(Press-News.org) (Boston) – U.S. Black women have a disproportionately higher burden of both preeclamptic pregnancy and stroke compared with white women, but virtually all existing evidence on the association between the two medical conditions has come from studies of white women.
A newly published study focuses on data gathered over 25 years from 59,000 Black women in the Black Women’s Health Study (BWHS) and is led by researchers from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine and Slone Epidemiology Center. The study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine Evidence, finds that Black women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDOP) have an estimated 66% increased long-term risk of stroke.
“Our results may explain, in part, the disproportionately high incidence of stroke in Black women relative to other populations,” said corresponding author Shanshan Sheehy, MD, ScD, assistant professor of medicine at the school and an investigator at the Slone Epidemiology Center.
Researchers looked at U.S. Black women enrolled in the BWHS , including 42,924 participants who had given birth and were free of cardiovascular disease before entry into the analysis. Biennial questionnaires had asked about preeclampsia, gestational hypertension, and stroke, among other conditions. Medical records were sought for self-reports of stroke and were reviewed by neurologists.
Over the period from 1995 through 2019, there were 1,555 strokes, including 310 among 4,938 women with a history of HDOP. Women who reported a history of HDOP were estimated to have 1.66 times the risk of stroke relative to parous women who had not had those pregnancy complications; for history of preeclampsia in particular, the estimated HR was 1.53. The association was present both among younger women (age less than 60) and older women. It was also present among women who were not overweight in young adulthood as well as women who were overweight or obese at that time.
Preeclampsia affects approximately 2 to 8% of pregnancies and is the second leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide. Preeclampsia/eclampsia among Black women in the U.S. is 60% higher than among white women (70 per 1,000 deliveries in 2014 for Black women vs. 43 per 1,000 for white women). In recent years, rates of severe preeclampsia have been increasing for Black women.
The American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines recently added pregnancy complications to their list of risk factors for stroke. However, the recommendations were based largely on data from women of Northern European ancestry and the AHA has called for more research on risk of stroke in women, especially women from underrepresented populations.
“Our study provides evidence that pregnancy history may be an important factor for risk assessment and prevention of long-term stroke,” said Sheehy. “Cardiovascular screening recommendations for Black women in particular should take the history of HODP into account.”
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, R01CA058420, U01CA164974, and R01MD015085. Dr. Aparicio is supported by an American Academy of Neurology Career Development Award and from the Boston University Aram V. Chobanian Assistant Professorship.
END
New study: Black women with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have increased stroke risk
Researchers estimate a 66% increased long-term risk of stroke
2023-07-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bezos Earth Fund grants $12 million to Smithsonian to support major forest carbon project
2023-07-06
By conserving and replanting forests, the world buys time until it brings other climate and sustainability solutions online. As a critical step toward this goal, the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) received a $12 million grant from the Bezos Earth Fund to support GEO-TREES. This international consortium is the first worldwide system to independently ensure the accuracy of satellite monitoring of forest biomass—a way to measure carbon stored in trees—in all forest types and conditions. The GEO-TREES alliance offers a freely accessible database that integrates ...
Legends of Norse Settlers drove Denmark towards Greenland
2023-07-06
In 985, Viking explorer Erik the Red led a group of Icelandic farmers to Greenland, where they established a settlement on the west coast. Archaeological evidence suggests that the settlement existed for over 400 years, but the impact of the settlement lasted much longer. It is little recognised today that the hope of finding the descendants of the settlers dominated European and American perspectives on Greenland for centuries
In his new book The Vanished Settlers of Greenland: In Search of a Legend and Its Legacy, Associate Professor Robert Rix argues that the lost Norse settlement played a decisive ...
Archaeology: The power of the Copper Age 'Ivory Lady' revealed
2023-07-06
The highest status individual in ancient Copper Age society in Iberia, was a woman and not a man as previously thought, according to peptide analysis reported in Scientific Reports. The individual, now re-dubbed the 'Ivory Lady', was buried in a tomb filled with the largest collection of rare and valuable items in the region, including ivory tusks, high-quality flint, ostrich eggshell, amber, and a rock crystal dagger. These findings reveal the high status women could hold in this ancient society.
In 2008, an individual was discovered in a tomb in Valencia, Spain dating to the Copper Age between 3,200 and 2,200 years ago. As well as being a rare example of a single occupancy ...
