU Dayu of Changzhou University, the user of China's Steady High Magnetic Field Facility (SHMFF), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with his collaborators proposed a facile mechanical strategy to optimize the electronic structures of the catalytic center by mechanically induced spin transition, and realized a new method for designing efficient biomimetic catalysts.
The results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
In recent years, the synthesis of transition-metal catalysts has received extensive attention. ...
2023-04-25
Organic peroxy radicals (RO2) are important intermediates in the degradation of atmospheric volatile organic compounds (VOCs). RO2 not only participates in the chain cycles of atmospheric radicals and influences oxidizing capacity of the atmosphere, but also controls the formation of secondary pollutants. Under low NOx conditions, peroxy radicals react mainly with HO2 radicals, as well as with themselves, and their products tend to have low volatility easily entering the particulate phase. However, the associated double radical ...
2023-04-25
A research team led by Prof. YANG Liangbao from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences found that hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) could effectively block electron tunneling and extend the ultimate plasmonic enhancement limits in a single-atom-layer gap, providing deep insights into quantum mechanical effects in plasmonic systems and enabling potential novel applications based on quantum plasmonics.
The results were published in Nano Letters.
The team have been working on developing surface-enhanced ...
2023-04-25
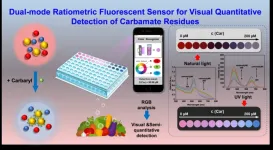
A team of researchers led by Prof. JIANG Changlong from Institute of Solid State Physics (ISSP), Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of of Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a new sensing system for detecting carbaryl residues.
The research findings have been published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Carbaryl is a widely used insecticide that can easily enter the body through respiratory intake and dermal contact, resulting in serious health hazards, including carcinogenicity and reproductive abnormalities. Therefore, it is crucial to detect carbaryl residues in environmental and food samples. However, ...
2023-04-25
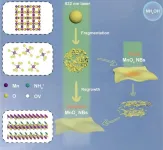
A recent study published in Sensors and Actuators: B. Chemical highlights the development of highly active oxidase mimics using MnOx nanobelts (NBs) generated through laser irradiation in liquid (LIL) techniques by researchers from Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institute of Physical Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Although nanozymes with oxidase mimic activity have shown promise for biomarker sensing, their lower activity compared to natural enzymes has constrained their wider application.
In this research, the team identified that MnOx NBs with an ultrathin layered structure ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Investment in education in shrinking cities
Effectiveness of increasing the investment in educational support for children in shrinking cities