(Press-News.org) Ohio residents who vote against tax renewals for parks and recreation spending could be costing themselves a significant amount of wealth in the form of their homes' value, a University of Cincinnati economist found.
David Brasington, PhD, the James C. and Caroline Kautz Chair in Political Economy and professor of economics in UC's Carl H. Lindner College of Business, studied the effect of cutting funding for the maintenance of local parks and recreational areas on housing values for a research article that was published in Journal of Regional Science.
Brasington found Ohio communities that vote to renew parks and recreation spending see 13% higher home values three years after the vote than similar communities that voted against the tax renewals. For the typical household, a vote against tax renewals saves $70 a year in taxes but costs $30,000 in house values.
“I was surprised by how strong the magnitude was,” Brasington said. “A 13% difference in house prices is really big. I was surprised a relatively small change in park funding could cause such a big change in house prices over time.”
In his research, Brasington focused on communities that according to data from the U.S. Census Bureau share similar demographic and economic characteristics. The only discernible difference was that some of them narrowly voted to renew tax levies while others narrowly voted against renewing their levies.
Using a housing data set, Brasington compared home values in the communities from 1991 through 2016.
While house prices didn't reflect a change immediately, three years after the votes the communities that approved the park and recreation maintenance saw 13% higher house values compared to the communities that voted against their levies. In subsequent years, the gap continued to grow.
“I didn't find any effects the first year after the vote or the second year after the vote, but they were noticeable three years later,” Brasington said. “The findings I have are consistent with the idea that right after you vote to cut parks and recreation taxes and funding, you don't notice any effects on house prices, but as time goes on, maybe this decrease in maintenance funding starts to be noticeable and maybe it's reflected in house prices.”
The data doesn't mean that communities that vote against renewing tax levies see a 13% decrease in housing values or that communities that vote in favor of their levies see a 13% increase. Rather, an example could be one community seeing a 7% increase in housing values while another sees a 20% increase, Brasington said.
“When a local government offers services, they're competing with other local governments for residents and businesses to build their tax base, so they want to offer good services that people care about,” he said.
The data shows parks are a service that people care about, Brasington said. It also shows that Ohio's local parks might be underfunded.
“Parks and recreation spending seems worth it in Ohio,” he said. “There may be places where it isn't, there may be places where it's really, really worthwhile. But overall the parks and recreation spending is worth it in Ohio because the estimate is just an average across all the communities.”
Brasington's findings on home prices aligns with his previous research on the value of local park funding. In a research article published in 2021, Brasington found communities that renewed tax funding for local parks had more residential development than those that cut park taxes and funding.
END
UC economist finds strong link between park funding, home values
House prices higher in Ohio communities that vote to renew tax levies for recreational areas
2023-08-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Is hip replacement safe for people in their 90s? Risks depend on patients' health as well as age
2023-08-25
August 25, 2023 – Potentially modifiable comorbid conditions and complications have a major impact on the risks of total hip arthroplasty (THA) for people in their nineties, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Patients ³90 years old have higher complication and mortality rates following THA, as compared with younger patients. But while age is a significant factor, the risks associated with THA in nonagenarians ...
SLU research: Erectile dysfunction linked to undiagnosed prediabetes, type 2 diabetes in young men
2023-08-25
ST. LOUIS — Erectile dysfunction (ED) is more common in older individuals with long-term Type 2 diabetes. However, emerging research at Saint Louis University School of Medicine has found that ED indicates undiagnosed prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in young men under 40.
Although the prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes declined in the United States from 1988 to 2020, 2.5% of the population has persistent undiagnosed diabetes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate 8.5 million adults have undiagnosed diabetes, and a quarter of these cases are among young persons 18 to 44.
In a recent study published ...
Children with SEND deserve authentic inclusion in the foreign languages classroom, report warns
2023-08-25
Pupils with special educational needs and disabilities should be given equal opportunities to learn languages, a new report argues.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that children with SEND are often removed from language lessons, because the subject is perceived as “difficult”, an assumption that is further exacerbated by trends with GCSE subject choices. Instead of withdrawing children with additional needs from the foreign languages classroom, opportunities should be provided for them to thrive within it.