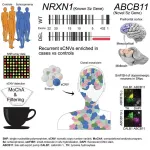
Schizophrenia is associated with somatic mutations occurring in utero
2023-07-06
As a psychiatric disorder with onset in adulthood, schizophrenia is thought to be triggered by some combination of environmental factors and genetics, although the exact cause is still not fully understood. In a study published in the journal Cell Genomics on July 6, researchers find a correlation between schizophrenia and somatic copy-number variants, a type of mutation that occurs early in development but after genetic material is inherited. This study is one of the first to rigorously describe the relationship between somatic—not inherited—genetic mutations and schizophrenia risk.
“We originally thought of genetics as the study of inheritance. But now we ...
Team develops all-species coronavirus test
2023-07-06
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In an advance that will help scientists track coronavirus variants in wild and domesticated animals, researchers report they can now detect exposure to the SARS-CoV-2 virus in any animal species. Most coronavirus antibody tests require specialized chemical reagents to detect host antibody responses against the virus in each species tested, impeding research across species.
The virus that causes COVID-19 in humans also infects a variety of animals, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign pathobiology professor and virologist Ying Fang, who led the new research. So far, ...
Shrinking Arctic glaciers are unearthing a new source of methane
2023-07-06
As the Arctic warms, shrinking glaciers are exposing bubbling groundwater springs which could provide an underestimated source of the potent greenhouse gas methane, finds new research published today in Nature Geoscience.
The study, led by researchers from the University of Cambridge and the University Centre in Svalbard, Norway, identified large stocks of methane gas leaking from groundwater springs unveiled by melting glaciers.
The research suggests that these methane emissions will likely increase as Arctic glaciers retreat and more ...
Health outcomes, cost-effectiveness of monoclonal SARS-CoV-2 antibodies as pre-exposure prophylaxis
2023-07-06
About The Study: This decision analytic model showed that within the context of a high SARS-CoV-2 probability, monoclonal antibodies pre-exposure prophylaxis (mAbs PrEP) provision was cost-saving when provided to individuals at increased risk of severe COVID-19 if drug prices decrease to $275 and effectiveness is 75% or higher. When newer mAbs PrEP combinations become available, guidance on implementation should be formulated ensuring a fast rollout. Nevertheless, advocacy for mAbs PrEP use and critical discussion on drug prices are necessary to ensuring cost-effectiveness for different epidemic settings.
Authors: Stephanie Popping, M.D., Ph.D., of the University ...
Hearing loss and fatigue in middle-age and older adults
2023-07-06
About The Study: Hearing loss was cross-sectionally associated with higher frequency of fatigue after adjustment for demographics, lifestyle factors, and comorbidities in this nationally representative sample of middle-age and older adults. Future studies with fatigue assessments capturing its multidimensionality are needed to understand how hearing loss might contribute to physical and mental fatigue differentially and clarify how hearing loss may be associated with downstream outcomes like physical impairment through fatigue.
Authors: Nicholas ...
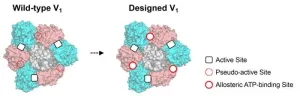
Scientists develop strategy to engineer artificial allosteric sites in protein complexes
2023-07-06
According to a recently published research paper by a team of scientists, a groundbreaking approach has been developed to create artificial allosteric sites (where by binding an effector molecule, activity at the distal active site is regulated) in protein complexes. This breakthrough research holds significant promise for a wide range of applications in industrial, biological, medical, and agricultural fields.
The team’s work is published in Nature Chemistry on 06 July 2023 at 16:00 (London time)
Protein complexes, such as hemoglobin and molecular motors, ...
New study shatters conventional wisdom and unlocks the future of electrochemical devices
2023-07-06
A new study by researchers at the University of Cambridge reveals a surprising discovery that could transform the future of electrochemical devices. The findings offer new opportunities for the development of advanced materials and improved performance in fields such as energy storage, brain-like computing, and bioelectronics.
Electrochemical devices rely on the movement of charged particles, both ions and electrons, to function properly. However, understanding how these charged particles move together has presented a significant challenge, hindering progress in creating new materials for these devices.
In ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
[Press-News.org] New study: Black women with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have increased stroke riskResearchers estimate a 66% increased long-term risk of stroke