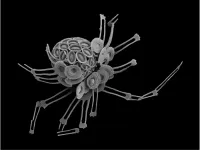
(Press-News.org) SEATTLE – MAY 24, 2023 – Researchers from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center in Seattle, Scripps Research in La Jolla, California, IAVI and other collaborating institutions have characterized robust T-cell responses in volunteers participating in the IAVI G001 Phase 1 clinical trial to test the safety and immune response of a self-assembling nanoparticle HIV vaccine.
Their work, published in Science Translational Medicine, signals a major step toward development of a vaccine approach to end the HIV/AIDS epidemic worldwide. The antigen used in this study was jointly developed by IAVI and Scripps Research and has been shown in previous analyses to stimulate VRC01-class B cells, an immune response considered promising enough for boosting in further studies.
“We were quite impressed that this vaccine candidate produced such a vigorous T-cell response in almost all trial participants who received the vaccine,” explained Julie McElrath, MD, PhD, senior vice president and director of Fred Hutch’s Vaccine and Infectious Disease Division and co-senior author of the study. “These results highlight the potential of this HIV-1 nanoparticle vaccine approach to induce the critical T-cell help needed for maturing antibodies toward the pathway of broadly neutralizing against HIV.”
However, she added, this is the first step, and heterologous booster vaccines will still be needed to eventually produce VRC01-class broadly neutralizing antibodies, which in previous studies have demonstrated the ability to neutralize approximately 90% of HIV strains.
“We showed previously that this vaccine induced the desired B-cell responses from HIV broadly neutralizing antibody precursors. Here we demonstrated strong CD4 T-cell responses, and we went beyond what is normally done by drilling down to identify the T cell epitopes and found several broadly immunogenic epitopes that might be useful for developing boosters and for other vaccines,” William Schief, PhD, executive director of vaccine design for IAVI’s Neutralizing Antibody Center at Scripps Research and professor, Department of Immunology and Microbiology, at Scripps Research, who is co-senior author of the study.
The trial is a phase 1, randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of a nanoparticle HIV vaccine in healthy adult volunteers without HIV. It was comprised of two groups with 18 vaccine and six placebo recipients per group, with 48 total enrollees. Participants were given two doses of the vaccine or placebo eight weeks apart.
McElrath acknowledged the groundbreaking work of her lab team, the biostatistical team and Fred Hutch’s Vaccine Trials Unit for their invaluable contributions to the study. The Vaccine Trials Unit conducts multiple vaccine trials and was one of only two sites for this study.
Findings from the study include:
Vaccine-specific CD4 T cells were induced in almost all vaccine recipients.
Lymph node GC T follicular helper cells increased after vaccination compared to placebo.
Lumazine synthase protein, needed for self-assembly of the particle, also induced T-cell responses that can provide additional help to ultimately enhance efficacy in a sequential vaccine strategy.
Vaccine-specific CD4 T cells were polyfunctional and had diverse phenotypes.
LumSyn-specific CD8 T cells were highly polyfunctional and had a predominantly effector memory phenotype.
CD4 T-cell responses were driven by immunodominant epitopes with diverse and promiscuous HLA restriction.
CD8 T-cell responses to LumSyn were driven by HLA-A*02-restricted immunodominant epitopes B- and T-cell responses correlated within but not between LN and peripheral blood compartments.
This study was funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery; IAVI Neutralizing Antibody Center; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; and Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard.
Study authors WRS and SM are inventors on a patent filed by Scripps and IAVI on the eOD-GT8 monomer and 60-mer immunogens (patent number 11248027, “Engineered outer domain (eOD) of HIV gp 120 and mutants thereof”). WRS, KWC and MJM are inventors on patents filed by Scripps, IAVI and Fred Hutch on immunodominant peptides from LumSyn (Title: Immunogenic compositions; filing no. 63127975).
For a comprehensive listing of funders, disclosures and authors, please see the journal article.
DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adf3309
# # #
Media Contact:
Claire Hudson
206-919-8300
crhudson@fredhutch.org
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center unites individualized care and advanced research to provide the latest cancer treatment options while accelerating discoveries that prevent, treat and cure cancer and infectious diseases worldwide.
