(Press-News.org) It’s generally accepted we will lose muscle strength and slow down as we age, making it more difficult to perform simple tasks such as getting up, walking and sitting down.
But new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research indicates this could also be a signal for another sinister health concern of ageing: late-life dementia.
To investigate the relationship between muscle function and dementia, the research teams from ECU’s Nutrition & Health Innovation Research Institute and Centre for Precision Health used data from the Perth Longitudinal Study of Ageing in Women to examine more than 1000 women with an average age of 75.
In collaboration with the University of Western Australia, the team measured the women’s grip strength and the time it took for them to rise from a chair, walk three metres, turn around and sit back down — known as a timed-up-and-go (TUG), test.
These tests were repeated after five years to monitor any loss of performance.
Over the next 15 years, almost 17 per cent of women involved in the study were found to have had a dementia event, categorised as a dementia-related hospitalisation or death.
The team found lower grip strength and slower TUG were significant risk factors for presenting with dementia, independent of genetic risk and lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol intake and physical activity levels.
Relationship established
The women with the weakest grip strength were found to be more than twice as likely to have a late-life dementia event than the strongest individuals.
A similar relationship emerged between TUG performance and dementia, with the slowest in their TUG test more than twice as likely to experience dementia than the quickest.
When researchers looked at the changes in grip strength and TUG test results after five years, a decrease in performance was also linked with greater dementia risk.
Those who had experienced the biggest decline in grip strength and TUG speed were approximately 2 and 2.5 times more likely, respectively, to have had a dementia event, compared to those in the group who recorded the smallest decline in performance.
Women with the biggest drop in TUG performance were found to be over four times more likely to have a dementia-related death than the fastest.
An early warning
Senior researcher Dr Marc Sim said grip strength, which can be easily measured using a handheld device known as a dynamometer, may be a measure of brain health due to the overlapping nature of cognitive and motor decline.
“Possibly due to a range of underlying similarities, grip strength may also present as a
surrogate measure of cardiovascular disease, inflammation and frailty, which are known risk factors for dementia,” Dr Sim said.
Dr Sim said the findings from the study could help health professionals to identify dementia risk in patients earlier.
“Both grip strength and TUG tests aren’t commonly performed in clinical practice, but both are inexpensive and simple screening tools,” he said.
“Incorporating muscle function tests as part of dementia screening could be useful to identify high-risk individuals, who might then benefit from primary prevention programs aimed at preventing the onset of the condition such as a healthy diet and a physically active lifestyle.
“The exciting findings were that decline in these measures was associated with substantially higher risk, suggesting that if we can halt this decline, we may be able to prevent late-life dementias. However, further research is needed in this area.”
Centre for Precision Health Director Professor Simon Laws said there has been encouraging progress in identifying early warning signs of dementia.
“We are now starting to see a number of simple yet indicative screening assessments that could be combined with other biological and clinical measures to provide a holistic risk-profile for individuals presenting to their GP with, for example, memory concerns,” he said.
‘Impaired muscle function, including its decline, is related to greater long-term late-life dementia risk in older women’ was published in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.
END
Slowing down in your old age? It may be a dementia warning sign.
It’s generally accepted we will lose muscle strength and slow down as we age, but new research indicates this could also be a sign on a more sinister health concern of ageing.
2023-05-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Air pollution exposure associated with increased risk of irregular heartbeat: Large study
2023-05-01
Does air pollution affect your heart? Acute exposure to air pollution was found to be associated with an increased risk of arrythmia — irregular heartbeat — in a large study of 322 Chinese cities published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.220929.
The common arrhythmia conditions atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, which can progress to more serious heart disease, affect an estimated 59.7 million people globally. Air pollution is a modifiable risk factor for heart disease, but the evidence linking it with ...
Study highlights risks for self-harm events in children and adolescents
2023-05-01
The United States is in the midst of a mental health crisis with rising rates of hospitalization for suicide and self-harm events among children and adolescents.
A study, “Characteristics Associated with Serious Self-Harm Events in Children and Adolescents,” set to be published in the June issue of Pediatrics, looked at how best to determine which children are at elevated risk for self-harm.
