How bacteria can organize themselves
A new model demonstrates that chasing interactions can induce dynamical patterns in the organization of bacterial species
2023-10-06
(Press-News.org)
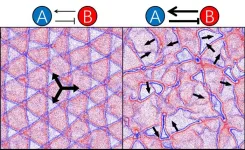
In a recent study, scientists from the department Living Matter Physics at MPI-DS developed a model describing communication pathways in bacterial populations. Bacteria show an overall organizational pattern by sensing the concentration of chemicals in their environment and adapting their motion.
The structure only becomes visible on a higher level
“We modeled the non-reciprocal interaction between two bacterial species”, first author Yu Duan explains. “This means that species A is chasing species B, whereas B is aiming to repel from A”, he continues. The researchers found, that just this chase-and-avoid interaction is sufficient to form a structural pattern. The type of the resulting pattern depends on the strength of the interaction. This complements a previous study, where a model was proposed that also included intraspecies interactions of the bacteria in order to form a pattern.
In this new model, which also includes the effect of bacterial motility, neither adhesion nor alignment are required to form complex super-structures encompassing millions of individuals. “Although the bacterial population dynamics show a global order, this is not the case on the individual bacterial level. In particular, a single bacterium seems to move in a disordered way, with the structure becoming visible only on a higher level, which is very fascinating”, summarizes Benoît Mahault, group leader in the department Living Matter Physics at MPI-DS.
A general model for collective behavior
The model also allows to consider more than two species, increasing the amount of possible interactions and emerging patterns. Notably, it is also not limited to bacteria but can be applied to a variety of collective behaviors. These include light-controlled microswimmers, social insects, animal groups and robotic swarms. The study therefore provides general insights on the mechanisms responsible for the formation of large-scale structures in networks with many components.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-06
The central question in the ongoing hunt for dark matter is: what is it made of? One possible answer is that dark matter consists of particles known as axions. A team of astrophysicists, led by researchers from the universities of Amsterdam and Princeton, has now shown that if dark matter consists of axions, it may reveal itself in the form of a subtle additional glow coming from pulsating stars.
Dark matter may be the most sought-for constituent of our universe. Surprisingly, this mysterious form of matter, ...
2023-10-06
A team of New York University computer scientists has created a neural network that can explain how it reaches its predictions. The work reveals what accounts for the functionality of neural networks—the engines that drive artificial intelligence and machine learning—thereby illuminating a process that has largely been concealed from users.
The breakthrough centers on a specific usage of neural networks that has become popular in recent years—tackling challenging biological questions. Among these are examinations of the intricacies of ...
2023-10-06
Astronomers have gotten very good at spotting the signs of planet formation around stars. But for a complete understanding of planet formation, we also need to study examples where planet formation has not yet started. Looking for something and not finding it can be even more difficult than finding it sometimes, but new detailed observations of the young star DG Taurus show that it has a smooth protoplanetary disk without signs of planet formation. This successful non-detection of planet formation may indicate ...
2023-10-06
Research sheds light on how genetics influences the growth of the placenta and reveals a link to increased risk of disease in the mother.
The placenta is an organ which grows in the womb alongside the foetus, which is attached to it by the umbilical cord. It is the only organ that contain tissue from both mother and child. The placenta provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing foetus and removes waste as the baby develops. A poorly functioning placenta is associated with pregnancy complications, and later risk of disease in the child.
Despite its key role, little is yet known ...
2023-10-06
Across Africa about two million premature deaths each year are caused by the effects of diabetes and hypertension.
In contrast, most people living with HIV are in regular care and virally suppressed, and HIV mortality rates have fallen five-fold since their peak of 2 million deaths annually in the early 2000s to less than 500,000 in 2022.
Dr Josephine Birungi, a co-author and Graduate Researcher-Public Health at La Trobe University, said that the similarities in chronic disease management of HIV and other chronic conditions should make integrated clinics beneficial.
“The only difference is the medicine they take. We’re seeing ...
2023-10-06
ROCKVILLE, Md.— Neary 240 scientific abstracts covering a variety of topics such as anti-obesity medications, body mass index and pediatric obesity will be featured at the 41st Annual Meeting of The Obesity Society’s (TOS) at ObesityWeek® 2023. This in-person event will take place Oct. 14–17, 2023 at the Kay Bailey Hutchison Convention Center in Dallas, Texas.
Innovative scientific research results will be presented in both oral and poster formats. These communications provide notable exposure and recognition for studies and authors, and represent cutting-edge research in obesity prevention and ...
2023-10-06
On October 2, 2023, BGI Genomics signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Colombian National Cancer Institute (INC or Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia). This collaboration, which aims to foster research and further develop cutting-edge solutions based on genetic sequencing for early diagnosis of cervical and colorectal cancer, reflects a shared dedication to enhancing health outcomes in the region.
The MoU was formally inked at INC facilities by Dr. Carolina Wiesner, INC Director, and Mr. Rainer Perez, alternate legal representative of BGI Genomics in Colombia. Mr. Marco Antonio Rincón, Latin America Business Director, BGI Genomics, notes: ...
2023-10-06
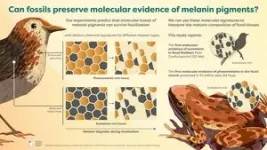
UCC palaeontologists discover molecular evidence of phaeomelanin, the pigment that produces ginger colouration.
“This will paint a more accurate picture of ancient animal colour.”
Phaeomelanin is now toxic to animals – discovery may be first step in understand its evolution.
Palaeontologists at University College Cork (UCC) have found the first molecular evidence of phaeomelanin, the pigment that produces ginger colouration, in the fossil record.
The new study reports ...
2023-10-06
A new study from Queen Mary University of London, published in The Lancet’s EClinicalMedicine, has found that people may experience long-term symptoms —or ‘long colds’—after acute respiratory infections that test negative for COVID-19.
Some of the most common symptoms of the ‘long cold’ included coughing, stomach pain, and diarrhea more than 4 weeks after the initial infection. While the severity of an illness appears to be a key driver of risk of long-term symptoms, ...
2023-10-06
Our five senses bombard us with environmental input 24/7. One way our brain makes sense of this abundance of information is by combining information from two or more senses, such as between smells and the smoothness of textures, pitch, color, and musical dimensions. This sensory integration also causes us to associate higher temperatures with warmer colors, lower sound pitches with less elevated positions, and colors with the flavor of particular foods – for example, the taste of oranges with the color of the same name.
Now, a study in Frontiers in Psychology has shown experimentally that such unconscious 'crossmodal' ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How bacteria can organize themselves
A new model demonstrates that chasing interactions can induce dynamical patterns in the organization of bacterial species