(Press-News.org) Reforms to New Jersey’s Medicaid program successfully spurred ongoing increases in buprenorphine prescriptions for the treatment of opioid addiction, according to a Rutgers analysis.
Although medications such as buprenorphine effectively combat opioid addiction, less than 30 percent of potential users receive them nationwide. New Jersey sought to increase prescription numbers with three Medicaid reforms that took effect in 2019. The reforms:
Removed prior authorization requirements for buprenorphine prescriptions
Increased reimbursement rates for in-office opioid addiction treatment
Established regional centers of excellence for addiction treatment
Medicaid records showed steady increases in buprenorphine prescriptions before 2019, but the rate of growth increased by 36 percent after the reforms took effect, and this increased rate of growth persisted until the end of the study period in December 2020.
A similar trend affected caregiver behavior. The percentage of caregivers prescribing buprenorphine had been rising before the reforms took effect, but it increased faster after their implementation.
New Jersey also experienced faster growth in buprenorphine prescriptions to Medicaid patients than did other states, the analysis reported, a strong indication that the boosts stemmed from the state’s reforms rather than some unrelated nationwide trend.
The only disappointment came from the study’s measurement of long-term usage. The percentage of buprenorphine prescriptions that remained active for more than 180 days didn’t rise during the study period.
“Usage remains far below the ideal where virtually everyone battling opioid addiction receives an effective medical treatment like buprenorphine,” said Peter Treitler, research project manager for the Rutgers Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research and lead author of the analysis published in JAMA Network Open. “However, our analysis suggests these reforms may get us to that point years before we would have reached it under the previous policies.”
Buprenorphine — a once-daily prescription pill sold in the United States as Suboxone, Zubsolv and Sublocade — works in two ways. First, it binds to the same brain cells as drugs such as opium, heroin, morphine, oxycodone and fentanyl. Once it’s in place, those other drugs struggle to dislodge it, bind to the target cells and produce addictive highs. Second, it stimulates a milder effect that reduces cravings for those other drugs and prevents withdrawal symptoms.
Regulators once placed extra restrictions on buprenorphine prescriptions because they worried its mood-altering effects would create more addicts than it cured. These restrictions, which forced caregivers to justify each new buprenorphine prescription at length and investigated providers who prescribed the drug “too often,” led many to avoid prescribing the drug at all, said Treitler, who added Medicaid’s low reimbursement rates for office-based addiction treatment further reduced buprenorphine availability to poor patients.
Regulators have relaxed many restrictions on buprenorphine because opioid addiction has increased. Recent research has shown buprenorphine to be both safer and more effective than previously thought. The reforms to New Jersey’s Medicaid program further reduced barriers to medication usage among its patients.
“They looked at what obstacles were blocking the usage of a valuable drug in this particularly underserved patient population,” Treitler said. “They removed several of the biggest obstacles. And the results so far suggest they’re getting the desired results.”
Indeed, the positive numbers seen in initiatives such as the one undertaken by New Jersey’s Medicaid program may finally be affecting the most important number of all: overdose deaths. After several decades of speedy increases, overdoses nationwide rose by just 500 in 2022.
The trend was even better in New Jersey. Total overdose deaths fell by 232 from 2021 to 2022, and they were 93 lower in the first three months of 2023 than in the first three months of 2022.
END
NJ Medicaid reforms tied to increased use of opioid addiction treatment
2023-05-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mechanical thrombectomy significantly improves patient outcomes and quality of life following a pulmonary embolism
2023-05-19
Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- Six month outcomes from the FlowTriever All-Comer Registry for Patient Safety and Hemodynamics (FLASH) registry were presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. The prospective multi-center study found that patients with pulmonary embolism (PE) who were treated with mechanical thrombectomy showed significant improvement in symptoms, quality of life and cardiac functions.
Pulmonary embolism, a blood clot that starts in a blood vessel in the body and travels to ...
New analysis of critical limb-ischemia patients places best-cli trial into context within real-world setting
2023-05-19
Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- New analysis of chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) treatment outcomes was presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. Following the initial results of the BEST-CLI (Best Endovascular vs. Best Surgical Therapy in Patients With Critical Limb Ischemia) trial in 2022 which found surgical intervention superior to endovascular revascularization, questions remained regarding how inclusive the enrolled patient population was, how reflective the specialty of the physicians who performed the procedures are compared to the broader ...
