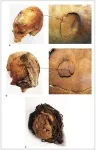
(Press-News.org) Interpersonal violence was a consistent part of life in ancient hunter-gatherer communities on the Atacama Desert coast of northern Chile, according to a study published September 20, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Vivien Standen of the University of Tarapacá, Chile and colleagues.
Archaeological research supports the notion that interpersonal violence and warfare have played an important role in the lives of hunter-gatherer groups over time, but many questions remain about the factors that influence such violence. The record of human populations in northern Chile extends across 10,000 years, providing a valuable opportunity to study patterns in violence over time.
In this study, Standen and colleagues examined signs of violent trauma on the remains of 288 adult individuals from funerary sites across the Atacama Desert coast, dating from 10,000 years ago to 1450 AD. The researchers also analyzed patterns in weaponry and in artistic depictions of combat during this time. They found that rates of violence were surprisingly static over time, though there was a notable increase in lethal violence during the Formative Period starting around 1000 BC, a trend also found in similar studies of the Andean region. Data from strontium isotopes indicate that this interpersonal violence was occurring between local groups, not between local and foreign populations.
These results indicate that violence was a consistent part of the lives of these ancient populations for many millennia. The absence of a centralized political system during this time might have been a factor leading to the consistency of violent tensions in the region. It’s also possible that violence was the result of competition for resources in the extreme environment of the desert, a factor which might have become exacerbated as farming became more prominent and widespread.
The authors add: “Despite all the technological advances, humanity has not learned to resolve its conflicts in a different way than our millenary ancestors, in peace and without war.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290690
Citation: Standen VG, Santoro CM, Valenzuela D, Arriaza B, Verano J, Monsalve S, et al. (2023) Violence in fishing, hunting, and gathering societies of the Atacama Desert coast: A long-term perspective (10,000 BP—AD 1450). PLoS ONE 18(9): e0290690. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0290690
Author Countries: Chile, USA
Funding: Grant: FONDECYT Nº1171708 “Violencia en la prehistoria del Norte de Chile: un estudio multidisciplinario.” The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Long-term history of violence in hunter-gatherer societies uncovered in the Atacama Desert
10,000 years of violent conflict revealed by skeletons, weaponry, and rock art
2023-09-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
US political donations are associated with policy issues prioritized in congressional speeches
2023-09-20
The first comprehensive analysis of the relationship between campaign donations and the issues legislators prioritize with congressional speech is published in the open access journal PLOS ONE this week. While prior research reaches mixed conclusions on associations between political donations in the US and voting patterns of legislators, this research suggests there are substantial associations between donations and policy priorities expressed in congressional speeches, and marks language use as an interesting and viable arena for looking at the impact political donors may have on congressional behavior.
Publicly traded corporations and labor unions in the US routinely raise funds ...
Job ads which use masculine rather than gender-inclusive language are perceived by women as sexist, leading them to feel ostracized, demotivated, and as though they don't belong at work
2023-09-20
Job ads which use masculine rather than gender-inclusive language are perceived by women as sexist, leading them to feel ostracized, demotivated, and as though they don't belong at work
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290709
Article Title: The impact of gender-exclusive language on women’s anticipated ostracism: A preregistered replication of Stout and Dasgupta (2011)
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Miami University Committee on Faculty Research, Heather M. Claypool Miami University College of Arts and Science, Heather M. Claypool. END ...
Only 1% of US kids who are obese in elementary school transition to a healthy weight within two years, although 1 in 4 overweight children progress to a healthy weight range
2023-09-20
Only 1% of US kids who are obese in elementary school transition to a healthy weight within two years, although 1 in 4 overweight children progress to a healthy weight range
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0290565
Article Title: Weight trajectories and obesity remission among school-aged children
Author Countries: USA
Funding: Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes And Digestive And Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of ...
Suppressing negative thoughts may be good for mental health after all, study suggests
2023-09-20
The commonly-held belief that attempting to suppress negative thoughts is bad for our mental health could be wrong, a new study from scientists at the University of Cambridge suggests.
Researchers at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Cognition and Brain Sciences Unit trained 120 volunteers worldwide to suppress thoughts about negative events that worried them, and found that not only did these become less vivid, but that the participants’ mental health also improved.
“We’re all familiar with the Freudian idea that if we suppress our feelings or thoughts, then these thoughts remain in our unconscious, influencing our behaviour and wellbeing ...
Ancient Amazonians intentionally created fertile “dark earth”
2023-09-20
The Amazon river basin is known for its immense and lush tropical forests, so one might assume that the Amazon’s land is equally rich. In fact, the soils underlying the forested vegetation, particularly in the hilly uplands, are surprisingly infertile. Much of the Amazon’s soil is acidic and low in nutrients, making it notoriously difficult to farm.
