(Press-News.org) Imagine shrinking light down to the size of a tiny water molecule, unlocking a world of quantum possibilities. This has been a long-held dream in the realms of light science and technology. Recent advancements have brought us closer to achieving this incredible feat, as researchers from Zhejiang University have made groundbreaking progress in confining light to subnanometer scales.
Traditionally, there have been two approaches to localize light beyond its typical diffraction limit: dielectric confinement and plasmonic confinement. However, challenges such as precision fabrication and optical loss have hindered the confinement of optical fields to sub-10 nanometer (nm) or even 1-nm levels. But now, a new waveguiding scheme reported in Advanced Photonics promises to unlock the potential of subnanometer optical fields.
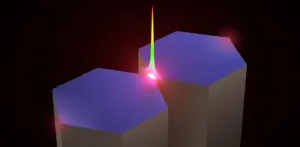
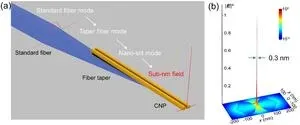
Picture this: light travels from a regular optical fiber, embarking on a transformative journey through a fiber taper, and finding its destination in a coupled-nanowire-pair (CNP). Within the CNP, the light morphs into a remarkable nano-slit mode, generating a confined optical field that can be as tiny as a mere fraction of a nanometer (approximately 0.3 nm). With an astonishing efficiency of up to 95 percent and a high peak-to-background ratio, this novel approach offers a whole new world of possibilities.
The new waveguiding scheme extends its reach into the mid-infrared spectral range, pushing the boundaries of the nano-universe even further. Optical confinement can now reach an astonishing scale of approximately 0.2 nm (λ/20000), offering even more opportunities for exploration and discovery.
Professor Limin Tong of the Zhejiang University Nanophotonics Group notes, “Unlike previous methods, the waveguiding scheme presents itself as a linear optical system, bringing a host of advantages. It enables broadband and ultrafast pulsed operation and allows for the combination of multiple sub-nanometer optical fields. The ability to engineer spatial, spectral, and temporal sequences within a single output opens up endless possibilities.”
The potential applications of such breakthroughs are awe-inspiring. An optical field so localized that it can interact with individual molecules or atoms holds promise for advancements in light–matter interactions, super-resolution nanoscopy, atom/molecule manipulation, and ultrasensitive detection. We stand at the precipice of a new era of discovery, where the tiniest realms of existence are within our grasp.
Check out this video summary with an animated demonstration from the authors:
https://players.brightcove.net/689254975001/SyeYVVul4l_default/index.html?videoId=6331129848112
Read the Gold Open Access article by L. Yang, Z. Zhou, et al., “Generating a sub-nanometer-confined optical field in a nanoslit waveguiding mode,” Adv. Photon. 5(4), 046003 (2023), doi 10.1117/1.AP.5.4.046003.
END
Shrinking light: Nanoscale optical breakthrough
Waveguiding scheme enables highly confined subnanometer optical fields
2023-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UMD researchers uncover privacy risks in cellphones purchased at police auctions
2023-07-17
Law enforcement agencies nationwide regularly sell items that are seized in criminal investigations or are unclaimed from lost-and-found inventories. Many of these items—vehicles, jewelry, watches and electronic devices like cellphones—end up at online auction houses.
People looking for a bargain can bid on cellphones in bulk, snatching up dozens at rock bottom prices for parts or other uses. This ultimately provides revenue for the police agencies, making for a good deal for everyone involved. Or is it?
A recent study by University of Maryland security experts found that many of the phones sold ...
Bacterial protein found in the urogenital tract may contribute to reduced fertility, birth defects
2023-07-17
A team of researchers from the University of Maryland School of Maryland’s (UMSOM) Institute of Human Virology (IHV), a Center of Excellence of the Global Virus Network (GVN), published new findings that emphasize the crucial role of the urinary and genital tract microbiota in adverse pregnancy outcomes and genomic instability that originate in the womb during fetal development.
The study, published on July 17 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), established a new link between genomic instability and a protein from Mycoplasma fermentans, a kind of bacterium that commonly ...
Picky green sea turtle has travelled to the same place to eat for generations
2023-07-17
For approximately 3,000 years, generations of green sea turtles have returned to the same seagrass meadows to eat. This was discovered by Willemien de Kock, a historical ecologist at the University of Groningen, by combining modern data with archaeological findings. Sea turtles migrate between specific breeding places and eating places throughout their lives–this much was known. But the fact that this stretches over many generations highlights the importance of protecting seagrass meadows along the coasts of North Africa. The results were published in PNAS on July 17.
When young green ...
