Further link identified between autoimmunity and schizophrenia
2023-05-31
(Press-News.org)
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify a protein in some people with schizophrenia that causes schizophrenia-like features in mice
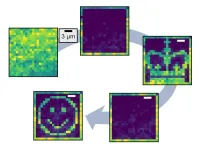
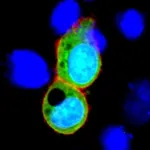
Tokyo, Japan – Links have been reported between schizophrenia and proteins produced by the immune system that can act against one’s own body, known as autoantibodies. In a study published last month in Brain Behavior and Immunity, Japanese researchers identified autoantibodies that target a ‘synaptic adhesion protein’, neurexin 1α, in a subset of patients with schizophrenia. When injected into mice, the autoantibodies caused many schizophrenia-related changes.
What is a synaptic protein, and why might it be linked to schizophrenia? Synaptic adhesion proteins are specialized proteins that bind to create physical connections between brain cells. These connections, called synapses, allow the cells to communicate by passing molecules back and forth. Both synapses and autoimmunity are known to be associated with schizophrenia, so the research team from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) decided to investigate autoantibodies that target synaptic proteins in patients with schizophrenia.
“In around 2% of our patient population, we identified autoantibodies against the synaptic protein neurexin 1α, which is expressed by one cell in the synapse and binds to proteins known as neuroligins on the other cell in the synapse,” says lead author of the study Hiroki Shiwaku. “Once we had identified these autoantibodies, we wanted to see if they were able to cause schizophrenia-related changes.”
To do this, the researchers isolated autoantibodies from some of the patients with schizophrenia and injected them into the cerebrospinal fluid of mice, so that the autoantibodies would travel into the brain. In these mice, the autoantibodies blocked neurexin 1α and neuroligin binding and altered some related synaptic properties. The administration of these autoantibodies also resulted in fewer synapses in the brains of mice and schizophrenia-related behaviors, such as reduced social behavior toward unfamiliar mice and reduced cognitive function.
“Together, our results strongly suggest that autoantibodies against neurexin 1α can cause schizophrenia-related changes, at least in mice,” explains Hiroki Shiwaku. “These autoantibodies may therefore represent a therapeutic target for a subset of patients with schizophrenia.”
Schizophrenia has a wide variety of both symptoms and treatment responses, and many patients have symptoms that are resistant to currently available treatment options. Therefore, the identification of possible disease-causing autoantibodies is important for improving symptom control in patients with schizophrenia. It is hoped that the results of this investigation will allow patients with autoantibodies that target neurexin 1α—all of whom were resistant to antipsychotic treatment in the present study—to better control their symptoms in the future.
###
The article, “Analyzing schizophrenia-related phenotypes in mice caused by autoantibodies against NRXN1α in schizophrenia,” was published in Brain Behavior and Immunity at DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.03.028
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-05-31
A research team affiliated with UNIST has made a significant breakthrough in uncovering the potential of ultra-photostable avalanching nanoparticles (ANP). Their study demonstrates that such particles can perform unlimited photoswitching, leading to new advancements in fields like optical probes, 3D optical memory, and super-resolution microscopy.
This breakthrough has been achieved through the efforts of Professor Yung Doug Suh and his research team in the Department of Chemistry at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), in collaboration with researchers from Columbia University and ...
2023-05-31
New York, NY—May 31, 2023—In 2021, lanthanide-doped nanoparticles made waves—or rather, an avalanche—when Changwan Lee, then a PhD student in Jim Schuck’s lab at Columbia Engineering, set off an extreme light-producing chain reaction from ultrasmall crystals developed at the Molecular Foundry at Berkeley Lab. Those same crystals are back again with a blink that can now be deliberately and indefinitely controlled.
“We’ve found the first fully photostable, fully photoswitchable nanoparticle—a holy grail of nanoprobe design,” said Schuck, associate ...
