(Press-News.org) Scientists ran simulations on the UK’s national supercomputer to investigate ocean-driven melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet: how much is unavoidable and must be adapted to, and how much melting the international community still has control over through reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Taking into account climate variability like El Niño, they found no significant difference between mid-range emissions scenarios and the most ambitious targets of the 2015 Paris Agreement. Even under a best-case scenario of 1.5°C global temperature rise, melting will increase three times faster than during the 20th century.
The West Antarctic Ice Sheet is losing ice and is Antarctica’s largest contributor to sea-level rise. Previous modelling finds this loss could be driven by warming of the Southern Ocean, particularly the Amundsen Sea region. Collectively the West Antarctic Ice Sheet contains enough ice to raise global mean sea-level by up to five metres.
Around the world millions of people live near the coast and these communities will be greatly impacted by sea level rise. A better understanding of the future changes will allow policymakers to plan ahead and adapt more readily.
Lead author Dr Kaitlin Naughten, a researcher at the British Antarctic Survey says:
“It looks like we’ve lost control of melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. If we wanted to preserve it in its historical state, we would have needed action on climate change decades ago. The bright side is that by recognising this situation in advance, the world will have more time to adapt to the sea level rise that’s coming. If you need to abandon or substantially re-engineer a coastal region, having 50 years lead time is going to make all the difference.”
The team simulated four future scenarios of the 21st century, plus one historical scenario of the 20th century. The future scenarios either stabilised global temperature rise at the targets set out by the Paris Agreement, 1.5°C and 2°C, or followed standard scenarios for medium and high carbon emissions.
All scenarios resulted in significant and widespread future warming of the Amundsen Sea and increased melting of its ice-shelves. The three lower-range scenarios followed nearly identical pathways over the 21st century. Even under the best-case scenario, warming of the Amundsen Sea sped up by about a factor of three, and melting of the floating ice shelves which stabilise the inland glaciers followed, though it did begin to flatten by the end of the century.
The worst-case scenario had more ice shelf melting than the others, but only after 2045. The authors heed that this high fossil fuel scenario, where emissions increase rapidly, is considered unlikely to occur.
This study presents sobering future projections of Amundsen Sea ice-shelf melting but does not undermine the importance of mitigation in limiting the impacts of climate change.
Naughten cautions: “We must not stop working to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. What we do now will help to slow the rate of sea level rise in the long term. The slower the sea level changes, the easier it will be for governments and society to adapt to, even if it can’t be stopped.”
Unavoidable future increase in West Antarctic ice-shelf melting over the 21st century by Kaitlin Naughten (BAS), Paul Holland (BAS), Jan De Rydt (Northumbria) is published in the journal Nature Climate Change.
END
Increased West Antarctic Ice Sheet melting ‘unavoidable’
2023-10-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Novel cause of brain mosaicism and focal epilepsy identified
2023-10-23
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) – In most people, every cell in their body contains the same genetic information. However, sometimes people can have two or more genetically different sets of cells. This usually happens during fetal development and is known as mosaicism. Sometimes one of those groups of cells has genetic changes that can cause diseases or disorders.
Neurologists, neurosurgeons and genomics experts have been working together to test for mosaicism in brain tissues resected during epilepsy surgery. Research has shown that mosaicism in the brain is a significant contributor to epilepsy.
In a new study, recently published in Nature ...
Multitarget stool RNA test for colorectal cancer screening
2023-10-23
About The Study: In a clinical trial that included 8,920 participants, a noninvasive, multitarget stool RNA test (ColoSense) for colorectal cancer screening showed high sensitivity for colorectal neoplasia (colorectal cancer and advanced adenoma) with significant improvement in sensitivity relative to the fecal immunochemical test. Specificity for no lesions on colonoscopy was comparable to existing molecular diagnostic tests.
Authors: Erica K. Barnell, M.D., Ph.D., of the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is the corresponding author.
To access ...
Plants transformed into detectors of dangerous chemicals
2023-10-23
What if your house plant could tell you your water isn’t safe? Scientists are closer to realizing this vision, having successfully engineered a plant to turn beet red in the presence of a banned, toxic pesticide.
To achieve this, UC Riverside researchers had to solve an engineering puzzle: how to enable a plant to sense and react to a chemical in the environment without damaging its ability to function normally in all other respects.
