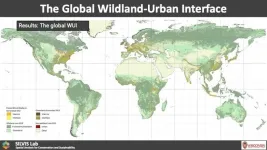
(Press-News.org) Researchers led by a team at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have created the first tool to map and visualize the areas where human settlements and nature meet on a global scale. The tool, which was part of a study recently published in Nature, could improve responses to environmental conflicts like wildfires, the spread of zoonotic diseases and loss of ecosystem biodiversity.
These areas where people and wildlands meet are called the wildland-urban interface, or WUI for short. More technically, a WUI (pronounced “woo-ee”) describes anywhere that has at least one house per 40 acres and is also 50% covered by wildland vegetation such as trees, shrubland, grassland, herbaceous wetland, mangroves, moss and lichen.
Franz Schug, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Forest and Wildlife Ecology at UW–Madison, explains that the areas were initially used by the U.S. Forest Service to assist with wildfire management in the Western United States.
Areas defined as WUI cover only about 4.7% of land on Earth, but about half of the human population lives within them. Many people enjoy living in these places because they like to be near the amenities of nature, explains Volker Radeloff, a professor of forest and wildlife ecology at UW–Madison.
“It reflects an affinity of people to nature, which is a good thing. If people said in general, ‘No, we rather not be anywhere near a forest,’ I'd be more worried with that,” Radeloff says.
But these areas are also hot spots for environmental conflicts like wildfires, the spread of diseases from animals, habitat fragmentation and loss of biodiversity. While climate change is projected to increase the potential environmental conflict in the WUI, population growth increases the frequency in which humans and wildlands come into contact in many places. Knowing where both is likely to happen globally is important for planning for the future.
Yet, the WUI has only been prominently described in the United States and a few other developed countries. Schug saw a gap in the research. He set out to investigate WUIs’ worldwide distribution, though mapping the high-resolution, global view required him to wrangle and make sense of a lot of information.
“I think the greatest challenge is just the amount of data that went into this,” he says. “We have two servers in the basement [of the lab building] that were reactivated for that purpose. I think the whole thing covers several terabytes of data processing.”
After setting up the computer program, it took three months to run through all the data, flagging the regions that qualify as a WUI. The land cover and building data they fed the computer was sourced from publicly available databases and stored on large servers.
Schug was able to record previously undocumented WUI in eastern Asia, East Africa and parts of South America.
Unsurprisingly, WUI around the world don’t all look the same or have the same kinds of ecosystems. If the goal is to be able to inform better management practices, Schug realized he would need to provide more context on what the kinds landscapes made up these WUIs. After all, managing rain forests is very different from managing grasslands.
“Especially in these biomes, where other studies predict that most likely climate change will have an impact on fire severity and fire frequencies, where a lot of people live, they’re definitely areas that will be a future interest,” Schug says.
The WUI is already being leveraged in countries like Poland, Argentina and Portugal, but Radeloff and Schug see this global view as a tool that can help land managers around the world know where they need to keep an eye on in the future.
As the climate changes, some of these biomes will see more wildfires, more people and animals coming into contact with each other for the first time and more opportunities for the spread of disease and ecosystem disruption.
Schug hopes this work will inspire further regionalized research around the WUIs they’ve documented, empowering local land managers to better prepare for change.
To learn more about the global distribution of wildlife-urban interfaces, explore the team’s interactive tool online. This project was funded by the NASA Land Cover and Land Use Change Program agreement 80NSSC21K0310. The work is also made possible by partnerships with the US Forest Service.
END
Picturing where wildlands and people meet at a global scale
Led by a team at UW–Madison, researchers have created the first global map of wildland-human interfaces
2023-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using new method, study highlights physician turnover trend
2023-07-19
Using an innovative method for measuring doctor turnover, Weill Cornell Medicine researchers determined that between 2010 and 2018, the annual rate at which physicians left their practices increased by 43 percent, from 5.3 percent to 7.6 percent a year. The causes of this trend are not known, but warrant further investigation, according to the researchers.
The study, published July 11 in the Annals of Internal Medicine, also found that the first three quarters of 2020 (the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States) were not associated with higher turnover. However, more data are needed to fully understand turnover trends related to COVID-19.
Whether doctors ...
Winery experiences affected by more than what is in your glass
2023-07-19
New research from the University of British Columbia's Okanagan campus has determined that enjoying a tasting at a winery goes well beyond the sip.
Professor Annamma Joy, with UBCO’s Faculty of Management, conducts research in the area of consumer behaviour and branding with a special focus on luxury brands, fashion brand experiences, wineries and wine tourism.
Dr. Joy, along with her collaborators and students, studied several Okanagan wineries over a three-year period to comprehensively document the experiences ...
Researchers use mass spectrometry to explore antimicrobial resistance
2023-07-19
Laura-Isobel McCall, Ph.D., and Zhibo Yang, Ph.D., co-principal investigators and associate professors of chemistry and biochemistry in the Dodge Family College of Arts and Sciences at the University of Oklahoma, have been awarded a prestigious R01 grant from the National Institutes of Health for their project, “Novel single-cell mass spectrometry to assess the role of intracellular drug concentration and metabolism in antimicrobial treatment failure.”
