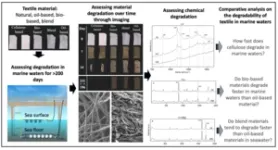
(Press-News.org) A widely used compostable plastic persists unchanged in marine environments for at least 14 months, according to a new study in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Sarah-Jeanne Royer and colleagues from Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego. The study highlights the distinction between textile materials that can be composted in a controlled, industrial setting (PLA), and the ones that can undergo biodegradation in natural environments (cellulose-based textiles).
The accumulation and persistence of oil-based plastic waste in the ocean is one of the major ecological problems facing marine life. Macroscopic plastic items, such as discarded water bottles, that enter the ocean may persist for decades in their original form; even when they break up into microscopic pieces, called microplastics, they are not biodegraded, but instead remain undigestible pollutants that permeate the oceans.
In recent years, substitutes have been developed to replace oil-based plastics, with the intention of both reducing fossil fuel use in creating plastic goods, and providing a more environmentally benign waste product when the item is discarded, through composting.
One of the most popular substitutes is polylactic acid (PLA), a polymer of lactic acid derived from fermentation of sugars and starches. PLA will break down back into lactic acid at the high temperatures found in very large compost piles; however, it does not do so reliably or quickly in colder conditions.
To examine the fate of PLA in a natural marine environment, the authors submerged samples of PLA, along with samples of oil-based materials, cellulose-based materials, and blend of cellulose-based and oil-based materials, in cages in the coastal waters off La Jolla, California. Samples were examined weekly for evidence of disintegration and returned to the ocean after a few hours.
The authors found that the cellulose-based material degraded quickly, in less than one month. Laboratory chemical analysis confirmed that the cellulose had been largely broken down by biological processes through CO2 production, not simple mechanical wear. In contrast, neither the oil-based plastic, the blend, nor the PLA showed signs of degradation throughout the 14 months of the experiment.
“Our results indicate that compostability does not imply environmental degradation,” Royer said. “Referring to compostable plastics as biodegradable plastics is misleading as it may convey the perception of a material that degrades in the environment. PLA-based plastics must be composted in appropriately controlled facilities in order to achieve their potential as compostable substitutes for oil-based plastics.”
The authors also add: “This work represents one of the few pioneer studies addressing the comparability between the biodegradability of different material types (natural to fully synthetic and bio-based materials) in natural environmental conditions and controlled closed systems. This study shows the need for standardizing tests to see if materials promoted as compostable or biodegradable such as PLA actually do biodegrade in a natural environment. In this case, consumers who are concerned about microfiber plastic pollution should be informed, knowledgeable and mindful of the materials they are buying.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0284681
Citation: Royer S-J, Greco F, Kogler M, Deheyn DD (2023) Not so biodegradable: Polylactic acid and cellulose/plastic blend textiles lack fast biodegradation in marine waters. PLoS ONE 18(5): e0284681. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0284681
Author Countries: USA, Israel
Funding: This work is being supported by the Deheyn lab BEST Initiative (Biomimicry for Emerging Science and Technology Initiative), which is a platform for facilitating the interaction between academia and industry for fundamental research on nature-inspired solutions." The funders can contribute to brainstorming about the study design to address specific questions, but have no role in data collection and analysis, and decision to publish. The funders can sometimes (if requested) be involved in brainstorming about interpretation of data outcome, which inherently can contribute to some extent to the preparation of the manuscript. Otherwise, the funders have no role in directing the publication with regards to its presentation, data content and conclusion. As a courtesy and if requested, drafts of the publications can be shared with the funders to show progress in the publishing process. For the Raman analyses, financial support was provided to FG from the Young Thousand Talents Plan of China (Grant Number 41720104002) and the funders in this case had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
A popular compostable plastic doesn’t break down in the ocean
“Biodegradable” is a misleading term for plastic substitutes that require heat to break down or industrial compositing conditions
2023-05-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Physical activity linked to higher pain tolerance
2023-05-24
A new analysis of data from more than 10,000 adults shows that people who were physically active had higher pain tolerance than those who were sedentary, and that those with a higher level of activity had a higher level of pain tolerance. Anders Årnes of the University Hospital of North Norway, Tromsø, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on May 24, 2023.
Prior research has suggested the possibility that a habit of engaging in a higher level of physical activity might help ease or prevent chronic pain by boosting pain tolerance. However, most studies on this topic have been small or focused on narrow groups of people.
To help clarify the ...