Based in Seattle, Fred Hutch is an independent, nonprofit organization and the only National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center in Washington. We have earned a global reputation for our track record of discoveries in cancer, infectious disease and basic research, including important advances in bone marrow transplantation, immunotherapy, HIV/AIDS prevention and COVID-19 vaccines. Fred Hutch operates eight clinical care sites that provide medical oncology, infusion, radiation, proton therapy and related services and has network affiliations with hospitals in four states. Fred Hutch also serves as UW Medicine’s cancer program.
END
AMHERST, Mass. – While an overwhelming majority of cancer patients experience taste disruption from their disease or treatment, they have consistently reported a lack of support from their doctors about this troubling side effect, according to research.
A new study by the University of Massachusetts Amherst, focusing for the first time on the issue from the cancer clinicians’ point of view, reveals not a lack of concern about their patients’ taste loss but a lack of access to educational materials, ...
(Memphis, Tenn.—May 24, 2023) Like thread tightly wrapped around a spool, DNA is wrapped around histones and packaged into structures called nucleosomes. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital are exploring how a type of transcription factor called a pioneer transcription factor accesses DNA even when it is tightly wound. Their work revealed how the epigenetic landscape influences transcription factor binding. Problems with transcription have been implicated in numerous cancers, so this more detailed understanding of the process may aid in developing future therapeutics. The study ...
A widely used compostable plastic persists unchanged in marine environments for at least 14 months, according to a new study in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Sarah-Jeanne Royer and colleagues from Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California, San Diego. The study highlights the distinction between textile materials that can be composted in a controlled, industrial setting (PLA), and the ones that can undergo biodegradation in natural environments (cellulose-based textiles).
The accumulation and persistence of oil-based plastic waste ...
A new analysis of data from more than 10,000 adults shows that people who were physically active had higher pain tolerance than those who were sedentary, and that those with a higher level of activity had a higher level of pain tolerance. Anders Årnes of the University Hospital of North Norway, Tromsø, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on May 24, 2023.
Prior research has suggested the possibility that a habit of engaging in a higher level of physical activity might help ease or prevent chronic pain by boosting pain tolerance. However, most studies on this topic have been small or focused on narrow groups of people.
To help clarify the ...
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285446
Article Title: Psychosocial correlates in patterns of adolescent emotional eating and dietary consumption
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Coccolithophores, a globally ubiquitous type of phytoplankton, play an essential role in the cycling of carbon between the ocean and atmosphere. New research from Bigelow Laboratory for Ocean Sciences shows that these vital microbes can survive in low-light conditions by taking up dissolved organic forms of carbon, forcing researchers to reconsider the processes that drive carbon cycling in the ocean. The findings were published this week in Science Advances.
The ability to extract carbon from the direct absorption of dissolved organic carbon is known as osmotrophy. ...
Plastic pollution is seemingly omnipresent in society, and while plastic bags, cups, and bottles may first come to mind, plastics are also increasingly used to make clothing, rugs, and other textiles.
A new study from UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography, published May 24 in the journal PLOS One, for the first time tracked the ability of natural, synthetic, and blended fabrics to biodegrade directly in the ocean.
Lead author Sarah-Jeanne Royer conducted an experiment off the Ellen Browning Scripps Memorial Pier and found that natural and wood-based cellulose fabrics degraded within a month. Synthetic textiles, including so-called compostable ...
Rising temperatures due to climate change are likely influencing human migration patterns, according to a new study by Rita Issa of University College London and colleagues, published May 24 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate.
In the last decade, heatwaves were frequent, and surface temperatures were the warmest on record. As the planet warms, many people are expected to leave their homes to escape extreme temperatures. However, the exact role of heat in human migration is not yet understood. To illuminate this relationship, Issa’s team conducted a review of research documents, ...
The epidemic of firearm injury and death in the USA is preventable, and the field of public health can offer practical solutions, argue Dr. Megan L. Ranney and colleagues in an opinion article in PLOS Global Public Health. Through harm reduction and community engagement programs, public health professionals, healthcare providers and community members can reduce the impact on individuals, families and communities.
Despite the attention school and public mass shootings in the US gain, they make up a minority of US firearm injuries and deaths. Most firearm deaths are from homicide and suicide: ...
Political parties regularly claim to have their finger on the pulse and be able to read the public mood. Yet a new study challenges the idea that being political makes you good at understanding others: it shows gender, not politics, is a far more important factor in determining people’s social skills.
Analysis of a sample of 4,000 people from across the UK, compiled by a team of psychologists at the University of Bath, highlights that being female and educated are the biggest determinants of whether you can understand or read others’ ...