(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA – A new study finds that people are more likely to recommend that a pregnant family member or friend get vaccinated to protect the infant from RSV illness if they are shown a chart outlining the rigorous process a vaccine undergoes to be approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
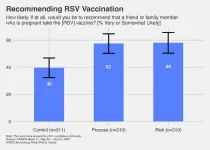
The experiment was conducted by an Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) team as part of a May 31-June 6, 2023, nationally representative panel survey on RSV, vaccination, and maternal health. Researchers found that 57% of those in a group exposed to a flowchart of the FDA vaccine approval process (see Appendix 1) were very or somewhat likely to recommend the RSV vaccine to a pregnant family member or friend, compared with 40% of those in a control group not shown the chart. Those in a third group, informed about the risks of RSV, were also more likely (58%) to recommend the vaccine (see graphic).
RSV, or respiratory syncytial virus, is the leading cause worldwide of lower respiratory tract infections in babies. Virtually all children get an RSV infection by the age of two. Though typically mild, the highly contagious RSV virus can cause serious illness, hospitalization, and even death among infants and the elderly.
The FDA has not yet approved an RSV vaccine for pregnant people. The FDA approved RSV vaccines by Pfizer and GSK for adults 60 and older and is considering the Pfizer vaccine for pregnant people, which would activate antibodies that would be passed on to the infants to protect them in their first six months. Separately, on Aug. 3, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended another form of preventive treatment against RSV, a monoclonal antibody injection for infants under eight months old and some older babies at risk of severe illness.
“Over the years the FDA and CDC have developed a sophisticated review system designed to protect the integrity of the data as well as the independence of the analysis on which the vaccination vetting and approval process relies,” said Kathleen Hall Jamieson, director of the Annenberg Public Policy Center and director of the survey. “The public would be well served if the press were to remind the public of this review process when a new vaccine is announced and vigilantly monitor it to ensure that it is doing its intended job well.”
Survey and study data on RSV
The study is part of a new white paper from the Annenberg Public Policy Center of the University of Pennsylvania that looks at misconceptions about vaccination during pregnancy. “Reducing susceptibilities to misconceptions about vaccination during pregnancy: RSV” is the second in a series of Vaccine Communication and Fact-Checking Toolkit reports produced in partnership with Critica, a nonprofit organization that seeks to improve public understanding and acceptance of scientific evidence and counteract health- and science-related misinformation.
The report contains survey data from the Annenberg Science and Public Health knowledge survey (ASAPH) of U.S. adults, first empaneled in April 2021 and conducted for APPC by the independent market research firm SSRS. The 11th wave of the panel, in which the experiment was embedded, was with 1,601 U.S. adults and fielded May 31-June 6, 2023. It has a margin of sampling error (MOE) of ± 3.3 percentage points at the 95% confidence level.
Correcting or contextualizing problematic claims about RSV or vaccination
The report “Reducing susceptibilities to misconceptions about vaccination during pregnancy: RSV” addresses ways to correct or contextualize misleading or false claims about maternal vaccination in general and vaccination against RSV among those who are pregnant in particular. These include misleading claims about the need for an RSV vaccine and unsupported claims about treatments that should be considered as options. Other examples include:
Distortions about the safety of an RSV vaccine for pregnant individuals
Distortions about vaccine ingredients
Distortions about the effects of the RSV vaccine
Recommendations
The report makes a series of recommendations for public health officials and others who communicate with the public about health about ways to minimize public susceptibility to misinformation about RSV and vaccination, including:
Visually represent the effects of RSV and offer clear and accurate information about the risks and benefits of vaccination compared with the likelihood of infection and its risks.
The CDC should create a webpage that complements existing information on RSV but focuses on vaccination during pregnancy.
Pre-emptively communicate about the changing nature of science by including caveats indicating that the guidance on RSV vaccination will be updated as more is learned about the vaccine.
Increase public understanding of the FDA review process.
The report and the experiment
To read more about these findings and recommendations:
Download the report here
Download Appendix 1 with the experiment on RSV
Read FactCheck.org’s Q&A on the RSV vaccines for older adults.
Read FactCheck.org’s Q&A on the RSV maternal vaccine to protect infants
Download the current version of the FDA vaccine approval chart from FactCheck.org
The experiment was designed by Patrick E. Jamieson, Ph.D., director of APPC’s Annenberg Health and Risk Communication Institute, the data analyzed by research analyst Shawn Patterson, Ph.D., and the chart created by FactCheck.org’s managing editor, Lori Robertson.
Some of the research included in the report was conducted as part of a grant from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the Foundation.
###
The Annenberg Public Policy Center was established in 1993 to educate the public and policy makers about communication’s role in advancing public understanding of political, science, and health issues at the local, state, and federal levels.
Critica is a nonprofit organization whose mission is to develop and test new methods of advancing public acceptance of scientific evidence, counteracting scientific misinformation, and promoting the use of scientific evidence in public policymaking.
END
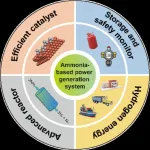
Due to the environmental and energy problems caused by fossil fuels, the search for alternative clean and renewable energy solutions has never been more urgent. Among these, hydrogen (H2) is emerging as a leading contender in the energy sector for both stationary and mobile applications. However, the commercial utilization of hydrogen fuel cells is hindered by the challenges of handling and transporting hydrogen due to its low volumetric energy density.