Researchers identified four separate profiles to help medical professionals better assess children at elevated ...
Researchers explore why some people get motion sick playing VR games while others don’t
2023-05-01
The way our senses adjust while playing high-intensity virtual reality games plays a critical role in understanding why some people experience severe cybersickness and others don’t.
Cybersickness is a form of motion sickness that occurs from exposure to immersive VR and augmented reality applications.
A new study, led by researchers at the University of Waterloo, found that the subjective visual vertical – a measure of how individuals perceive the orientation of vertical lines – shifted considerably after participants played a high-intensity ...
Life on land and water teeters between haves and have-nots
2023-04-30
In the race to make the world more livable for people and nature, progress on land outpaced successes in the seas, raising red flags that wealthier countries’ advantages may be upsetting a balance, a Michigan State University study shows.
Progress in oceans actually slowed after the United Nations member states adopted the 17 Sustainable Development Goals in 2015. That action aims to facilitate global partnerships among developed and developing countries in sustainable development.
So far, though, a new study in the open-access journal iScience reveals evidence that ...
Community health workers in early childhood well-child care for Medicaid-insured children
2023-04-30
About The Study: The intervention examined in this randomized clinical trial resulted in improvements in the receipt of preventive care services versus usual care for children insured by Medicaid by incorporating community health workers in a team-based approach to early childhood well-child care.
Authors: Tumaini R. Coker, M.D., M.B.A., of Seattle Children’s Research Institute in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.7197)
Editor’s ...
Prostate cancer in transgender women in the VA health system
2023-04-29
About The Study: This case series demonstrated that prostate cancer occurs in transgender women and is not as rare as published case reports might suggest. However, rates were lower than expected based on prior prostate cancer incidence estimates in cisgender male veterans.
Authors: Farnoosh Nik-Ahd, M.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.6028)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Transgender women are still at risk for prostate cancer
2023-04-29
Transgender women keep their prostates even after gender-affirming surgery, but the extent to which they remain at risk of prostate cancer has been unclear.
Now a first of its kind study led by UC San Francisco has estimated the risk at about 14 cases per 10,000 people.
The study drew on 22 years of data from the Veterans Affairs Health System. Although the sample size was necessarily small, it is still the largest study of its kind. It publishes Saturday, April 29, 2023 in the Journal ...
New Jersey’s temporary health care license program expanded mental health services during pandemic
2023-04-29
At least 3,700 out-of-state mental health providers utilized New Jersey’s COVID-19 Temporary Emergency Reciprocity Licensure program to provide mental health services to more than 30,000 New Jersey patients during the first year of the pandemic, according to a Rutgers study.
The study, published in The Journal of Medical Regulation, surveyed health care practitioners who received a temporary license in New Jersey to examine the impact of the temporary licensure program on access to mental health care.
“The New Jersey program enabled patients with ...
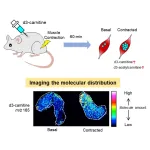
Scientists pinpoint where compound that helps metabolism hangs out in muscle cells
2023-04-29
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way of mapping the distribution of carnitine in skeletal muscle cells. Carnitine is a small compound that helps transport fatty acids and reduce metabolic byproducts. They discovered that slow-type muscle fibers contained the most, and that activity promptly led to rises in acetylcarnitine, a product of the immediate response of carnitine contained in the cell. Their technique promises new insights into how muscle cells work.
Our muscles require ...
Previously unknown intracellular electricity may power biology
2023-04-28
The human body relies heavily on electrical charges. Lightning-like pulses of energy fly through the brain and nerves and most biological processes depend on electrical ions traveling across the membranes of each cell in our body.
These electrical signals are possible, in part, because of an imbalance in electrical charges that exists on either side of a cellular membrane. Until recently, researchers believed the membrane was an essential component to creating this imbalance. But that thought was turned on its head when researchers at Stanford University discovered that similar imbalanced electrical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Slowing down in your old age? It may be a dementia warning sign.It’s generally accepted we will lose muscle strength and slow down as we age, but new research indicates this could also be a sign on a more sinister health concern of ageing.