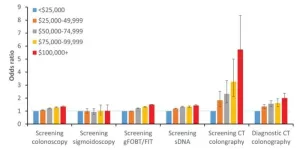
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, July 19, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), lacking Medicare coverage could contribute to greater income-based differences in use of screening CT colonography (CTC) than of other recommended screening strategies or of diagnostic CTC.
Noting that Medicare’s non-coverage for screening CTC may account for lower adherence with screening guidelines among lower-income beneficiaries, “Medicare coverage of CTC could reduce income-based disparities for individuals avoiding optical colonoscopy due to invasiveness, need for anesthesia, or complication risk,” concluded first author Eric W. Christensen, PhD, from the Harvey L. Neiman Health Policy Institute in Reston, VA.
Christensen et al.’s AJR accepted manuscript used CMS Research Identifiable Files—which contain claim information for 5% of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries—from January 1, 2011 to December 31, 2020. Extracting individuals 45–85 years old, excluding those with high CRC risk, models were then constructed to determine likelihood of undergoing CRC screening (as well as the CMS-covered test with similar access: diagnostic CTC) as a function of income, race and ethnicity, and urbanicity. Data were controlled for sex, age, Charlson comorbidity index, U.S. census region, screening year, and related conditions and procedures.
Ultimately, compared with Medicare beneficiaries in communities where per capita income was under $25,000 when controlling for race and ethnicity, those in communities with income greater than or equal to $100,000 were 5.7 times more likely to undergo screening CTC. Notably, this was a larger difference than observed for other CRC screening strategies (odds ratio, 1.03-1.50) or for diagnostic CTC (odds ratio, 2.00).
North America’s first radiological society, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) remains dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of medical imaging and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in radiology since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with the world’s longest continuously published radiology journal—American Journal of Roentgenology—the ARRS Annual Meeting, InPractice magazine, topical symposia, myriad multimedia educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
END
AJR on sociodemographic factors and screening CTC among Medicare beneficiaries
lacking Medicare coverage could contribute to greater income-based differences in use of screening CT colonography (CTC) than of other recommended screening strategies or of diagnostic CTC
2023-07-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study sheds light on cellular interactions that lead to liver transplant survival
2023-07-20
A new study identifies how certain proteins in the immune system interact leading to organ rejection. The study, which involved experiments on mice and human patients, uncovered an important communication pathway between two molecules called CEACAM1 (CC1) and TIM-3, finding that the pathway plays a crucial role in controlling the body's immune response during liver transplantation.
When an organ is transplanted from a donor to a recipient, the recipient's immune system recognizes the transplanted tissue as foreign, activating an immune response that can lead to rejection. T cells play a significant role ...
A potential new biomarker for Alzheimer’s
2023-07-20
Alzheimer’s is considered a disease of old age, with most people being diagnosed after 65. But the condition actually begins developing out of sight many years before any symptoms emerge. Tiny proteins, known as amyloid-beta peptides, clump together in the brain to form plaques. These plaques lead to inflammation and eventually cause neuronal cell death.
Interplay of proteins in the brain reveals disease mechanism
Exactly what triggers these pathological changes is still unclear. “We’re lacking good diagnostic markers that would allow us to reliably detect the disease at an early stage or make predictions about its course,” says Professor ...
A non-covalent bonding experience
2023-07-19
UPTON, NY—Putting a suite of new materials synthesis and characterization methods to the test, a team of scientists from the University of Iowa and the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory has developed 14 organic-inorganic hybrid materials, seven of which are entirely new. These uranium-based materials, as well as the detailed report of their bonding mechanisms, will help advance clean energy solutions, including safe nuclear energy. The work, currently published online, was recognized as both a Very Important Paper and a Hot Topic: Crystal Engineering in ...
Research analyzes kidney functions and predictors of disease
2023-07-19
Research is shedding light on kidneys, their critical functions, and predictors of disease.
The research co-led by Matthias Kretzler, M.D. describes the creation of a cellular atlas of the kidney describing nearly 100 cell types and states. It represents the most comprehensive study of cellular states, neighborhoods, and outcome-associated signatures in the kidney.
Researchers from more than twenty institutions collaborated on this project.
Kidneys monitor and maintain the internal balance in the body, filter out ...
SARS-CoV-2 infects liver, stimulating glucose production and contributing to severe form of COVID-19
2023-07-19
Research conducted at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil shows that SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can infect liver cells (hepatocytes), stimulating glucose production and leading to a condition similar to diabetes (hyperglycemia) in hospitalized patients, even if their blood sugar level was normal before they were admitted to hospital.
An article on the study is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The findings describe part of the mechanism used by the virus to infect liver cells and impair glucose metabolism, and point ...
Research could pave way to greener, more sustainable products made with renewable carbon
2023-07-19
Carbon-based materials have several qualities that make them attractive as catalysts for speeding up chemical reactions. They are low-cost, lightweight and their high surface area provides a good scaffold on which to anchor catalysts, keeping them stable and dispersed far apart, while providing molecules a lot of surface area to work. This makes carbons useful for energy storage and sensors. Over the last 10 years, carbons have been used in electrochemistry to catalyze reactions to make chemicals and fuel cells.
However, ...
Unlocking the power of molecular crystals: a possible solution to nuclear waste
2023-07-19
In a world increasingly concerned about the environmental and geopolitical implications of fossil fuel usage, nuclear energy has resurfaced as a subject of great interest. Its ability to generate electricity at scale without greenhouse gas emissions holds promise as a sustainable clean energy source that could bridge society’s transition away from fossil fuels to a net-zero future. However, nuclear power generation does produce radioactive waste. The safe management of nuclear waste remains a crucial challenge that must be addressed to gain public confidence in this transformative power solution.
Now, a team of University of Houston researchers has come up with an innovative ...
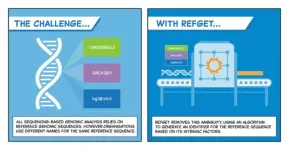
refget v2.0 links the hidden dictionaries of DNA
2023-07-19
A widely-used tool that finds the exact references needed to pinpoint differences in our DNA just got a refresh.
On 17 July, the Standards Steering Committee of the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) voted to release refget v2.0. With better compatibility for a range of reference genome names, formats, and systems, the new version of refget makes it easier than ever to retrieve verified genomic reference sequences.
A vital infrastructure
You may not even realise that you’re using refget already.
“Almost ...
Do certain amino acids modify the risk of dementia linked to air pollution?
2023-07-19
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JULY 19, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Higher levels of vitamin B-related amino acids may be linked to the risk of dementia associated with a certain type of air pollutants called particulate matter, according to a study published in the July 19, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that pollution or amino acids cause dementia, but it suggests a possible link among them.
Researchers ...
CHOP and Penn researchers find behavioral economics strategies can help patients quit smoking after a cancer diagnosis
2023-07-19
Philadelphia, July 19, 2023 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania found that cancer patients who continued to smoke after their diagnosis were significantly more likely to receive treatment for tobacco use when “nudges” to provide tobacco treatment were directed at clinicians through the electronic health record. The findings strengthen the case for using behavioral economics, or targeting predictable patterns in human decision-making to overcome ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] AJR on sociodemographic factors and screening CTC among Medicare beneficiarieslacking Medicare coverage could contribute to greater income-based differences in use of screening CT colonography (CTC) than of other recommended screening strategies or of diagnostic CTC