(Press-News.org) Key Takeaways
In a survey-based study of US adults, those living in communities in which most people seldom left home at certain times during the COVID-19 pandemic were more likely to report symptoms of depression
The link remained strong even after considering COVID-19 activity, weather, and county-level economics
Accounting for state-level pandemic restrictions only modestly attenuated the association
BOSTON – Higher levels of depressive symptoms have been reported during the COVID-19 pandemic compared with other times in history, and as much as three times higher than prior to the pandemic. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has found that social isolation may have been a contributing factor. Their findings are published in JAMA Network Open.
In surveys conducted between May 2020 and April 2022 that were completed by 192,271 adults living the all 50 US states and the District of Columbia, the average county-level proportion of individuals not leaving home on a daily basis was associated with a greater level of depressive symptoms.
“We integrated our data with another data set compiled by Facebook that looked at aspects of mobility on the basis of an app, including how often people in a particular area left home,” explains lead author Roy H. Perlis, MD, MSc, associate chief of research in the department of psychiatry and director of the Center for Quantitative Health at MGH. “We found that in communities and at times when fewer people left home, levels of depression in our survey were greater.”
This link held even after considering local COVID-19 activity, weather, and county-level economics. Certain pandemic restrictions—in particular, mandatory mask-wearing in public and policies cancelling public events—were modestly related to depressive symptom severity, but these associations were substantially smaller than the magnitude of the association with community mobility.
“In most of the analysis we used cross-sectional data—measurements at the same time of community mobility and depression. But when we looked at the relationship between mobility in a community and subsequent depression, we observed similar effects,” says Perlis.
The investigators note that finding ways to increase social engagement and limit social isolation during times of limited mobility may be important for mitigating the effects of future pandemics or other long-lasting disasters to potentially decrease some of their mental health impacts.
Co-authors include Kristin Lunz Trujillo, PhD, Alauna Safarpour, PhD, Alexi Quintana, BA, Matthew D. Simonson, PhD, Jasper Perlis, Mauricio Santillana, PhD, Katherine Ognyanova, PhD, Matthew A. Baum, PhD, James N. Druckman, PhD, and David Lazer, PhD.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation, the National Institute of Mental Health, Northeastern University, Harvard Kennedy School of Government, and Rutgers University.
About the Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The Mass General Research Institute conducts the largest hospital-based research program in the nation, with annual research operations of more than $1 billion and comprises more than 9,500 researchers working across more than 30 institutes, centers and departments. In July 2022, Mass General was named #8 in the U.S. News & World Report list of "America’s Best Hospitals." MGH is a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system.
END
Study reveals more depression in communities where people rarely left home during the COVID-19 pandemic
Results indicate a link between reduced mobility during the pandemic and greater risk for depressive symptoms
2023-09-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Intense lasers shine new light on the electron dynamics of liquids
2023-09-28
An international team of researchers from the Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter (MPSD) in Hamburg and ETH Zurich has now demonstrated that it is possible to probe electron dynamics in liquids using intense laser fields and to retrieve the electron mean free path – the average distance an electron can travel before colliding with another particle. They found that the mechanism by which liquids emit a particular light spectrum known as the high-harmonic spectrum is markedly different from the one in other phases of matter like gases and solids. The team’s findings open the door to a deeper understanding of ultrafast dynamics in liquids.
Using ...
Study helps explain how COVID-19 heightens risk of heart attack and stroke
2023-09-28
In some patients, infection with the pandemic virus SARS-CoV-2 can trigger a dangerous immune response in hardened fatty deposits (plaques) lining the heart’s largest blood vessels, a new study shows.
The findings are based on the body’s immune system, which evolved to destroy invading microbes but also drives disease when triggered in the wrong context. Doing so brings on a set of responses termed inflammation, including swelling, which results as immune cells and signaling proteins home in on infection sites. ...
People who use alternative medicine favor risk and novelty, and distrust science
2023-09-28
Over 40 per cent of Canadians have used at least one risk-associated alternative health-care treatment in the past 12 months, says a new UBC study published in PLOS One.
The researchers explored alternative health-care therapies where the proven benefits do not justify the risks involved. They found that people who access these therapies tend to be wealthier, like novelty and taking risks, and are also more likely to distrust conventional medicine.