Fortunately, ammonia (NH3) is emerging as a promising hydrogen carrier due to its high hydrogen content (17.6 wt%) and potential economic benefits for energy production. When used as a fuel, it produces only ...
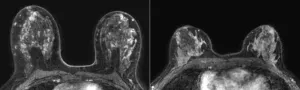
OAK BROOK, Ill. – A machine learning model found that background parenchymal enhancement (BPE) on breast MRI is an indicator of breast cancer risk in women with extremely dense breasts, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Women with extremely dense breasts are at a three- to six-times higher risk of developing breast cancer compared to women who have fatty breasts. Since mammography is less sensitive in detecting early-stage breast cancer in women with dense breasts, women between the ages ...
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL AUG. 8, 2023 AT 10 A.M. ET) – Blood disorders known as myelodysplastic syndromes/neoplasms (MDS) are difficult to diagnose – and are commonly misdiagnosed – putting patients at increased risk for treatment mistakes and other potentially harmful consequences, according to researchers with Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and collaborating organizations.
Their findings, published Aug. 8 in Blood Advances, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Society of Hematology, highlight the vital need for strong coordination between clinicians and skilled pathologists to ensure ...
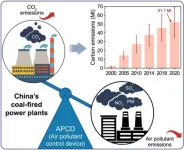
To combat this issue, China has implemented various environmental regulations, including the widespread use of air pollution control devices (APCDs) in CFPPs. While APCDs have successfully reduced air pollutants, their electricity consumption has led to indirect carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. The extent of these CO2 emissions has remained uncertain, prompting researchers to delve deeper into this overlooked environmental concern.
In a new study published in Volume 17 of the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, researchers from Shandong University conducted a study revealing that the proportion of APCD CO2 emissions in total ...
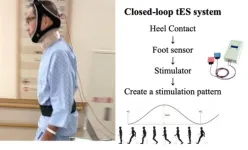
Gait-related disturbances adversely affect the quality of life of patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD), a condition affecting millions worldwide. Although various pharmacological, surgical, and rehabilitative treatments exist, their effectiveness is limited. Now, a team of researchers from Japan has successfully addressed this limitation. Using a novel neuromodulation approach that incorporates gait-combined closed-loop transcranial electrical stimulation, the team demonstrated significant gait improvements in patients with various neurological disorders including PD.
Parkinson’s disease ...
Pollinosis, or hay fever, makes people miserable around the world, and Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollen is a significant cause of the suffering in the 38.8% of Japanese people who are allergic. Japanese cedar is also the country's most important timber species. A single mature tree produces on the order of three hundred million grains of pollen. Saneyoshi Ueno and colleagues investigated the genes required to produce this massive amount of genetic material. Previous research by Ueno’s team identified ...
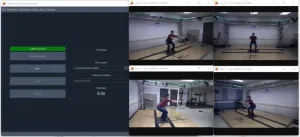
SAN ANTONIO — August 8, 2023 – Southwest Research Institute is launching its new Engine for Automatic Biomechanical Evaluation (ENABLE™) markerless biomechanics system during the American Society of Biomechanics (ABS) Annual Conference, August 8-11, in Knoxville, Tennessee. ABS attendees can see a demonstration by visiting Booth No. 11.
ENABLE is a user-friendly markerless motion capture system that leverages artificial intelligence, computer vision algorithms and biomechanical modeling. The key advantage of ENABLE is it efficiently captures ...
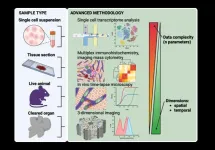
This review manuscript highlights the relevance of spatially-resolved macrophage phenotyping in liver disease-related research.
The liver is a vital organ heavily populated with macrophages, which represent key players of the innate immune response but also hold key functions in the maintenance of a healthy organ. Liver macrophages are mostly distributed across two populations of different origins and functions during homeostasis and disease: liver resident macrophages (referred to as Kupffer cells, KCs), and monocytic macrophages derived from the bone-marrow (MoMFs). The KC: MoMF ratio, as well as their respective spatial distribution through the liver, are increasingly ...
A study looks at the mechanisms behind genetic variation in the bacteria that cause Lyme disease. Lyme disease is the most common vector-transmitted disease in the United States, with around 476,000 human cases annually. Most Lyme disease is caused by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb), which is transmitted by ticks and can infect a wide range of mammals and birds. Matthew Combs and colleagues analyzed the genetic diversity of Bb, specifically focusing on the pathogen’s outer surface protein C (ospC) gene, a well-known virulence factor that is essential for survival of the pathogen inside the tick and the early stages of infection in vertebrates. ...
***Embargo 14:00 UK / 10:00 BRT / 9:00 ET / 6:00 PT Tuesday, August 8, 2023***
SEATTLE, Wash. August 8, 2023 – 569,000 deaths were linked to bacterial antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in all 35 countries of the WHO Region of the Americas, according to a new peer-reviewed paper published in The Lancet Regional Health – Americas. This analysis on the burden of AMR in the Americas is the most comprehensive yet for the region, providing data for 35 countries, 23 bacterial pathogens, and 88 pathogen-drug combinations.
The ...