U.S. teens who are food insecure are more likely to engage in emotional eating and consume sugar-sweetened beverages and junk foods
2023-05-24
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285446
Article Title: Psychosocial correlates in patterns of adolescent emotional eating and dietary consumption
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Scientists provide first field observations of coccolithophore osmotrophy
2023-05-24
Coccolithophores, a globally ubiquitous type of phytoplankton, play an essential role in the cycling of carbon between the ocean and atmosphere. New research from Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences shows that these vital microbes can survive in low-light conditions by taking up dissolved organic forms of carbon, forcing researchers to reconsider the processes that drive carbon cycling in the ocean. The findings were published this week in Science Advances.
The ability to extract carbon from the direct absorption of dissolved organic carbon is known as osmotrophy. ...
Not so biodegradable: new study finds bio-based plastic and plastic-blend textiles do not biodegrade in the ocean
2023-05-24
Plastic pollution is seemingly omnipresent in society, and while plastic bags, cups, and bottles may first come to mind, plastics are also increasingly used to make clothing, rugs, and other textiles.
A new study from UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, published May 24 in the journal PLOS One, for the first time tracked the ability of natural, synthetic, and blended fabrics to biodegrade directly in the ocean.
Lead author Sarah-Jeanne Royer conducted an experiment off the Ellen Browning Scripps Memorial Pier and found that natural and wood-based cellulose fabrics degraded within a month. Synthetic textiles, including so-called compostable ...
Increasing heat likely a major factor in human migration
2023-05-24
Rising temperatures due to climate change are likely influencing human migration patterns, according to a new study by Rita Issa of University College London and colleagues, published May 24 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate.
In the last decade, heatwaves were frequent, and surface temperatures were the warmest on record. As the planet warms, many people are expected to leave their homes to escape extreme temperatures. However, the exact role of heat in human migration is not yet understood. To illuminate this relationship, Issa’s team conducted a review of research documents, ...
Public health solutions to disrupt the US firearm crisis
2023-05-24
The epidemic of firearm injury and death in the USA is preventable, and the field of public health can offer practical solutions, argue Dr. Megan L. Ranney and colleagues in an opinion article in PLOS Global Public Health. Through harm reduction and community engagement programs, public health professionals, healthcare providers and community members can reduce the impact on individuals, families and communities.
Despite the attention school and public mass shootings in the US gain, they make up a minority of US firearm injuries and deaths. Most firearm deaths are from homicide and suicide: ...
Gender trumps politics in determining people’s ability to read others’ minds
2023-05-24
Political parties regularly claim to have their finger on the pulse and be able to read the public mood. Yet a new study challenges the idea that being political makes you good at understanding others: it shows gender, not politics, is a far more important factor in determining people’s social skills.
Analysis of a sample of 4,000 people from across the UK, compiled by a team of psychologists at the University of Bath, highlights that being female and educated are the biggest determinants of whether you can understand or read others’ ...
Georgia Tech researchers develop wireless monitoring patch system to detect sleep apnea at home
2023-05-24
The prevalence of sleep disorders, like sleep apnea, is on the rise in the U.S., but current protocols to conduct clinically accepted assessments are expensive and inconvenient.
Georgia Tech researchers have created a wearable device to accurately measure obstructive sleep apnea — when the body repeatedly stops and restarts breathing for a period — as well as the quality of sleep people get when they are at rest.
Under conventional methods, people who are suspected of having some sleep issue or disorder ...
How tasty is the food?
2023-05-24
To know when it’s time for a meal – and when to stop eating again – is important to survive and to stay healthy, for humans and animals alike. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biological Intelligence investigated how the brain regulates feeding behavior in mice. The team found that the hormone ghrelin activates specialized nerve cells in a brain region known as the amygdala. Here, the interaction between ghrelin and the specialized neurons promotes food consumption and conveys ...
Discovery slows down muscular dystrophy
2023-05-24
A team of researchers at the University of Houston College of Pharmacy is reporting that by manipulating TAK1, a signaling protein that plays an important role in development of the immune system, they can slow down disease progression and improve muscle function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
DMD, caused by mutations in dystrophin gene, is an inheritable neuromuscular disorder that occurs in one out of 3,600 male births. DMD patients undergo severe muscle wasting, inability to walk and eventually death in their early thirties due to respiratory failure. The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] A popular compostable plastic doesn’t break down in the ocean“Biodegradable” is a misleading term for plastic substitutes that require heat to break down or industrial compositing conditions