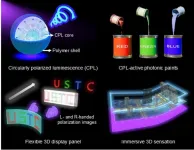
Printable circularly polarized luminescence materials enables flexible, stereoscopic displaying
2023-10-25
(Press-News.org)
Flexible three-dimensional (3D) displays drive innovation in the next-generation display technology, as they allow for the creation of versatile and adaptable displays that can be easily manipulated and customized to fit various viewing scenarios.
Printing circularly polarized luminescence (CPL, generated by the intrinsic chirality of luminescent materials) materials on moving, deformable and free-form surfaces serves to fabricate large-scale and high-performance integral imaging 3D displays: CPL provides a helping hand using its unusual optical rotation characteristics to achieve considerable contrast ratio and wide viewing angle.
Scientists led by Professor Taotao Zhuang and Professor Shu-Hong Yu at the University of Science and Technology of China have made progress in the field of processable circularly polarized luminescence materials, enabling flexible 3D imaging. The research, entitled “Processable circularly polarized luminescence material enables flexible stereoscopic 3D imaging”, published in the journal Science Advances on October 25th (Sci. Adv. 2023, 10.1126/sciadv.adi9944), opens up new possibilities for novel CPL-active materials in advances of both performance and processability with related applications.
The authors reported a category of CPL-active photonic paints (CPL-PPs) based on chiral liquid crystals, which realized the large-scale production of printable CPL-active materials. These paints exhibited intense CPL emission, providing the desired performance for practice.
Moreover, it was able to directly write customized graphics on a range of substrates such as polypropylene, cotton fabric, and polyester fabric using CPL-PPs, and exhibited meter-long luminous coatings with strong circularly polarized characteristics.
By printing CPL-PPs as pixel arrays on flexible substrates, the researchers created flexible 3D display panels featuring two sets of full-color pixel arrays based on orthogonal CPL emission. This approach enables the creation of immersive 3D images via presenting distinct images with orthogonal circular polarization states to the left and right eyes.
The researchers further envisioned the integration of these flexible 3D display panels into wearable devices, such as smartwatches. This advancement is expected to have a profound impact on various applications, including virtual reality, medical imaging, scientific visualization, and more.
Experts in the field appreciated that this progress has the potential to reshape multiple industries and transform how humans perceive and interact with visual information. The advent of printable CPL-active materials will significantly broaden the applications of CPL-optic-achievable materials in various fields, including information security, spintronics, quantum computing, biological detection, etc.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-10-25
Zika virus infection in pregnant rhesus macaques slows fetal growth and affects how infants and mothers interact in the first month of life, according to a new study from researchers at the California National Primate Research Center at the University of California, Davis. The work, published Oct. 25 in Science Translational Medicine, has implications for both humans exposed to Zika virus and for other viruses that can cross the placenta, including SARS-CoV2, responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Initially I thought this was a story about Zika, but as I looked at the results I think this is also a story about ...
2023-10-25
Scientists have long known that chloroplasts help plants turn the sun’s energy into food, but a new study, led by plant biologists at the University of California, Davis, shows that they are also essential for plant immunity to viral and bacterial pathogens.
Chloroplasts are generally spherical, but a small percentage of them change their shape and send out tube-like projections called “stromules.” First observed over a century ago, the biological function of stromules has remained ...
2023-10-25
For four years, NASA’s InSight lander recorded tremors on Mars with its seismometer. Researchers at ETH Zurich collected and analysed the data transmitted to Earth to determine the planet’s internal structure. “Although the mission ended in December 2022, we’ve now discovered something very interesting,” says Amir Khan, a Senior Scientist in the Department of Earth Sciences at ETH Zurich.
An analysis of recorded marsquakes, combined with computer simulations, paint ...
2023-10-25
LAWRENCE — For the past 50 years, standardized tests have been the norm in American schools, a method proponents say determines which schools are not performing and helps hold educators accountable. Yet for the past 20 years, it has become clear that testing has failed to improve education or hold many accountable, according to a University of Kansas researcher whose new book details its history.
“An Age of Accountability: How Standardized Testing Came to Dominate American Schools and Compromise Education” by John Rury, professor emeritus of educational leadership & policy studies at KU, tells the story of how testing became ...
2023-10-25
October 25, 2023
On the Trail of the Silver King: Researchers at UMass Amherst Reveal Unprecedented Look at Tarpon Migration
Culmination of more than five-years’ research, $1.1 million in grants and collaborations with anglers, industry and Bonefish & Tarpon Trust promises to reshape conservation efforts
AMHERST, Mass. – New research led by the University of Massachusetts and published recently in Marine Biology unveils a first-of-its-kind dataset, gathered over five years, that gives the finest-grained ...
2023-10-25
During the summer of 2022, the Indus River in Pakistan overflowed its banks and swept through the homes of between 30-40 million people. Eight million were permanently displaced, and at least 1,700 people died. Damages to crops, infrastructure, industry, and livelihoods were estimated at $30 billion. In response to this, Stanford researchers from the Natural Capital Project (NatCap) and the Carnegie Institution for Science collaborated on a new way to quickly calculate the approximate depths of ...
2023-10-25
Rutgers researchers have used neuroimaging to demonstrate that cocaine addiction alters the brain’s system for evaluating how rewarding various outcomes associated with our decisions will feel. This dampens an error signal that guides learning and adaptive behavior.
The observed changes likely propagate a mysterious aspect of some addictive behavior—the tendency to keep doing harmful things that sometimes have no immediate benefit. Those changes also make it harder for long-term users of cocaine to correctly estimate how much benefit they’ll derive from other available actions.
Experts have long hypothesized that cocaine and other addictive ...
2023-10-25
A new study by UC Davis Health endocrinology researchers has shown a high prevalence of thyroid cancer among transgender female veterans. It’s the first evidence of such a disparity in the transgender female population in the United States.
The researchers presented their findings this month at the American Thyroid Association Annual Meeting.
The study was prompted by what the doctors noticed while caring for patients.
“As a group of physicians, we observed anecdotally through clinical observation that among 50 transgender women in our clinic, two were diagnosed with thyroid ...
2023-10-25
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
In a mouse study designed to explore the impact of marijuana’s major psychoactive compound, THC, on teenage brains, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they found changes to the structure of microglia, which are specialized brain immune cells, that may worsen a genetic predisposition to schizophrenia. The findings, published Oct. 25 in Nature Communications, add to growing evidence of risk to brain development in adolescents who smoke or eat marijuana products.
“Recreational ...
2023-10-25
A team of scientists has used multiple space and ground-based telescopes, including NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, and NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, to observe an exceptionally bright gamma-ray burst, GRB 230307A, and identify the neutron star merger that generated an explosion that created the burst. Webb also helped scientists detect the chemical element tellurium in the explosion’s aftermath.
Other elements near tellurium on the periodic table – like iodine, which is needed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Printable circularly polarized luminescence materials enables flexible, stereoscopic displaying