2023-05-31
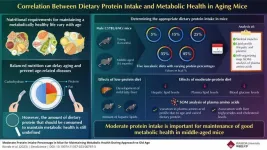
As the proverb “You are what you eat” goes, the type of food we consume influences our health and longevity all through our lives. In fact, there is a direct association between age-related nutritional requirements and metabolic health. Optimal nutrition according to age can help maintain metabolic health, thereby improving the health span (period of life without diseases) and lifespan of an individual. Different nutritional interventions involving varied calorie and protein intake have been known to improve the health and lifespan of rodents and primates. Furthermore, recent studies have also reported the association of dietary macronutrients (proteins, ...
2023-05-31
Sixty per cent of roughly 1,600 Canadians who took part in a new McGill University study say their lifestyle habits either stayed the same or improved during the COVID-19 pandemic. On the flip side, 40% of participants say they adopted less healthy lifestyle habits, including worsened eating habits, sleep quality, decreased physical activity and weight gain. The research is based on the Canadian COVIDiet study of Canadians between the ages of 18 to 89 years old. Researchers from McGill’s School of Human Nutrition collected data from across the country during the first wave of infections. ...
2023-05-31
Hypervelocity impacts of Micrometeoroid and Orbital Debris (M/OD) seriously threaten the safety of manned spacecraft and astronauts in orbit. At present, M/OD above 10 cm, which can be monitored and predicted in advance, can usually be avoided by orbital maneuver. As for the small-size M/OD, because of the difficulty of monitoring, it is the main impact threat, as well as the main object of impact risk assessment and protection design of manned spacecraft. The probability of no penetration (PNP) of the sealed cabin under M/OD impact is usually used as ...
2023-05-31
SAN ANTONIO — May 31, 2023 —Dr. Thomas E. Briggs, an Institute engineer in Southwest Research Institute’s Powertrain Engineering Division, has received the Forest R. McFarland Award by SAE International, an organization that works to advance mobility, knowledge and solutions for humanity’s benefit.
Established in 1979, the award serves to honor the late Forest R. McFarland, a long-time SAE International member, for his many contributions to the organization. The award recognizes outstanding contributions by volunteers who further the goals of SAE ...
2023-05-31
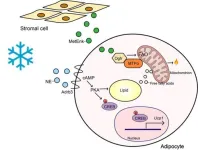
Overweight and obesity pose significant health risks, including an increased likelihood of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Researchers are seeking practical ways to promote the oxidation of lipids, which could help balance energy storage and consumption. A recent study has identified opioid growth factor receptor (Ogfr) gene as a promising new target for this process.
Rodents possess thermogenic fat that includes brown and beige adipocytes, which have a high capacity to uptake and utilize glucose ...
2023-05-31
More than 80% of New Yorkers who inject drugs test positive for the opioid fentanyl, despite only 18% reporting using it intentionally, according to a new study by researchers at the NYU School of Global Public Health.
The findings, published in the International Journal of Drug Policy, suggest that many people who inject drugs are unknowingly using fentanyl, which may increase their risk for overdose and potentially their tolerance to fentanyl if it is used over time.
In 2021, more than 100,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States, with 66% of these deaths involving illicit fentanyl—a synthetic opioid that is 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine.
In ...
2023-05-31
Washington, DC – Cats can play a role in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and their contaminated environment (pens in this study) can be infectious, according to new research. The study was published in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“In practice, after introduction of SARS-CoV-2 in our household, we should see our cat as part of the family regarding virus transmission,” said study coauthor Wim van der Poel DVM, Ph.D., Professor of Emerging and Zoonotic Viruses, Wageningen University and Research, in the Netherlands.
Van der Poel and colleagues conducted the study to gain better insight ...
2023-05-31
Researchers from University of Connecticut, Texas A&M University, University of Colorado at Boulder, and University of Florida published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines whether price promotions on some products differentially impact demand for other products depending on their relative locations within a display.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “The Negative and Positive Consequences of Placing Products Next to Promoted Products” and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Further link identified between autoimmunity and schizophrenia