There are various ways to image biological samples on a microscopic level, and each has its own pros and cons. For the first time, a team of researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, has combined aspects from two of the leading imaging techniques to craft a new method of imaging and analyzing biological samples. Its concept, known as RESORT, paves the way to observe living systems in unprecedented detail.
For as long as humanity has been able to manipulate glass, we have used optical devices to peer at the microscopic world in ever increasing detail. The more we can see, the more we can understand, hence the pressure to improve upon tools we use to explore the world around, and inside, us. Contemporary microscopic imaging techniques go far beyond what traditional microscopes can offer. Two leading technologies are super-resolution fluorescence imaging, which offers good spatial resolution, and vibrational imaging, which compromises spatial resolution but can use a broad range of colors to help label many kinds of constituents in cells.
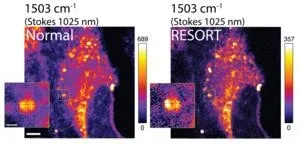
“We were motivated by the limitations of these kinds of imaging techniques to try and create something better, and with RESORT we are confident that we have achieved this,” said Professor Yasuyuki Ozeki from the University of Tokyo’s Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology. “RESORT stands for reversible saturable optical Raman transitions, and it combines the benefits of super-resolution fluorescence and vibrational imaging without inheriting the detriments of either. It is a laser-based technique that uses something known as Raman scattering, a special interaction between molecules and light which helps identify what’s in a sample under the microscope. We successfully performed RESORT imaging of mitochondria in cells to validate the technique.”
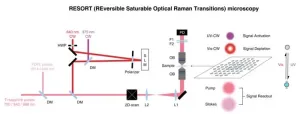
There are several stages to RESORT imaging, and although it might seem complicated, the setup is less complicated than that of the techniques it’s aiming to replace. Firstly, the specific components of the sample to be imaged need to be labeled, or stained, with special chemicals called photoswitchable Raman probes, whose Raman scattering can be controlled by the different kinds of laser light employed by RESORT. Next, the sample is placed within an optical apparatus used to correctly illuminate the sample and build an image of it. For that to occur, the sample is then irradiated with two-color infrared laser pulses for detecting Raman scattering, ultraviolet light and a special donut-shaped beam of visible light. Together, these constrain the area where Raman scattering can occur, which means the final stage, imaging, can detect the probe at the very precise point, which leads to a high spatial resolution.
“It’s not just about gaining higher-resolution images of microscopic samples; after all, electron microscopes can image these things in far greater detail,” said Ozeki. “However, electron microscopes necessarily damage or impede the samples they observe. Through the future development adding more colors to the palette of Raman probes, RESORT will be able to image many components in living samples in action to analyze complex interactions like never before. This will contribute to a deeper understanding of fundamental biological processes, disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions.”
The team’s main aim was to improve microscopic imaging for use in the medical research field and related areas. But the advancements it has made in the design of the laser could be used in other laser applications as well, where high power or precise control is required, such as materials science.
###
Journal article: Jingwen Shou, Ayumi Komazawa, Yuusaku Wachi, Minoru Kawatani, Hiroyoshi Fujioka, Spencer John Spratt, Takaha Mizuguchi, Kenichi Oguchi, Hikaru Akaboshi, Fumiaki Obata, Ryo Tachibana, Shun Yasunaga, Yoshio Mita, Yoshihiro Misawa, Ryosuke Kojima, Yasuteru Urano, Mako Kamiya & Yasuyuki Ozeki. “Super-resolution vibrational imaging based on photoswitchable Raman probe”, Science Advances. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ade9118
Funding:
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP20H05724, JP20H05725, JP20H05726, JP19K22242, JP20H02650, JP22H02193, and JP19J22546, by JSPS Core-to-Core Program, A. Advanced Research Networks, by JST CREST JPMJCR1872, by Nakatani Foundation Grant for Technology Development Research (to Y.O.), by The Naito Foundation (to M.K.), by The Mitsubishi Foundation (to M.K.), by Daiichi Sankyo Foundation of Life Science (to M.K.), Advanced Research Infrastructure for Materials and Nanotechnology in Japan (ARIM)” of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) JPMXP1222UT1055, and by Quantum Leap Flagship Program of MEXT JPMXS0118067246. J.S. is supported by International Research Fellow of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Useful links:
Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology
https://www.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Department of Electrical Engineering and Information Systems
https://www.eeis.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences
https://www.f.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Research contact:
Professor Yasuyuki Ozeki
Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo
4-6-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8904 JAPAN
ozeki@ee.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press contact:
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Public Relations Group, The University of Tokyo,
7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 113-8656, Japan
press-releases.adm@gs.mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About The University of Tokyo: The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 4,000 international students. Find out more at www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter at @UTokyo_News_en.
END