(Press-News.org) DALLAS, August 7, 2023 — Nancy Brown, chief executive officer of the American Heart Association, has again been recognized for elite leadership in the 26th annual listing of The NonProfit Times Power & Influence Top 50. For more than three decades, The NonProfit Times has been a leading trade publication providing news, information and insight into nonprofit management.
Brown, who is now appearing for the 8th time on this list, was recognized specifically for her leadership as a champion for equitable health. The NonProfit Times writes: “The name has “heart” in it, but Brown is a warrior for equitable health, connecting science, technology, and overall public health. Every impact can’t be included in a small space. Start with the AHA Center for Accelerated Drug Discovery, her $85 million research and innovation enterprise One Brave Idea, and the roughly dozen board and World Economic Forum leadership roles.”
The American Heart Association, under Brown’s leadership as CEO since 2008, has become the global thought leadership authority on cardiovascular and brain health, as well as overall health and well-being. With an industry reputation for forging powerful collaborations – together with 40 million volunteers, supporters and staff – Brown is known for consistently championing equitable health for everyone everywhere while remaining committed to innovation at the intersection of science, technology and public health.
“I am honored to be in company with so many respected leaders who are recognized this year by The NonProfit Times Power & Influence Top 50,” said Nancy Brown, CEO American Heart Association. “The remarkable staff, volunteers and supporters at the American Heart Association are the essence of this honor, and I am grateful for their dedicated efforts to advance our lifesaving mission.”
The 2023 honorees identified for exclusive membership in the 26th annual Power & Influence Top 50 were selected from a group of roughly 300 top nonprofit executives. A diverse committee of The NonProfit Times editorial staff, independent contributors and other key executive stakeholders were involved in the final selection process.
The honorees and their guests will be celebrated in person next month in Washington, D.C. during the annual NPT Power & Influence Top 50 Gala at The National Press Club. At that time, one of the honorees will also receive the NPT Influencer of the Year award.
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. We are dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities. Through collaboration with numerous organizations, and powered by millions of volunteers, we fund innovative research, advocate for the public’s health and share lifesaving resources. The Dallas-based organization has been a leading source of health information for nearly a century. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, Twitter or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
###
END
American Heart Association CEO again honored as elite nonprofit leader, health equity champion
The NonProfit Times names 26th annual Power & Influence Top 50
2023-08-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Department of Energy announces $4.7 million for research on integrative computational tools for systems biology research
2023-08-07
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $4.7 million in funding for five new research projects in computational biology. These projects will develop new software and analytical tools to manage the growing quantities of genomics and other data stemming from the study of microbes and other biological systems.
“The Biological and Environmental Research (BER) Genomic Science program is at the forefront of using genome-enabled approaches to identify the basic principles that drive biological systems underlying functional processes of organisms,” said Todd Anderson, DOE Acting Associate Director for BER. “To gain ...
Tiny, flexible spinal probe system could lead to better therapies
2023-08-07
HOUSTON – (Aug.7, 2023) – The spinal cord is harder to access and study than even the brain. The challenges posed by its mobility and anatomical structure have made understanding exactly how it functions difficult.
Rice University engineers will work with collaborators to optimize an array of nanoelectronic threads, or NETs ⎯ already used successfully for gathering high-fidelity, long-term data from neurons in the brain ⎯ for use in the spine, supported by a $6.25 million, four-year grant from the National Institutes of Health.
In addition to neuronal activity recordings, NET probes can provide tunable, localized stimulation of adjacent neurons. Rice ...
Advancing environmental justice research and student engagement in energy
2023-08-07
HOUSTON, Aug. 7, 2023 – The Baker Hughes Foundation announced a $100,000 grant to the University of Houston Energy Transition Institute (ETI) to support environmental justice research and workforce development programs.
The institute, which focuses on the creation and use of reliable, affordable, environmentally responsible energy for all through a just and equity-driven pathway, is looking forward to using the grant to amplify its mission.
“Thanks to the generous support of the Baker Hughes Foundation, the UH ...
