(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, September 14, 2023 – Up to an hour after their hearts had stopped, some patients revived by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) had clear memories afterward of experiencing death and had brain patterns while unconscious linked to thought and memory, report investigators in the journal Resuscitation, published by Elsevier.
In a study led by researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, in cooperation with 25 mostly US and British hospitals, some survivors of cardiac arrest described lucid death experiences that occurred while they were seemingly unconscious. Despite immediate treatment, fewer than 10% of the 567 patients studied, who received CPR in the hospital, recovered sufficiently to be discharged. Four in 10 of patients who survived, however, recalled some degree of consciousness during CPR not captured by standard measures.
The study also found that in a subset of these patients, who received brain monitoring, nearly 40% had brain activity that returned to normal, or nearly normal, from a “flatline” state, at points even an hour into CPR. As captured by EEG, a technology that records brain activity with electrodes, the patients saw spikes in the gamma, delta, theta, alpha, and beta waves associated with higher mental function.
Survivors have long reported having heightened awareness and powerful, lucid experiences, say the study authors. These have included a perception of separation from the body, observing events without pain or distress, and a meaningful evaluation of their actions and relationships. This new work found these experiences of death to be different from hallucinations, delusions, illusions, dreams, or CPR-induced consciousness.
The study authors hypothesize that the “flatlined,” dying brain removes natural inhibitory (braking) systems. These processes, known collectively as disinhibition, may open access to “new dimensions of reality,” they say, including lucid recall of all stored memories from early childhood to death, evaluated from the perspective of morality. While no one knows the evolutionary purpose of this phenomenon, it “opens the door to a systematic exploration of what happens when a person dies.”
Senior study author Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Medicine at NYU Langone Health and director of critical care and resuscitation research at NYU Langone, says, “Although doctors have long thought that the brain suffers permanent damage about 10 minutes after the heart stops supplying it with oxygen, our work found that the brain can show signs of electrical recovery long into ongoing CPR. This is the first large study to show that these recollections and brain wave changes may be signs of universal, shared elements of so-called near-death experiences.”
Dr. Parnia adds, “These experiences provide a glimpse into a real, yet little understood dimension of human consciousness that becomes uncovered with death. The findings may also guide the design of new ways to restart the heart or prevent brain injuries and hold implications for transplantation.”
Called the AWAreness during REsuscitation (AWARE)-II study – it followed 567 men and women who suffered cardiac arrest during hospital stays between May 2017 and March 2020 in the United States and United Kingdom. Only hospitalized patients were enrolled to standardize the CPR and resuscitation methods used, as well as recording methods for brain activity. A subset of 85 patients received brain monitoring during CPR. Additional testimony from 126 community survivors of cardiac arrest with self-reported memories was also examined to provide greater understanding of the themes related to the recalled experience of death.
The study authors conclude that research to date has neither proved nor disproved the reality or meaning of patients’ experiences and claims of awareness in relation to death. They say the recalled experience surrounding death merits further empirical investigation and plan to conduct studies that more precisely define biomarkers of clinical consciousness and that monitor the long-term psychological effects of resuscitation after cardiac arrest.
END
New evidence indicates patients recall death experiences after cardiac arrest
Researchers report in Resuscitation that awareness and consciousness, including a lucid recalled experience of death, are identified and for the first time using brain monitors to identify markers of consciousness and mental activity
2023-09-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Clinical whole genome sequencing test developed at JAX
2023-09-14
Until quite recently, it was extremely difficult to detect the variants underlying many genetic disorders. In the absence of a defined cause, clinicians have little to guide treatment for those left without a genetic diagnosis, forcing patients and families to embark on a diagnostic odyssey with no guarantee of finding answers.
A decade ago, sequencing centers began offering clinical whole exome sequencing, but these only cover the portion of the genome that codes for proteins – approximately 1.5 percent of the entire genome. While relatively successful, the diagnostic yield for most clinical exome sequencing programs is roughly 25 percent, leaving 75 percent of cases without ...
UCI researchers announce publication of an open-label clinical trial suggesting that N-acetylglucosamine restores neurological function in Multiple Sclerosis patients
2023-09-14
Irvine, CA – Sept. 14, 2023 – UCI researchers have found that a simple sugar, N-acetylglucosamine, reduces multiple inflammation and neurodegeneration markers in people who suffer from multiple sclerosis (MS). In addition, they also found this dietary supplement improved neurological function in 30% of patients.
According to the World Health Organization, MS affects more than 1.8 million people, and while there are treatments to prevent relapses and improve quality of life, there is no cure.
The study, N-acetylglucosamine ...
Vocal learning linked to problem solving skills and brain size
2023-09-14
The European starling boasts a remarkable repertoire. Versatile songbirds that learn warbles, whistles, calls, and songs throughout their lives, starlings rank among the most advanced avian vocal learners. Now a new study published in Science finds that starlings, along with other complex vocal learners, are also superior problem solvers.
