(Press-News.org) EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, OCTOBER 25, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have experienced traumatic events in childhood such as abuse, neglect or household dysfunction may be more likely to experience headache disorders as adults, according to a meta-analysis published in the October 25, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. This research does not prove that such experiences cause headaches; it only shows an association.
“Traumatic events in childhood can have serious health implications later in life,” said study author Catherine Kreatsoulas, PhD, of Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts. “Our meta-analysis confirms that childhood traumatic events are important risk factors for headache disorders in adulthood, including migraine, tension headaches, cluster headaches, and chronic or severe headaches. This is a risk factor that we cannot ignore.”
The meta-analysis involved 28 studies, including 154,739 participants across 19 countries.
Of the total participants, 48,625 people, or 31%, reported at least one traumatic childhood event, and 24,956 people, or 16%, were diagnosed with primary headaches. Among participants with at least one traumatic childhood event, 26% were diagnosed with a primary headache disorder, compared to 12% of participants that had no traumatic childhood events.
Researchers found that people who had experienced one or more traumatic childhood events were 48% more likely to have headache disorders than those who had not experienced such traumatic events.
They also found that as the number of traumatic childhood events increased, the odds of having headaches also increased. When compared to people who have not experienced childhood trauma, people who had experienced one type of traumatic event had a 24% increased risk of a headache disorder, while people who had experienced four or more types of traumatic events were more than twice as likely to have a headache disorder.
Researchers also looked at the association between types of traumatic childhood events. Events categorized as threat traumas included physical abuse, sexual abuse, emotional abuse, witnessing and/or threat of violence, or serious family conflicts. Events categorized as deprivation traumas included neglect, economic adversities, having an incarcerated household member, divorce or separation, parental death, and living in a household with mental illness, chronic disability or disease, or alcohol or substance abuse.
They found that threat traumas were linked to a 46% increase in headaches and deprivation traumas were linked to a 35% increase in headaches. Among the top types of threat traumas, experiencing physical and sexual abuse was linked to a 60% increased risk for headaches; among deprivation traumas, those who experienced neglect in childhood had an almost three-fold increased risk for headache disorders.
“This meta-analysis highlights that childhood traumatic events categorized as threat or deprivation traumas are important and independent risk factors for headache disorders in adulthood,” said Kreatsoulas. “Identifying the specific types of childhood experiences may help guide prevention and treatment strategies for one of the leading disabling disorders worldwide. A comprehensive public health plan and clinical intervention strategies are needed to address these underlying traumatic childhood events.”
“It is important to note that the true estimate of the association is likely higher due to the sensitive nature of reporting childhood traumatic events,” Kreatsoulas added.
Learn more about headaches at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
Childhood trauma linked to headaches in adulthood
New study finds one or more traumatic childhood experiences linked to headaches
2023-10-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brittle star fossils found in South Africa are over 410 million years old, the oldest known examples who lived at high latitude
2023-10-25
Brittle star fossils found in South Africa are over 410 million years old, the oldest known examples who lived at high latitude
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0292636
Article Title: Earliest known ophiuroids from high palaeolatitude, southern Gondwana, recovered from the Pragian to earliest Emsian Baviaanskloof Formation (Table Mountain Group, Cape Supergroup) South Africa
Author Countries: South Africa, Luxembourg
Funding: RWG: Millennium Trust, South Africa (no number). https://www.mtrust.co.za ...
New distractibility “d factor” may be linked with ADHD
2023-10-25
In a study of different types of distraction involving more than 1,000 participants, researchers statistically derived a novel measure—dubbed the “d factor”—that could represent a person’s general tendency towards distraction and may be linked with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Han Zhang of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on October 25, 2023.
Prior research has explored various types of distraction, such as external stimulations, repetitive ...
Deepfake videos during Russian invasion of Ukraine could undermine trust
2023-10-25
A new study explores themes in Twitter discussions of deepfake videos related to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, highlighting the potential for real videos to be mistaken for deepfakes and for deepfakes to fuel conspiracy theories. John Twomey of University College Cork, Ireland, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on October 25, 2023.
Created using artificial intelligence, deepfake videos typically feature a person saying and doing things they never actually did in real life. Deepfake technology has advanced considerably, sparking concerns about its potential harms. ...