The multidisciplinary study between UBC School of Nursing and the University of Alberta Health Law Institute involved a survey of 1,492 Canadians ages 16 and over ...
SARS-CoV-2 infects coronary arteries, increases plaque inflammation
2023-09-28
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can directly infect the arteries of the heart and cause the fatty plaque inside arteries to become highly inflamed, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health. The findings, published in the journal Nature Cardiovascular Research, may help explain why certain people who get COVID-19 have a greater chance of developing cardiovascular disease, or if they already have it, develop more heart-related complications.
In the study, researchers focused on older people with fatty buildup, known as atherosclerotic plaque, who ...
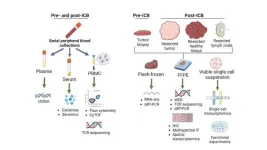
Immune checkpoint blockade prior to surgery promising in multiple cancer types
2023-09-28
Treating cancer with immunotherapies known as an immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) prior to surgery (so-called neoadjuvant immunotherapy) has been a rapidly growing area of research, but the scientific community is just scratching the surface of what is possible, according to a review article co-authored by several current and former investigators from the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy and the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center.
“We consider this approach to cancer immunotherapy to be a gold mine ...
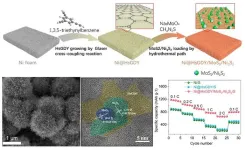
HsGDY on Ni foam for loading MoS2/Ni3S2 to enhance the performance on lithium-sulfur batteries
2023-09-28
They published their work on Sep. 26 in Energy Material Advances.
"The booming progress of electric vehicles demands next-generation energy storage technologies with high energy density, low cost, and longevity." said Lu, a professor at the college of chemistry and chemical engineering in Shantou university. "Lithium-sulfur batteries are identified as a promising energy storage system because of their high ultrahigh energy density and large theoretical capacity. However, they are limited by the poor electronic conductivity of sulfur, volume changes of the cathode, and shuttle effect."
Lu explained that the conversion of polysulfides (Li2Sn, ...
Brief dialysis may be best for some kidney patients
2023-09-28
Patients with acute kidney injury requiring outpatient dialysis after hospital discharge receive the same care as those with the more common end-stage kidney disease, according to a study led by UC San Francisco.
But while patients with the latter diagnosis – typically caused by long-standing hypertension or diabetes – must remain on lifelong dialysis or receive a new kidney, some patients on dialysis for acute kidney injury have the potential to recover, the researchers reported in their study in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology on Sept. 28, 2023.
“For ...
COOPERATE: Empowering minoritized patients with chronic back and other musculoskeletal pain to receive the care they need
2023-09-28
INDIANAPOLIS – A new study led by a U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Medicine researcher focuses on empowering minoritized patients with chronic back and other musculoskeletal pain to receive care best suited to their individual values and preferences. Black patients continue to experience greater pain severity, worse pain outcomes and inadequate pain treatment compared to White patients, despite national priorities focused on health equity.
COOPERATE (Communication and Activation in Pain to Enhance Relationships ...
Novel battery technology with negligible voltage decay developed at CityU, a world’s first
2023-09-28
A pivotal breakthrough in battery technology that has profound implications for our energy future has been achieved by a joint-research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU).
The new development overcomes the persistent challenge of voltage decay and can lead to significantly higher energy storage capacity.
Lithium-ion batteries (LiBs) are widely used in electronic devices, while lithium-(Li) and manganese-rich (LMR) layered oxides are a promising class of cathodes for LiBs due to their high ...
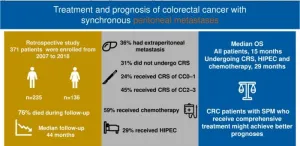
Comprehensive treatment strategy could change CRC with SPM
2023-09-28
Colorectal cancer (CRC) with synchronous peritoneal metastases (SPM) is a challenging disease to treat, with a relatively poor prognosis. However, recent advances in treatment strategies have led to improved outcomes for patients with SPM.
The optimal treatment approach for CRC with SPM remains controversial. A growing body of evidence suggests that comprehensive treatment, including cytoreductive surgery (CRS), chemotherapy, and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), may improve patient outcomes.
A ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Study reveals more depression in communities where people rarely left home during the COVID-19 pandemicResults indicate a link between reduced mobility during the pandemic and greater risk for depressive symptoms