(Press-News.org) Researchers from Radboud University and the UMC Utrecht have succeeded in transforming brain signals into audible speech. By decoding signals from the brain through a combination of implants and AI, they were able to predict the words people wanted to say with an accuracy of 92 to 100%. Their findings are published in the Journal of Neural Engineering this month.
The research indicates a promising development in the field of Brain-Computer Interfaces, according to lead author Julia Berezutskaya, researcher at Radboud University's Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behaviour and UMC Utrecht. Berezutskaya and colleagues at the UMC Utrecht and Radboud University used brain implants in patients with epilepsy to infer what people were saying.
Bringing back voices
‘Ultimately, we hope to make this technology available to patients in a locked-in state, who are paralyzed and unable to communicate,’ says Berezutskaya. ‘These people lose the ability to move their muscles, and thus to speak. By developing a brain-computer interface, we can analyse brain activity and give them a voice again.’
For the experiment in their new paper, the researchers asked non-paralyzed people with temporary brain implants to speak a number of words out loud while their brain activity was being measured. Berezutskaya: ‘We were then able to establish direct mapping between brain activity on the one hand, and speech on the other hand. We also used advanced artificial intelligence models to translate that brain activity directly into audible speech. That means we weren't just able to guess what people were saying, but we could immediately transform those words into intelligible, understandable sounds. In addition, the reconstructed speech even sounded like the original speaker in their tone of voice and manner of speaking.’
Researchers around the world are working on ways to recognize words and sentences in brain patterns. The researchers were able to reconstruct intelligible speech with relatively small datasets, showing their models can uncover the complex mapping between brain activity and speech with limited data. Crucially, they also conducted listening tests with volunteers to evaluate how identifiable the synthesized words were. The positive results from those tests indicate the technology isn't just succeeding at identifying words correctly, but also at getting those words across audibly and understandably, just like a real voice.
Limitations
‘For now, there's still a number of limitations,’ warns Berezutskaya. ‘In these experiments, we asked participants to say twelve words out loud, and those were the words we tried to detect. In general, predicting individual words is less complicated than predicting entire sentences. In the future, large language models that are used in AI research can be beneficial. Our goal is to predict full sentences and paragraphs of what people are trying to say based on their brain activity alone. To get there, we'll need more experiments, more advanced implants, larger datasets and advanced AI models. All these processes will still take a number of years, but it looks like we're heading in the right direction.’
END
Brain signals transformed into speech through implants and AI
Researchers from Radboud University and the UMC Utrecht have succeeded in transforming brain signals into audible speech.
2023-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How plants pass down genetic memories
2023-08-28
When organisms pass their genes on to future generations, they include more than the code spelled out in DNA. Some also pass along chemical markers that instruct cells how to use that code. The passage of these markers to future generations is known as epigenetic inheritance. It’s particularly common in plants. So, significant findings here may have implications for agriculture, food supplies, and the environment.
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professors and HHMI Investigators Rob Martienssen and Leemor Joshua-Tor have been researching how plants pass along the markers that ...
BU CTE Center publishes largest CTE case series ever in youth, high school and college athletes who died young
2023-08-28
EMBARGOED by JAMA Neurology until 11 a.m. EDT Aug. 28, 2023
Contact: Maria Ober, 617-224-8963, mpober@bu.edu
(Boston)— A new BU Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) Center study has found that, among a sample of 152 young athletes exposed to repetitive head impacts (RHI) who were under age 30 at the time of death, 41.4% (63) had neuropathological evidence of CTE, a degenerative brain disease caused by RHI. The study published in JAMA Neurology includes the first American woman athlete diagnosed with CTE, a 28-year-old collegiate soccer player whose identity remains private.
“This study clearly shows that the pathology of CTE starts early,” said corresponding ...
NIH study shows association between better neighborhood conditions and lower childhood asthma rates
2023-08-28
Living in a neighborhood with better access to resources such as high-quality housing, healthy food, parks and playgrounds, and clean air during the early stages of childhood was associated with lower asthma incidence in a new study from NIH’s Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO) Program.