But over the years, archaeologists have dug up mysteriously black and fertile patches of ancient soils in hundreds of sites across the Amazon. This “dark earth” has been found in and around human settlements dating ...
MD Anderson expands breakthrough research campus with groundbreaking of innovative new facility
2023-09-20
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today broke ground on a 600,000-square-foot facility intended to anchor the institution’s expansive south campus research park. The building was purposefully built to enable collaborative science and impactful breakthrough discoveries that will accelerate efforts to end cancer.
A $668 million institutional investment will support the construction of MD Anderson’s South Campus Research Building 5 (SCRB5), a 7-story building designed by Elkus Manfredi Architects with state-of-the-art research facilities and inspiring public spaces to facilitate exceptional science. ...
Genetic biomarker may predict severity of food allergy
2023-09-20
Researchers from Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago and colleagues reported for the first time that a genetic biomarker may be able to help predict the severity of food allergy reactions. Currently there is no reliable or readily available clinical biomarker that accurately distinguishes patients with food allergies who are at risk for severe life-threatening reactions versus more mild symptoms. Findings were published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Dr. Lang and colleagues found that the presence of an enzyme isoform called α-tryptase, ...
Researchers reveal novel AI-based camera alert system to promote coexistence between tigers and humans
2023-09-20
For decades, wildlife biologists have dreamt of a “smart” camera alerting system capable of detecting tigers and other endangered species on the prowl. Legacy camera-trap technology, while valuable for many research applications, has historically been hindered by false positives and an inability to facilitate rapid responses.
Writing in BioScience, Jeremy Dertien of Clemson University and colleagues announce that for the first time ever, wild tigers and elephants have been detected by an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered, cryptic camera-alert system, TrailGuard AI, that transmits images to the ...
New Mars gravity analysis improves understanding of possible ancient ocean
2023-09-20
The first use of a novel method of analyzing Mars’ gravitational force supports the idea that the planet once had an extensive northern ocean.
In doing so, the method defines the scope of what scientists refer to as the northern Martian paleo-ocean in more detail.
The work was published in July in the journal Icarus, which is affiliated with the American Astronomical Society’s Division for Planetary Sciences.
The research was led by Jaroslav Klokočník, professor emeritus at the Astronomical Institute of the Czech Academy of Sciences. Gunther ...
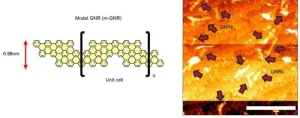
Making contact: Researchers wire up individual graphene nanoribbons
2023-09-20
Researchers have developed a method of “wiring up” graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), a class of one-dimensional materials that are of interest in the scaling of microelectronic devices. Using a direct-write scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) based process, the nanometer-scale metal contacts were fabricated on individual GNRs and could control the electronic character of the GNRs. The researchers say that this is the first demonstration of making metal contacts to specific GNRs with certainty and that those contacts induce device functionality needed for transistor function.
The results of this research, led by electrical and computer engineering (ECE) professor Joseph Lyding, along ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
In football players with repeated head impacts, inflammation related to brain changes
Being an early bird, getting more physical activity linked to lower risk of ALS
The Lancet: Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Single daily pill shows promise as replacement for complex, multi-tablet HIV treatment regimens
Black Americans face increasingly higher risk of gun homicide death than White Americans
Flagging claims about cancer treatment on social media as potentially false might help reduce spreading of misinformation, per online experiment with 1,051 US adults
Yawns in healthy fetuses might indicate mild distress
Conservation agriculture, including no-dig, crop-rotation and mulching methods, reduces water runoff and soil loss and boosts crop yield by as much as 122%, in Ethiopian trial
Tropical flowers are blooming weeks later than they used to through climate change
Risk of whale entanglement in fishing gear tied to size of cool-water habitat
Climate change could fragment habitat for monarch butterflies, disrupting mass migration
Neurosurgeons are really good at removing brain tumors, and they’re about to get even better
Almost 1-in-3 American adolescents has diabetes or prediabetes, with waist-to-height ratio the strongest independent predictor of prediabetes/diabetes, reveals survey of 1,998 adolescents (10-19 years
Researchers sharpen understanding of how the body responds to energy demands from exercise
New “lock-and-key” chemistry
Benzodiazepine use declines across the U.S., led by reductions in older adults
How recycled sewage could make the moon or Mars suitable for growing crops
Don’t Panic: ‘Humanity’s Last Exam’ has begun
A robust new telecom qubit in silicon
Vertebrate paleontology has a numbers problem. Computer vision can help
[Press-News.org] Long-term history of violence in hunter-gatherer societies uncovered in the Atacama Desert10,000 years of violent conflict revealed by skeletons, weaponry, and rock art