(Press-News.org) A new study by University of Maryland Economist Louis Preonas provides empirical evidence that railroads are likely to cut transportation prices to prop up coal-fired plants if U.S. climate policies further disadvantage coal in favor of less carbon-intensive energy sources.
One strategy being considered to help reduce the country’s contribution to global climate change is a tax or fee on greenhouse gas emissions by coal-burning power plants. The hope is that such fees will reduce competitiveness of coal-fired energy and consumers will chose lower-emission options at a competitive cost. The new study, published September 7, 2023, in The Review of Economic Studies shows that rail transportation companies could reduce the effectiveness of those fees.
”These findings underscore the importance of looking at the whole fossil fuel supply chain,” said Preonas, an assistant professor in the Department of Agricultural and Resource Economics. “If policymakers ignore real distortions in the market, like monopoly power in rail shipping, their climate policy efforts may not achieve the intended results.”
For his study, Preonas used the drop in natural gas prices over the past decade as a natural experiment for understanding how market pressures effect the price of coal-fired power generation. By analyzing data on coal deliveries, rail carrier use of the U.S. rail network and hourly energy generation from power plants, Preonas showed that as competition from natural gas forced coal fired plants to reduce electricity prices, railroad companies reduced their coal transportation fees. By absorbing some of the cost difference between coal and natural gas, the railroads propped up the coal market to avoid losing business.
Preonas calculated that without the railroad’s propping up of the coal industry, natural gas use would have increased even more, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by an additional 10% over current levels.
According to the study, the rail industry’s response to price competition in the coal market indicates that they are likely to absorb a significant portion of any carbon tax or fee that may be applied to coal-burning plants. This would ultimately benefit the coal industry at the expense of the railroads and their shareholders.
Preonas also showed that railroads can only absorb a carbon tax for certain power plants. About 44% of U.S. coal-burning plants are served by a single railroad. Those plants are most reliant on their rail carrier, which means those carriers have higher profit margins and are better positioned to reduce costs to keep a coal plant operational. Where plants are served by multiple railroads or able to receive shipments by water such as a nearby river or lake, rail companies face more competition and may have less room for price cuts.
The study underscores the need for future research to explore the long-term implications of market power among rail transportation companies, including their potential impact on coal-fired plant retirements and the fiscal health of coal mining communities.
Preonas said that this work also serves as a broader call to incorporate market power distortions into climate policy projects for other carbon-intensive industries such as petroleum refining and aluminum production.
Data used for the study included Energy Information Administration data on coal deliveries to power plants and power plant characteristics in the United States; hourly generation data from the Environmental Protection Agency's Continuous Emissions Monitoring System, which determines how much coal each plant consumes based on the relative prices of coal and natural gas; and data from the Bureau of Transportation Statistics which provides detailed information about the U.S. rail network, including the rail carriers operating on each track segment.
END
New study reveals the power of railroads to buffer coal plants from a carbon emissions tax
UMD economist emphasizes the need to factor similar market distortions into US climate policy to reduce emissions from carbon-intensive industries
2023-09-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mount Sinai scientists unlock secrets of red blood cell transporter, potentially paving the way for new drugs
2023-09-07
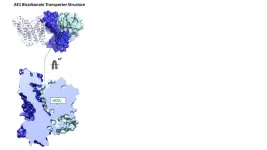
New York, NY (September 7, 2023)—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have identified the structure of a special transporter found in red blood cells and how it interacts with drugs. Details on the findings, which were reported in the September 7 issue of Nature Structural & Molecular Biology [DOI: 10.1038/s41594-023-01085-6], could lead to the development of more targeted medicines.
The research team, led by Daniel Wacker, PhD, Bin Zhang, PhD, and Avner Schlessinger, PhD, found that this transporter facilitates ...
Research spotlight: History of Adverse Childhood Events (ACEs) linked to increased risk of head or neck injury and concussion
2023-09-07
Altaf Saadi, MD, MSc, principal investigator of the Neurodisparities & Health Justice Lab in the Department of Neurology at Mass General and an assistant professor of Neurology at Harvard Medical School, is lead author of a new study in the Journal of Head Trauma and Rehabilitation, Examining the Association Between Adverse Childhood Experiences and Lifetime History of Head or Neck Injury or Concussion in Children From the United States.
What Question Were You Investigating?
Is there an association between adverse childhood experiences ...
