(Press-News.org) A new study has shown that women are underrepresented in late-breaking cardiovascular clinical trials (LBCT) presented at national meetings. The study is published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Women’s Health. Click here to read the article now.
LBCT can have an impact on novel drug and device approvals, intervention indications, and patient management, according to Martha Gulati, MD, MS, from Smidt Heart Institute, and coauthors of the current study. The study investigators assessed the inclusion of women participants in LBCT presented at recent American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and European Society of Cardiology annual meetings. They also identified trial characteristics associated with improved inclusion of women.
The investigators reported that the inclusion to prevalence ratio was 0.76 for all trials and was significantly lower for procedural studies compared with medication trials.
‘These findings warrant further investigation to increase inclusion of women in trials, including potential enrollment requirements for consideration as LBCT by meeting organizers,” concluded the investigators.
About the Journal
Journal of Women’s Health, published monthly, is a core multidisciplinary journal dedicated to the diseases and conditions that hold greater risk for or are more prevalent among women, as well as diseases that present differently in women. Led by Editor-in-Chief Susan G. Kornstein, MD, Executive Director of the Virginia Commonwealth University Institute for Women’s Health, Richmond, VA, the Journal covers the latest advances and clinical applications of new diagnostic procedures and therapeutic protocols for the prevention and management of women’s healthcare issues. Complete tables of content and a sample issue may be viewed on the Journal of Women’s Health website. Journal of Women’s Health is the official journal of the Society for Women’s Health Research.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is a global media company dedicated to creating, curating, and delivering impactful peer-reviewed research and authoritative content services to advance the fields of biotechnology and the life sciences, specialized clinical medicine, and public health and policy. For complete information, please visit the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website.
END
Women are underrepresented in cardiovascular clinical trials
2023-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Veterans Affairs healthcare is as good as non-VA care for many operations
2023-05-08
Key takeaways
Quality and safety: The quality and safety of care across surgical specialties at VA healthcare sites is as good as, or better than, non-VA health centers on several quality measures.
Cost and efficiency: When looking at several studies that assessed differences in cost and efficiency, non-VA medical centers performed better than VA centers.
CHICAGO: By most measures, surgical care provided to United States military veterans in Veterans Affairs (VA) centers across the country is as good as, or better than, the same care delivered at non-VA medical centers, according to a new ...
National trends in pediatric deaths from fentanyl
2023-05-08
About The Study: Mirroring trends seen among adults, pediatric deaths from fentanyl began to increase substantially in 2013, resulting in a more than 30-fold increase in mortality between 2013 and 2021. A surge that began in 2018 has led to a nearly 3-fold increase in deaths among older adolescents and a nearly 6-fold increase among children younger than 5 years. Across age groups, annual deaths peaked in 2020 and 2021, suggesting that the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated this public health crisis.
Authors: Julie R. Gaither, Ph.D., M.P.H., R.N., of the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, ...
Ransomware attack associated with disruptions at adjacent emergency departments
2023-05-08
About The Study: This study found that hospitals adjacent to health care delivery organizations affected by ransomware attacks may see increases in patient census and may experience resource constraints affecting time-sensitive care for conditions such as acute stroke. These findings suggest that targeted hospital cyberattacks may be associated with disruptions of health care delivery at nontargeted hospitals within a community and should be considered a regional disaster.
Authors: Christian Dameff, M.D., M.S., of the University of California, San Diego, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Air pollution from oil and gas production responsible for $77 billion in annual US health damages, contributes to thousands of early deaths, childhood asthma cases nationwide
2023-05-08
These health impacts affected communities in states with high oil and gas production, as well as states with limited or no gas activity, underlining the need for comprehensive regulatory action to protect Americans from the pollutants generated by this sector.
Despite global efforts to transition from fossil fuels to clean energy, oil and gas (O&G) production is nearing record levels in the United States, posing concern among health experts about what this O&G growth means for air quality and human health. While ...
A sharp increase in the price of the gout drug colchicine led to lower use and poorer disease control, UCLA research suggests
2023-05-08
FINDINGS
Due to a policy decision in 2010 by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the price of a prescription for the therapeutic gout drug colchicine increased nearly 16-fold from $11.25 in 2009 to $190.49 in 2011. Out-of-pocket costs for patients who took the drug jumped more than four-fold from $7.37 to $39.49 over the same period. Use of colchicine dropped 17% during this time and 27% over the following decade. Patients turned to alternative medications for gout such as allopurinol and corticosteroids. However, disease ...
An unprecedented view of gene regulation
2023-05-08
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Much of the human genome is made of regulatory regions that control which genes are expressed at a given time within a cell. Those regulatory elements can be located near a target gene or up to 2 million base pairs away from the target.
To enable those interactions, the genome loops itself in a 3D structure that brings distant regions close together. Using a new technique, MIT researchers have shown that they can map these interactions with 100 times higher resolution than has previously been possible.
“Using this method, we generate the highest-resolution maps of the 3D genome that have ever been generated, and what we see are a lot of interactions between ...
AI helps create better, simpler hepatitis, COVID-19 tests
2023-05-08
Going beyond pregnancy and COVID-19, the world could someday soon come to rely on at-home tests for many diseases thanks in part to AI-fueled improvements.
University of Florida scientists have used artificial intelligence tools to simplify a test that works for both hepatitis C and SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The simplified test happens in one small test tube in just a few minutes. With further refinement, it could come to doctor’s offices soon and, one day, even home tests that are as easy as a pregnancy test.
“We are trying to build a home-based test that is as reliable as a lab-based test,” said Piyush ...
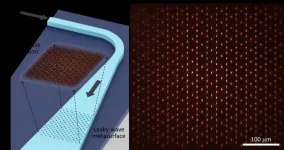
Leaky-wave metasurfaces: A perfect interface between free-space and integrated optical systems
2023-05-08
New York, NY—May 8, 2023—Researchers at Columbia Engineering have developed a new class of integrated photonic devices--“leaky-wave metasurfaces”--that can convert light initially confined in an optical waveguide to an arbitrary optical pattern in free space. These devices are the first to demonstrate simultaneous control of all four optical degrees of freedom, namely, amplitude, phase, polarization ellipticity, and polarization orientation--a world record. Because the devices are so thin, transparent, and compatible with photonic integrated circuits ...
AI predicts future pancreatic cancer
2023-05-08
An artificial intelligence tool has successfully identified people at the highest risk for pancreatic cancer up to three years before diagnosis using solely the patients’ medical records, according to new research led by investigators at Harvard Medical School and the University of Copenhagen, in collaboration with VA Boston Healthcare System, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
The findings, published May 8 in Nature Medicine, suggest that AI-based population screening could be valuable in finding those at elevated risk for the disease and could expedite the diagnosis of a condition ...
Tiny microbes could brew big benefits for green biomanufacturing
2023-05-08
A research team led by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley has engineered bacteria to produce new-to-nature carbon products that could provide a powerful route to sustainable biochemicals.
The advance – which was recently announced in the journal Nature – uses bacteria to combine natural enzymatic reactions with a new-to-nature reaction called the “carbene transfer reaction.” This work could also one day help reduce industrial emissions because it offers sustainable ...