“There is a long-standing hypothesis that only the most intelligent animals are capable of complex vocal learning,” says Jean-Nicolas Audet, a research ...
Study finds spiritual coping behaviors may be key to enhanced trauma recovery of Black men who survive firearm injury
2023-09-14
PHILADELPHIA (September 14, 2023) – High rates of firearm injury among urban Black men in the U.S. can lead to long physical and psychological recovery times, worsened by limited access to mental health services. In the face of firearm injury, urban Black men may feel they have lost control over their lives, leading to fear, paranoia, lack of forgiveness, and different dimensions of mental health challenges, which can be difficult to overcome.
In a pilot study from the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing ...
In the “I” of the beholder: People believe self-relevant artwork is more beautiful
2023-09-14
People have fairly consistent preferences when it comes to judging the beauty of things in the real world—it’s well known, for example, that humans prefer symmetrical faces. But our feelings about art may be more personal, causing us to prefer art that speaks to our sense of self, research in Psychological Science suggests.
“When there is personal meaning in an image, that can dominate your aesthetic judgments way more than any image feature,” said Edward A. Vessel (The City College of New York) in an interview. Though self-relevant ...
Aspergillus fumigatus is a saprotrophic fungus that can cause serious life-threatening invasive infections in immunocompromised individuals
2023-09-14
Aspergillus fumigatus is a saprotrophic fungus that can cause serious life-threatening invasive infections in immunocompromised individuals; by constructing a recombination map, this study shows that A. fumigatus produces the highest number of crossovers per chromosome ever described (~30 per chromosome pair).
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002278
Article Title: The human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus can produce ...
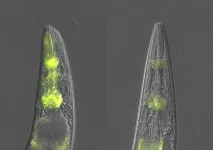
During failure of core protein quality control in the nematode C. elegans, a specialized anti-aggregation mechanism relying on pathogen response factors and lysosomal mediated degradation is triggered
2023-09-14
During failure of core protein quality control in the nematode C. elegans, a specialized anti-aggregation mechanism relying on pathogen response factors and lysosomal mediated degradation is triggered, promoting tissue-specific resilience to age-dependent protein aggregation and its proteotoxicity.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002284
Article Title: A safety mechanism enables tissue-specific resistance to protein aggregation during aging in C. ...
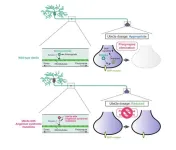
How a molecule deletes neural chat might help treat Angelman syndrome
2023-09-14
Researchers from the University of Tokyo reveal how the presynaptic Ube3a E3 ligase, a causal factor in Angelman syndrome, eliminates neural chat. The study helps find a better drug target for the Angelman syndrome treatment.
Neurons chat through electrical signals, transmitting information via connection sites between neurons—the synapses. After birth, the number of synapses increases. During childhood, the brain starts to mature and removes many unnecessary synapses. But sometimes, the development of the nervous system goes awry, leading to developmental disorders.
Kotaro ...
In songbirds, complex vocal learning predicts problem-solving abilities and brain size
2023-09-14
Vocal learning complexity, or the ability to imitate sounds, is associated with better problem-solving abilities and larger brains in songbird species, according to a new study. Whether vocal learning complexity was linked with such cognitive phenotypes was previously unknown. The approach used in the study, to study a lineage of birds, serves as a model for testing similar patterns in other vocal learning species. Complex vocal learning – the ability to imitate heard sounds – is a crucial component of human spoken language and has been assumed to be associated with more advanced cognitive abilities. Outside of humans, it has ...
Governance reforms could strengthen the Sustainable Development Goal implementation
2023-09-14
In a Policy Forum, Frank Biermann and colleagues outline demanding – yet realistic – policy reforms to strengthen the governance and implementation of the United Nations’ (UN) ambitious Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In 2015, the UN General Assembly agreed on 17 SDGs with 169 targets intended to be achieved by 2030. However, recent research has shown that the political impact of these goals has been limited and has not yet succeeded in reorienting political systems, institutions, or societies ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
Scientists identify key protein that stops malaria parasite growth
Wildfire smoke linked to rise in violent assaults, new 11-year study finds
New technology could use sunlight to break down ‘forever chemicals’
Green hydrogen without forever chemicals and iridium
Billion-DKK grant for research in green transformation of the built environment
For solar power to truly provide affordable energy access, we need to deploy it better
Middle-aged men are most vulnerable to faster aging due to ‘forever chemicals’
Starving cancer: Nutrient deprivation effects on synovial sarcoma
Speaking from the heart: Study identifies key concerns of parenting with an early-onset cardiovascular condition
From the Late Bronze Age to today - Old Irish Goat carries 3,000 years of Irish history
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
[Press-News.org] New evidence indicates patients recall death experiences after cardiac arrestResearchers report in Resuscitation that awareness and consciousness, including a lucid recalled experience of death, are identified and for the first time using brain monitors to identify markers of consciousness and mental activity