In Prehispanic Cancun, immigrants were treated just like Maya locals
2023-10-25
Ancient people immigrated to Cancun Island and were treated just like locals, according to a study published October 25, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Andrea Cucina of the Autonomous University of Yucatan, Mexico and colleagues.
The Late Postclassic (AD 1200-1500) in the northern Maya lowlands was a period of major changes, including the development of many settlements along the east coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, influenced in part by expanded trade routes. Previous research has found that these settlements were home to many non-local individuals, but it remains unclear whether these people were treated as “foreigners” ...
Climate change likely impacted human populations in the Neolithic and Bronze Age
2023-10-25
Human populations in Neolithic Europe fluctuated with changing climates, according to a study published October 25, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ralph Großmann of Kiel University, Germany and colleagues.
The archaeological record is a valuable resource for exploring the relationship between humans and the environment, particularly how each is affected by the other. In this study, researchers examined Central European regions rich in archaeological remains and geologic sources of climate data, using these resources to identify correlations between human population trends and climate change.
The ...
First ever study of wartime deepfakes reveals their impact on news media
2023-10-25
A first ever study of wartime deepfake videos reveals their impact on news media and outlines implications for social media companies, media organisations and governments.
Deepfakes are artificially manipulated audio-visual material. Most deepfake videos involve the production of a fake ‘face’ constructed by Artificial Intelligence, that is merged with an authentic video, in order to create a video of an event that never really took place. Although fake, they can look convincing and are often produced to imitate or mimic an individual.
Researchers at University ...
Anti-anxiety drug may improve brain cancer survival chances
2023-10-25
A new research study shows that cerebrospinal fluid reduces current treatment efficacy in brain cancer and identifies new therapeutic opportunities.
Cerebrospinal fluid, the clear colourless liquid that protects the brain, also may be a factor that makes brain cancers resistant to treatment, Australian researchers led by Associate Professor Cedric Bardy at the South Austraila Health and Medical Research Institute (SAHMRI) and Flinders University reveal in the journal Science Advances.
Reporting how this occurs, the study in high-profile journal Science Advances shows that a decades-old anti-anxiety drug can improve the effectiveness of chemo-radiotherapy ...
Something in the eyes: Java Sparrows in love show enhanced eye rings
2023-10-25
Pair-bonded Java sparrows show enlarged eye rings to signal breeding readiness.
Birds are known for their elaborate courtship rituals and romantic gestures that are replete with beautiful songs, complex dances, gift-giving practices, preening, and flamboyant plumage. While changes in colorful external attributes during this period has attracted much attention, the role of facial features remains an under-investigated aspect of this behavior.
Associate Professor Masayo Soma and her research group at the Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University, reported increased swelling in Java sparrows’ eye rings—an area of blushed bare skin around the eyes—upon ...
New atrial fibrillation diagnosis may increase risk of memory decline
2023-10-25
Atrial fibrillation (AF) diagnosis was associated with a 45% increased risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among a cohort of 4.3 million individuals in the UK, according to a new study published in JACC: Advances. These findings suggest that cardiovascular risk factors and multiple comorbidities could further the progression from MCI to dementia in this cohort.
MCI is an early stage of cognitive function decline. In some cases it can be reversed, but it can indicate development of early dementia-associated disease. There has not been sufficient research on the development of MCI in AF patients and the subsequent development of dementia, so the authors of this study sought to ...
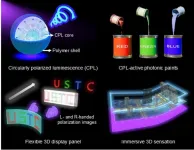
Printable circularly polarized luminescence materials enables flexible, stereoscopic displaying
2023-10-25
Flexible three-dimensional (3D) displays drive innovation in the next-generation display technology, as they allow for the creation of versatile and adaptable displays that can be easily manipulated and customized to fit various viewing scenarios.
Printing circularly polarized luminescence (CPL, generated by the intrinsic chirality of luminescent materials) materials on moving, deformable and free-form surfaces serves to fabricate large-scale and high-performance integral imaging 3D displays: CPL provides a helping hand using its unusual optical rotation characteristics to achieve considerable contrast ratio and wide viewing angle.
Scientists led by Professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
[Press-News.org] Childhood trauma linked to headaches in adulthoodNew study finds one or more traumatic childhood experiences linked to headaches