Children born in high-opportunity neighborhoods had an asthma incidence rate of 23.3 cases per 1,000 children, while those born in very low and low-opportunity neighborhoods had rates of 35.3 per 1,000 ...
Scientists use quantum device to slow down simulated chemical reaction 100 billion times
2023-08-28
Scientists at the University of Sydney have, for the first time, used a quantum computer to engineer and directly observe a process critical in chemical reactions by slowing it down by a factor of 100 billion times.
Joint lead researcher and PhD student, Vanessa Olaya Agudelo, said: “It is by understanding these basic processes inside and between molecules that we can open up a new world of possibilities in materials science, drug design, or solar energy harvesting.
“It could also help improve ...
Assessment of hospital-onset SARS-CoV-2 infection rates and testing practices
2023-08-28
About The Study: In this study of hospitals reporting SARS-CoV-2 infections, there was an increase of hospital-onset SARS-CoV-2 infections when community-onset infections were higher, indicating a need for ongoing and enhanced surveillance and prevention efforts to reduce in-hospital transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infections, particularly when community-incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infections is high.
Authors: Kelly M. Hatfield, M.S.P.H., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in Atlanta, is the ...
Trends in suicide rates among post-9/11 veterans with and without traumatic brain injury
2023-08-28
About The Study: In a large cohort of U.S. military veterans serving after 9/11, suicide rates increased more than 10-fold from 2006-2020, a significantly greater rate of change than in the U.S. adult population. Over the 15-year period, veterans with traumatic brain injury (TBI) had suicide rates 56% higher than veterans without TBI and three times higher than the U.S. adult population.
Authors: Jeffrey T. Howard, Ph.D., of the University of Texas at San Antonio, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2893)
Editor’s ...
Estimated lifetime gained with cancer screening tests
2023-08-28
About The Study: The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis of 18 long-term randomized clinical trials involving 2.1 million individuals suggest that current evidence does not substantiate the claim that common cancer screening tests save lives by extending lifetime, except possibly for colorectal cancer screening with sigmoidoscopy.
Authors: Michael Bretthauer, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Oslo in Oslo, Norway, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.3798)
Editor’s ...
Neuropathologic and clinical findings in young contact sport athletes exposed to repetitive head impacts
2023-08-28
About The Study: This case series found that young brain donors exposed to repetitive head impacts were highly symptomatic regardless of chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) status, and the causes of symptoms in this sample are likely multifactorial. Future studies that include young brain donors unexposed to repetitive head impacts are needed to clarify the association among exposure, white matter and microvascular pathologic findings, CTE, and clinical symptoms.
Authors: Ann C. McKee, M.D., of the U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Due to sea-ice retreat, zooplankton could remain in the deep longer
2023-08-28
Due to intensifying sea-ice melting in the Arctic, sunlight is now penetrating deeper and deeper into the ocean. Since marine zooplankton respond to the available light, this is also changing their behaviour – especially how the tiny organisms rise and fall within the water column. As an international team of researchers led by the Alfred Wegener Institute has now shown, in the future this could lead to more frequent food shortages for the zooplankton, and to negative effects for larger species including seals and whales. The study ...
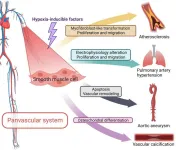
Hypoxia and panvascular diseases: exploring the role of hypoxia-inducible factors in vascular smooth muscle cells under panvascular pathologies
2023-08-28
This study is led by Prof. Junbo Ge (Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases), Prof. Hua Li (Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases), and Prof. Hao Lu (Department of Cardiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases).
As an emerging concept, panvascular diseases encompass a group of cardiovascular disorders characterized mainly by atherosclerosis, involving crucial organs such as the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] Brain signals transformed into speech through implants and AIResearchers from Radboud University and the UMC Utrecht have succeeded in transforming brain signals into audible speech.