“Our project builds upon Dr. ...
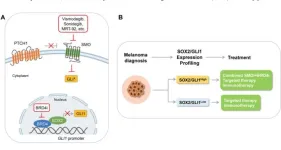
Novel therapeutic strategy against melanoma: combined targeting of hedgehog signaling and BRD4
2023-07-19
“This evidence strengthens the relevance of the findings by Pietrobono et al., shedding light on the potential application of SMO inhibitors in concert with BRD4 inhibitors.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 19, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on May 26, 2023, entitled, “Combined targeting of HEDGEHOG signaling and BRD4 as a novel therapeutic option against melanoma.”
The Hedgehog-GLI (HH/GLI) pathway is aberrantly activated in several types of cancer. Canonical HH/ GLI pathway is triggered by binding of HH ligands to the twelve-pass transmembrane receptor Patched 1 (PTCH1), which retrieves its inhibition ...
Large study finds small associations between systemic inflammation and later dementia
2023-07-19
A study of data from about 500,000 people in the UK Biobank has uncovered small but statistically significant associations between signs of systemic inflammation and later risk of dementia. Dr. Krisztina Mekli of The University of Manchester, UK, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on July 19, 2023.
Millions of people around the world have Alzheimer’s disease or other types of dementia, and researchers are working to tease out the complex mechanisms behind these conditions. Prior research has suggested that inflammation—activation of the body’s innate immune system—may ...
STEM instructors who are women drive disclosure of concealable stigmatized identities to undergraduates
2023-07-19
Women working as STEM instructors are more likely than men in the same profession to disclose to their undergraduate students identities which could carry stigma, such as depression or growing up in a low-income household. In the new study, published July 19, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, Carly Busch of Arizona State University, USA, and colleagues suggest that these decisions to disclose may be in order to act as role models for students.
Concealable stigmatized identities (CSIs) are identities that ...
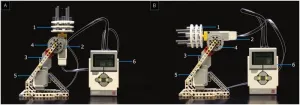
Researchers used a LEGO robotics kit as a cheap, effective way to purify self-assembling DNA origami
2023-07-19
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283134
Article Title: Gradient-mixing LEGO robots for purifying DNA origami nanostructures of multiple components by rate-zonal centrifugation
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The research in Hariadi lab was supported by the National Institutes of Health Director’s New Innovator Award (1DP2AI144247), National Science Foundation SemiSynBio II (2027215), and Arizona Biomedical Research Consortium (ADHS17-00007401). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. END ...
A 300,000 year-old double-pointed wooden stick was produced by Middle Pleistocene humans using sophisticated woodworking techniques and was likely used for throwing during hunts
2023-07-19
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0287719
Article Title: A double-pointed wooden throwing stick from Schöningen, Germany: Results and new insights from a multianalytical study
Author Countries: UK, Germany
Funding: T.T. and this project are funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) – project number 447423357. https://www.dfg.de/. The project is further funded by the Lower Saxony Ministry for Science and Culture, with funds from the Future Lower Saxony Programme of the Volkswagen Foundation – project ...
1 in 5 rabbit owners in the UK report painful or debilitating ear disease in their pet, though it may be under-diagnosed and under-treated, with lop-eared and older rabbits being most at risk
2023-07-19
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0285372
Article Title: Ear health and quality of life in pet rabbits of differing ear conformations: A UK survey of owner-reported signalment risk factors and effects on rabbit welfare and behaviour
Author Countries: UK
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. M.R.D.K included some of this questionnaire in part-fulfilment of her Bachelor of Veterinary Medicine at Royal Veterinary College. ...
CHOP researchers reveal how NSAIDs worsen C. difficile infections
2023-07-19
Philadelphia, July 19, 2023—Why do nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) exacerbate gastrointestinal infections by Clostridioides difficile, the leading cause of antibiotic-associated diarrhea worldwide? In a new paperpublished in Science Advances, researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have begun to answer that question, showing that NSAIDs disrupt the mitochondria of cells lining the colon, sensitizing them to damage by pathogenic toxins.
Clostridioides ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Unique Rubisco subunit boosts carbon assimilation in land plants
Climate change will drive increasing forest disturbances across Europe throughout the next century
Enhanced brain cells clear away dementia-related proteins
This odd little plant could help turbocharge crop yields
Flipped chromosomal segments drive natural selection
Whole-genome study of koalas transforms how we understand genetic risk in endangered species
Worcester Polytechnic Institute identifies new tool for predicting Alzheimer’s disease
HSS studies highlight advantages of osseointegration for people with an amputation
[Press-News.org] Picturing where wildlands and people meet at a global scaleLed by a team at UW–Madison, researchers have created the first global map of wildland-human interfaces