Evidence shows learning new languages can be possible and hugely beneficial for many children with ...
New guideline details dental pain management strategies for pediatric patients
2023-08-25
CHICAGO, Aug. 25, 2023 – Acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen are recommended as first-line treatments for managing short-term dental pain in children under age 12, according to a new clinical practice guideline developed by the American Dental Association Science & Research Institute (ADASRI), the University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine and the Center for Integrative Global Oral Health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine. The guideline has been endorsed by the American Dental Association.
A guideline panel determined that, when used as directed, acetaminophen alone, ...
In Type 1 diabetes, verapamil prevents decline of IGF-1 and promotes beta-cell IGF-1 signaling
2023-08-25
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In 2012, University of Alabama at Birmingham researcher Anath Shalev, M.D., reported that a decades-old blood pressure medication called verapamil completely reversed diabetes in animal models. In 2018, the team had translated these findings into a randomized, controlled, clinical trial, demonstrating significantly improved beta cell function for one year in human subjects with recent onset Type 1 diabetes. By last year, in a small follow-up study, Shalev and colleagues had found that adult Type 1 diabetes patients taking oral verapamil required less daily insulin ...
How being in space impairs astronauts’ immune system
2023-08-25
A new study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden has examined how T cells of the immune system are affected by weightlessness. The results, which are published in the journal Science Advances, could explain why astronauts’ T cells become less active and less effective at fighting infection.
The next steps in the exploration of space are human missions to the moon and to Mars. Space is an extremely hostile environment that poses threats to human health. One such threat is changes to the immune system that occur in astronauts while in space and ...
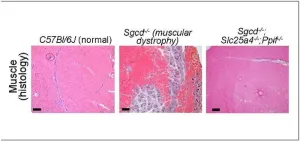
Mitochondria pore emerges as potential key to managing muscular dystrophies
2023-08-25
Ever since the Jerry Lewis telethons began in the 1960s, millions of people have become familiar with an otherwise rare disease called muscular dystrophy (MD).
The medical world has learned much over the ensuing years, including that more than 30 closely related disorders exist that can produce the gradual muscle degeneration that steals a child’s ability to walk and eventually disrupts other organ functions. An estimated 250,000 people in the U.S. are living with a muscular dystrophy. While many are living longer lives thanks to improved treatments, no cure has been found.
Now an eye-opening study ...
Unlocking the secrets of cell antennas
2023-08-25
Cilia are thin, eyelash-like extensions on the surface of cells. They perform a wide variety of functions, acting as mechanosensors or chemosensors, and play a crucial role in many signaling pathways. In the last few decades, the organelle has undergone a remarkable, but at the same time sinister, career transformation. It evolved from an organelle whose relevance was unclear to becoming a central player in the pathogenesis of a large group of diseases. These so-called ciliopathies are associated with a wide range of symptoms, including hearing loss, visual impairment, obesity, kidney disease, and mental disability. Different gene mutations impair cilia formation, ...
How origami might inform disease diagnoses
2023-08-25
Researchers at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering looked to origami to create new sensors that could someday be employed to detect deformations in organs and also for use in wearables and soft robotics.
Their paper, “High-Stretchability and Low-Hysteresis Strain Sensors Using Origami-Inspired 3D Mesostructures,” featured in Science Advances explains how USC researchers Hangbo Zhao, Xinghao Huang, Liangshu Liu, Yung Hsin Lin, Rui Feng, Yiyang Shen, and Yuanning Chang developed “stretchable strain sensors,” ...
Weight loss medication benefits patients with heart failure and obesity
2023-08-25
Amsterdam, Netherlands – 25 Aug 2023: Semaglutide improves heart failure-related symptoms and physical function and results in greater weight loss compared with placebo in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and obesity, according to late breaking research presented in a Hot Line session today at ESC Congress 2023.1
Approximately half of patients with heart failure in the community have HFpEF.2 Most patients with HFpEF are overweight or obese, and growing evidence suggests that obesity and excess adiposity are not simply comorbidities, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
[Press-News.org] UC economist finds strong link between park funding, home valuesHouse prices higher in Ohio communities that vote to renew tax levies for recreational areas