Carbon dioxide – not water – triggers explosive basaltic volcanoes
2023-08-07
ITHACA, N.Y. – Geoscientists have long thought that water – along with shallow magma stored in Earth’s crust – drives volcanoes to erupt. Now, thanks to newly developed research tools at Cornell, scientists have learned that gaseous carbon dioxide can trigger explosive eruptions.
A new model suggests that basaltic volcanoes, typically located on the interior of tectonic plates, are fed by a deep magma within the mantle, stored about 20 to 30 kilometers below Earth’s surface.
The research, which offers a clearer picture of our planet’s deep internal dynamics and composition, with ...
Inside job: Finding exposes unexpected killer of immune cells lacking self marker
2023-08-07
Researchers at Kobe University discovered an entirely new and unexpected mechanism by which the immune system can get rid of cells lacking molecules that identify them as part of the self in mice. The finding, published in PNAS, has possible implications for cancer treatment.
The immune system comprises many types of cells that work together to fight off diseases. Two important types are dendritic cells and T cells. Dendritic cells are located in strategic positions throughout the body including the gut and skin, as well as in the lymph nodes, sample their environment and present small components derived from these samples on their ...
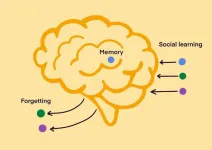
Memory, forgetting, and social learning
2023-08-07
Social learning is typically thought to be most beneficial when the environments in which individuals live change quite slowly – they can safely learn tried and tested information from one another and it does not go out of date quickly. Innovating brand-new information, on the other hand, is thought to be useful in dynamic and rapidly changing environments.
Researchers Madeleine Ammar, Laurel Fogarty and Anne Kandler at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology developed an agent-based simulation model of the evolution ...
New method to identify mutations in childhood brain tumors
2023-08-07
Researchers at Uppsala university have developed a new method to find mutations in brain tumors in children. They could also show that the mutations identified by them changes how cancer cells respond to a cancer drug. These findings could lead to better diagnostics and more individualized treatment of children with brain tumors. The study is published in the journal PNAS.
Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor in children. It usually develops in the cerebellum and even if modern treatment has improved the prognosis so that over 70% live more than five years, not all patients ...
Climate influences the spread of a life-threatening zoonotic disease in the Amazon
2023-08-07
Outbreaks of polycystic echicnococcosis, a life-threatening zoonotic disease, are driven by regional climate changes, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation. The findings, published in PNAS, provide evidence of the impact of climate on neglected tropical diseases in the Amazon region, with implications for other zoonoses.
Polycystic echinococcosis (PE) is a neglected life-threatening zoonosis caused by an intestinal worm (Echinococcus vogeli) ...
Research discovers key cause of restricted blood flow to the brain in vascular dementia
2023-08-07
Groundbreaking new research has uncovered a potential route to developing the first ever drug treatments for vascular dementia, that directly target a cause of the condition. The research, funded by the British Heart Foundation and published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, [1] has shed light on how high blood pressure causes changes to arteries in the brain, a process that leads to the devastating condition.
High blood pressure is a main cause of vascular dementia, a condition characterised by poor blood flow to the brain. The reduced blood supply starves brain cells of nutrients and over time they become damaged ...
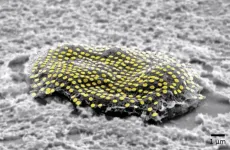
Latest in body art? ‘Tattoos’ for individual cells
2023-08-07
Engineers have developed nanoscale tattoos—dots and wires that adhere to live cells—in a breakthrough that puts researchers one step closer to tracking the health of individual cells.
The new technology allows for the first time the placement of optical elements or electronics on live cells with tattoo-like arrays that stick on cells while flexing and conforming to the cells’wet and fluid outer structure.
“If you imagine where this is all going in the future, we would like to have sensors to remotely monitor and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
[Press-News.org] American Heart Association CEO again honored as elite nonprofit leader, health equity championThe NonProfit Times names 26th annual Power & Influence Top 50