“The biggest piece here is we’ve created an environmental sensor without modifying ...
How long should kids isolate after they’ve contracted COVID-19?
2023-10-23
School policies that require students with COVID-19 to stay out of the classroom for five days are more than sufficient. That’s because children infected with the Omicron variant remained infectious for a median time of three days after testing positive for the virus, according to a study by the USC Schaeffer Center for Health Policy & Economics and Stanford University.
“We're basically saying five days is more than sufficient; public-health and education leaders may consider shorter durations,” said co-author Neeraj ...
Homeless people are 16 times more likely to die suddenly
2023-10-23
A study led by UC San Francisco has found that people who are experiencing homelessness have a 16-fold higher rate of sudden death from heart attacks, as well as other causes.
The study focused on San Francisco County, which has one of the nation’s highest concentrations of homeless people. It found that the rate of sudden cardiac death was 7 times higher than the general population.
Some of these deaths may have been prevented with defibrillators and other public policy measures to improve health in this vulnerable population, according to the authors.
The paper published ...
New study shows surprising effects of fire in North America’s boreal forests
2023-10-23
A new study, using a first-of-its-kind approach to analyze satellite imagery from boreal forests over the last three decades, found that fire may be changing the face of the region in a way researchers did not previously anticipate.
Historically, fires in North American boreal forests have led to coniferous trees being supplanted by deciduous trees, which are faster growing, take up more carbon and reflect more light, leading to cooling of the climate and decreased likelihood of fire.
The study, led by Northern Arizona University and published today in Nature Climate Change, found that, surprisingly, while forests do become more deciduous, ...
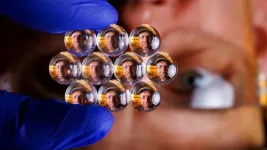
Chemists, engineers craft adjustable arrays of microscopic lenses
2023-10-23
They number in the thousands, light striking the phalanx of lenses arrayed on a face in geometric pattern, the beams refracting through transparent mounds no wider than a hair.
A fly’s eye boasts roughly 4,000 microscopic lenses, a honeybee’s up to twice that many. These lenses, though, belong not to a compound eye but to polydimethylsiloxane — a flexible polymer long ranking as a favored playground of Nebraska’s Stephen Morin and his band of fellow chemists.
With the aid of engineers Ruiguo Yang and Grayson Minnick, Morin’s team can now arrange and ...
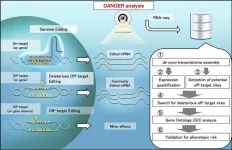
Researchers develop DANGER analysis tool for the safer design of gene editing
2023-10-23
A team of researchers has developed a software tool called DANGER (Deleterious and ANticipatable Guides Evaluated by RNA-sequencing) analysis that provides a way for the safer design of genome editing in all organisms with a transcriptome. For about a decade, researchers have used the CRISPR technology for genome editing. However, there are some challenges in the use of CRISPR. The DANGER analysis overcomes these challenges and allows researchers to perform safer on- and off-target assessments without a reference genome. It holds the potential for applications in medicine, agriculture, and biological research.
Their ...
Lung cancer outcomes significantly improved with immunotherapy-based treatment given before and after surgery
2023-10-23
HOUSTON ― A regimen of pre-surgical immunotherapy and chemotherapy followed by post-surgical immunotherapy significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) and pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared to chemotherapy alone for patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to results of a Phase III trial reported by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, were first presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
The AEGEAN trial evaluated durvalumab given perioperatively, meaning therapy ...
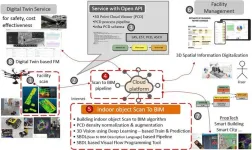
KICT develops scan to BIM for reverse engineering from 3D vision data
2023-10-23
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-suk) has developed building scan to BIM (Building Information Modeling)-based reverse engineering technology required for 3D geospatial information modeling domains such as digital twin information modeling.
Scan to BIM-based reverse engineering technology was studied to prevent errors and rework caused by manual work when modeling shapes or BIM from 3D scan data. Existing reverse engineering work is either done based on a lot of manual work or semi-automatically using expensive overseas software.
KICT Research Fellow Dr. Kang Tae-wook ...