University of Houston researcher aids in creation of groundbreaking report on invasive species
2023-09-07
A new report by the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) presents major findings on the gravity of impacts from invasive alien species on our planet. Researchers found more than 37,000 alien species have been introduced by human activities over the centuries, and this conservative estimate is rising at unprecedented rates. Additionally, more than 3,500 of these are harmful invasive alien species, impacting humans, animals and plants.
Dozens of international biodiversity ...
CAR-T-cell therapy without side effects? Hollings researchers show results in preclinical models
2023-09-07
When Richard O’Neil, Ph.D., joined MUSC Hollings Cancer Center two years ago, he knew that he wanted to continue finding ways to make CAR-T-cell therapy easier on patients.
What he didn’t expect was that a side project – worked on by Megan Tennant, a graduate student in his lab, as a way to keep busy while a key piece of equipment was being serviced – would potentially open up this treatment beyond the world of cancer.
“I don't think that either of us expected that first initial experiment to work,” Tennant said. “But when we saw how well it worked and really started to conceptualize where this could go and how important ...
The timing of fireworks-caused wildfire ignitions during the 4th of July holiday season
2023-09-07
Every year on the 4th of July, fireworks cause cause a precipitous increase of wildfire ignitions in the United States (U.S.). This human-environmental phenomenon is noteworthy and highlights the impact of American culture on wildfire activity in the U.S. In other regions of the world, research has increasingly shown that human culture impacts fire activity, with weekly cycles of fire activity reflecting the local structures of workweeks and the timing of religious days of rest (e.g., Saturdays and Sundays). Although 4th of July peak in wildfire igntions has ...
Dosage tweaks may hint at undiscovered interactions between medications
2023-09-07
Analysis of data from more than 1 million Danish inpatients identifies nearly 4,000 drug pairings that are associated with more frequent dosage adjustments when prescribed together—potentially hinting at previously undiscovered drug interactions. Søren Brunak of the University of Copenhagen, Denmark, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Digital Health.
In some cases, especially among elderly populations, a person may be prescribed several different medications at once in order to treat one or multiple health conditions—a phenomenon known as polypharmacy. Polypharmacy is associated with increased health risks due to the potential ...
How bright-light treatment improves sleep in stressed mice
2023-09-07
Chronic stress is associated with sleep disturbance. In their new study, Lu Huang and colleagues identify the neural pathway behind this behavior, and at the same time, explain how bright-light treatment is able to counter it. The research was conducted in mice at Jinan University in China and published September 7th in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
Bright-light treatment is known to improve sleep in those with sleep disorders, but how it works – and whether it works in cases of stress-induced sleep disturbances – was unknown. The researchers hypothesized that a part of the brain called the lateral habenula is deeply involved in this phenomenon because ...
Lack of evidence hampers progress on corporate-led ecosystem restoration
2023-09-07
A ‘near total’ lack of transparency is making it impossible to assess the quality of corporate-led ecosystem restoration projects, according to a Lancaster University-led study published today in Science.
Efforts to rebuild degraded environments are vital for achieving global biodiversity targets. The United Nations has launched a Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, and in recent years businesses around the world have collectively pledged to plant billions of trees, hundreds of thousands of corals and tens of ...
Implantable device enables earlier detection of kidney transplant failure in rats
2023-09-07
An implantable sensor provided advanced warning of kidney transplant failure in rats as much as several weeks earlier than commonly used biomarkers of kidney function, researchers report. The device, tested in a rat model of kidney transplantation, provides real-time continuous monitoring of organ temperature and thermal conductivity, detecting inflammatory processes associated with graft rejection. Although lifesaving for patients with end-stage kidney disease, long-term kidney transplantation survival remains a major challenge. Graft failure ...
2022 Hunga-Tonga eruption triggered fast and destructive submarine volcanic flows
2023-09-07
In 2022, the eruption of the submerged Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha apai volcano triggered a fast-moving and destructive underwater debris flow that severed telecommunication cables and reshaped the surrounding seafloor. The findings – representing some of the first fieldwork to document what happens when large volumes of erupted volcanic material are delivered directly into the ocean – provide new insights into the behavior and hazards of submerged volcanoes. Explosive volcanic eruptions on land create pyroclastic flows of hot ash and rock that, when they reach the ocean, can trigger damaging ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] New study reveals the power of railroads to buffer coal plants from a carbon emissions taxUMD economist emphasizes the need to factor similar market distortions into US climate policy to reduce emissions from carbon-intensive industries