Insights from largest chronic limb-threatening ischemia study to inform quality of care improvements
2023-05-19
Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- Data from a cohort of one million patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) were presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. Using data from Medicare, the cohort, Chronic Limb threatening Ischemia Process PERformance (CLIPPER), found one out of six patients with CLTI died within their first year of diagnosis and 50% survived at five years.
CLTI is a serious condition in ...
Next generation transcatheter aortic valve replacement system improves clinician deliverability, tracking and deployment in real-world setting
2023-05-19
Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- Results from the Evolut FX TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement) Clinical Survey were presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. The survey, comprised of feedback from physicians across the United States, reported improved deliverability, tracking, and deployment of the next-generation device compared to its predecessor.
Aortic stenosis (AS), is one of the most common valvular heart diseases and can potentially lead to heart failure. Once symptoms of AS begin, average ...
Long term use of blood thinners shows promise in reducing complications for patients following a heart attack
2023-05-19
Phoenix, AZ (May 19, 2023)- A new study examining the criteria proposed by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) to prescribe long-term treatment with more than one blood thinner after percutaneous coronary intervention was presented today as late-breaking clinical research at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions. The study confirmed that patients presenting the characteristics proposed in the ESC guidelines are more likely to experience complications due to blood clotting in the coronary arteries. These patients may therefore benefit from a long-term treatment with more ...
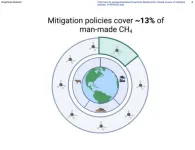
Only 13% of global methane emissions are covered by policy, and those policies are often ineffective
2023-05-19
Methane, a greenhouse gas known to do about 80 times more damage to the atmosphere than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period, is often overlooked by policymakers and governments. In a review publishing in the journal One Earth on May 19, researchers analyzed the coverage, stringency, and real-world impact of current global methane emissions policies for the first time. They found that only 13% of emissions are currently covered by direct mitigation policies.
In order to limit climate warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius in accordance with the Paris Agreement, global methane emissions need to be cut by at least 40%–45%, according to the 2021 Global Methane Assessment—a feat that the ...
Scientists urge crackdown on methane emissions with only 13% regulated
2023-05-19
New research from Queen Mary University of London shows that only around 13% of global methane emissions are regulated, despite methane emissions causing at least 25% of current global warming.
The global review, published on 19 May in One Earth, also found that little is known about the effectiveness of the policies that exist, with potentially unrepresentative methane emission estimations used rather than actual measurements. Inaccurate estimations can also mean the issue is taken less seriously by decision-makers by masking its severity.
The researchers argue that the lack ...
Novel gene-editing strategy leverages unusual genetic alteration to block HIV spread in cells
2023-05-19
(Philadelphia, PA) – Genetic alterations that give rise to a rare, fatal disorder known as MOGS-CDG paradoxically also protect cells against infection by viruses. Now, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University have harnessed this unusual protective ability in a novel gene-editing strategy aimed at eliminating HIV-1 infection with no adverse effects on cell mortality.
The new approach, described online April 28 in the journal Molecular Therapy – Nucleic Acids, is based on a combination of two gene-editing constructs, one that ...
Perceived influence of incentives on COVID-19 vaccination decision-making and trust
2023-05-19
About The Study: This survey study found that although there has been substantial policy attention around incentivizing COVID-19 vaccination, fewer than 1 in 10 vaccinated individuals in a nationally representative sample of U.S. adults reported receiving an incentive. Most vaccinated respondents reported that an incentive did not make a difference in their decision-making to get the COVID-19 vaccine.
Authors: Laura J. Faherty, M.D., M.P.H., M.S.H.P., of the RAND Corporation in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the ...
Estimated pediatric hospitalizations and school absenteeism associated with accelerated COVID-19 bivalent booster vaccination
2023-05-19
About The Study: In this decision analytical model, increased uptake of bivalent booster vaccination among eligible age groups was associated with decreased hospitalizations and school absenteeism in the pediatric population. These findings suggest that although COVID-19 prevention strategies often focus on older populations, the benefits of booster campaigns for children may be substantial.
Authors: Alison P. Galvani, Ph.D., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...