How skin cancer virus outcompetes host cell replication
2023-07-17
University of Pittsburgh researchers have shown for the first time how Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV), which causes an aggressive skin cancer called Merkel cell carcinoma, initiates DNA replication in host cells.
Published today in the journal PNAS, the study sheds light on the fundamental question of how viruses override their host cells’ carefully regulated DNA replicating system to make hundreds of new copies of themselves.
“Understanding how MCV replicates gives us really important clues about ...
All about the Benjamins: Researchers decipher the secrets of Benjamin Franklin’s paper money
2023-07-17
Benjamin Franklin may be best known as the creator of bifocals and the lightning rod, but a group of University of Notre Dame researchers suggest he should also be known for his innovative ways of making (literal) money.
During his career, Franklin printed nearly 2,500,000 money notes for the American Colonies using what the researchers have identified as highly original techniques, as reported in a study published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research team, led by Khachatur ...
Redlining linked to higher heart failure risk among Black adults in US
2023-07-17
Research Highlights:
An analysis of more than two million adults in the U.S. found that present day heart failure risk was higher among Black adults who lived in zip codes historically impacted by redlining compared to Black adults living in non-redlined areas.
Redlining did not have the same impact on heart failure risk among white adults living in historically redlined zip codes.
Among Black adults living in historically redlined communities, approximately half of the excess risk of heart failure appeared to be explained by higher levels of socioeconomic distress.
Embargoed until 1 p.m. CT/2 p.m. ET Monday, July 17, ...
Racial disparities discovered in patients with cardiac devices
2023-07-17
Black patients with implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) have a significantly higher burden of disease than white patients with the same device, according to a new study from University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) cardiology researchers. Analyzing data from clinical trials conducted over a 20-year period by the Clinical Cardiovascular Research Center (CCRC) at URMC, investigators concluded that not only did Black patients with ICDs tend to be significantly younger than white patients, but they also had a higher ...
SwRI team identifies giant swirling waves at the edge of Jupiter’s magnetosphere
2023-07-17
SAN ANTONIO — July 17, 2023 —A team led by Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) and The University of Texas at San Antonio (UTSA) has found that NASA’s Juno spacecraft orbiting Jupiter frequently encounters giant swirling waves at the boundary between the solar wind and Jupiter’s magnetosphere. The waves are an important process for transferring energy and mass from the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emitted by the Sun, to planetary space environments.
Jake Montgomery, a doctoral student in the joint space physics program ...
Immune cells in single file
2023-07-17
The cells of the immune system circulate mainly in the blood and migrate into the body's tissues after an inflammation. Some types of immune cells, however, are permanently located in the tissues, where they come together to form three-dimensional networks.
How do these networks form and how are they maintained? For the long-lived macrophages (phagocytes), the answer is already known: They settle in so-called niches. These are environments of connective tissue cells that supply the macrophages with nutrients and keep them ...
New research shows babies’ immunological weak spot and strength
2023-07-17
NEW YORK, NY--A pair of new studies led by researchers at Columbia University explains why babies get so many common respiratory infections and identifies a specialized cluster of immune cells found only in babies that help them better cope with new pathogens.
“We know little about how the immune system develops throughout life, and most of what we know about immune system development in children comes from animal studies,” says Donna Farber, PhD, an expert in immune system development at Columbia University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
How studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
Chemists thought phosphorus had shown all its cards. It surprised them with a new move
A feedback loop of rising submissions and overburdened peer reviewers threatens the peer review system of the scientific literature
Rediscovered music may never sound the same twice, according to new Surrey study
Ochsner Baton Rouge expands specialty physicians and providers at area clinics and O’Neal hospital
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
Ambitious climate policy ensures reduction of CO2 emissions
Frontiers in Science Deep Dive webinar series: How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
UMaine researcher develops model to protect freshwater fish worldwide from extinction
Illinois and UChicago physicists develop a new method to measure the expansion rate of the universe
Pathway to residency program helps kids and the pediatrician shortage
How the color of a theater affects sound perception
Ensuring smartphones have not been tampered with
Overdiagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer
Association of dual eligibility and medicare type with quality of postacute care after stroke
Shine a light, build a crystal
AI-powered platform accelerates discovery of new mRNA delivery materials
Quantum effect could power the next generation of battery-free devices
New research finds heart health benefits in combining mango and avocado daily
New research finds peanut butter consumption builds muscle power in older adults
Study identifies aging-associated mitochondrial circular RNAs
The brain’s primitive ‘fear center’ is actually a sophisticated mediator
Brain Healthy Campus Collaborative announces winner of first-ever Brain Health Prize
[Press-News.org] Shrinking light: Nanoscale optical breakthroughWaveguiding scheme enables highly confined subnanometer optical fields