(Press-News.org) A new research study shows that cerebrospinal fluid reduces current treatment efficacy in brain cancer and identifies new therapeutic opportunities.
Cerebrospinal fluid, the clear colourless liquid that protects the brain, also may be a factor that makes brain cancers resistant to treatment, Australian researchers led by Associate Professor Cedric Bardy at the South Austraila Health and Medical Research Institute (SAHMRI) and Flinders University reveal in the journal Science Advances.
Reporting how this occurs, the study in high-profile journal Science Advances shows that a decades-old anti-anxiety drug can improve the effectiveness of chemo-radiotherapy towards glioblastoma, or GBM, the most common and lethal brain cancer.
Brain cancers kill more children and adults under 40 than any other cancer. They are resistant to therapies that kill cancers elsewhere in the body. The study team speculates that unique brain features might contribute to this.
The collaborative Australian team of neurobiologists, neurosurgeons and oncologists tested the effect of the precious resource of human cerebrospinal fluid on the growth of tumour cells collected from 25 local patients with glioblastoma.
Among their findings, the tumour cells quickly changed their identity and became more resistant to radiation and the drug temozolomide, which are mainstays of glioblastoma therapy.
Associate Professor Cedric Bardy says, “Glioblastoma kills so many people who are otherwise fit, healthy and young, within months. This is a horrible disease, and the treatments available are just not effective enough despite serious side effects.
“This study helps us understand the limitations of the current chemotherapies and provides new hope for repurposing a class of drugs that could be added to the standard of care. We are working hard now to try this on patients in a clinical trial.”
Investigating the molecular basis for these changes, the team found glioblastoma cells exposed to cerebrospinal fluid were more resistant to ferroptosis, a form of therapy-induced cell death.
Importantly, they showed that trifluoperazine, an anti-anxiety drug used since the 1950s, could re-sensitise glioblastoma cells to both therapies. In contrast, trifluoperazine was found not to harm healthy brain cells. The researchers concluded that combining trifluoperazine with standard care may improve GBM patient survival.
The paper – ‘Human cerebrospinal fluid affects chemoradiotherapy sensitivities in tumor cells from patients with glioblastoma’ (2023) BW Str27inger, MI De Silva, Z Greenberg, AN Puerta, R Adams, B Milky, M Zabolocki, M van den Hurk, LM Ebert, CF Bishop, SJ Conn, G Kichenadasse, MZ Michael, RJ Ormsby, S Poonoose and C Bardy – is published in Science Advances journal. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adf1332
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adf1332
END
Anti-anxiety drug may improve brain cancer survival chances
2023-10-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Something in the eyes: Java Sparrows in love show enhanced eye rings
2023-10-25
Pair-bonded Java sparrows show enlarged eye rings to signal breeding readiness.
Birds are known for their elaborate courtship rituals and romantic gestures that are replete with beautiful songs, complex dances, gift-giving practices, preening, and flamboyant plumage. While changes in colorful external attributes during this period has attracted much attention, the role of facial features remains an under-investigated aspect of this behavior.
Associate Professor Masayo Soma and her research group at the Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University, reported increased swelling in Java sparrows’ eye rings—an area of blushed bare skin around the eyes—upon ...
New atrial fibrillation diagnosis may increase risk of memory decline
2023-10-25
Atrial fibrillation (AF) diagnosis was associated with a 45% increased risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among a cohort of 4.3 million individuals in the UK, according to a new study published in JACC: Advances. These findings suggest that cardiovascular risk factors and multiple comorbidities could further the progression from MCI to dementia in this cohort.
MCI is an early stage of cognitive function decline. In some cases it can be reversed, but it can indicate development of early dementia-associated disease. There has not been sufficient research on the development of MCI in AF patients and the subsequent development of dementia, so the authors of this study sought to ...
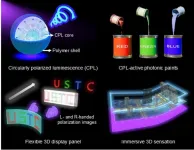
Printable circularly polarized luminescence materials enables flexible, stereoscopic displaying
2023-10-25
Flexible three-dimensional (3D) displays drive innovation in the next-generation display technology, as they allow for the creation of versatile and adaptable displays that can be easily manipulated and customized to fit various viewing scenarios.
Printing circularly polarized luminescence (CPL, generated by the intrinsic chirality of luminescent materials) materials on moving, deformable and free-form surfaces serves to fabricate large-scale and high-performance integral imaging 3D displays: CPL provides a helping hand using its unusual optical rotation characteristics to achieve considerable contrast ratio and wide viewing angle.
Scientists led by Professor ...
Zika infection in pregnant macaques slows fetal growth
2023-10-25
Zika virus infection in pregnant rhesus macaques slows fetal growth and affects how infants and mothers interact in the first month of life, according to a new study from researchers at the California National Primate Research Center at the University of California, Davis. The work, published Oct. 25 in Science Translational Medicine, has implications for both humans exposed to Zika virus and for other viruses that can cross the placenta, including SARS-CoV2, responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Initially I thought this was a story about Zika, but as I looked at the results I think this is also a story about ...
Chloroplasts do more than photosynthesis: They’re also a key player in plant immunity
2023-10-25
Scientists have long known that chloroplasts help plants turn the sun’s energy into food, but a new study, led by plant biologists at the University of California, Davis, shows that they are also essential for plant immunity to viral and bacterial pathogens.
Chloroplasts are generally spherical, but a small percentage of them change their shape and send out tube-like projections called “stromules.” First observed over a century ago, the biological function of stromules has remained ...
Mystery of the Martian core solved
2023-10-25
For four years, NASA’s InSight lander recorded tremors on Mars with its seismometer. Researchers at ETH Zurich collected and analysed the data transmitted to Earth to determine the planet’s internal structure. “Although the mission ended in December 2022, we’ve now discovered something very interesting,” says Amir Khan, a Senior Scientist in the Department of Earth Sciences at ETH Zurich.
An analysis of recorded marsquakes, combined with computer simulations, paint ...
Book examines history of standardized tests in American schools, why they persist
2023-10-25
LAWRENCE — For the past 50 years, standardized tests have been the norm in American schools, a method proponents say determines which schools are not performing and helps hold educators accountable. Yet for the past 20 years, it has become clear that testing has failed to improve education or hold many accountable, according to a University of Kansas researcher whose new book details its history.
“An Age of Accountability: How Standardized Testing Came to Dominate American Schools and Compromise Education” by John Rury, professor emeritus of educational leadership & policy studies at KU, tells the story of how testing became ...
On the trail of the silver king: Researchers at UMass Amherst reveal unprecedented look at tarpon migration
2023-10-25
October 25, 2023
On the Trail of the Silver King: Researchers at UMass Amherst Reveal Unprecedented Look at Tarpon Migration
Culmination of more than five-years’ research, $1.1 million in grants and collaborations with anglers, industry and Bonefish & Tarpon Trust promises to reshape conservation efforts
AMHERST, Mass. – New research led by the University of Massachusetts and published recently in Marine Biology unveils a first-of-its-kind dataset, gathered over five years, that gives the finest-grained ...
Stanford collaboration offers new method to analyze implications of large-scale flood adaptation
2023-10-25
During the summer of 2022, the Indus River in Pakistan overflowed its banks and swept through the homes of between 30-40 million people. Eight million were permanently displaced, and at least 1,700 people died. Damages to crops, infrastructure, industry, and livelihoods were estimated at $30 billion. In response to this, Stanford researchers from the Natural Capital Project (NatCap) and the Carnegie Institution for Science collaborated on a new way to quickly calculate the approximate depths of ...
Amid cocaine addiction, the brain struggles to evaluate which behaviors will be rewarding
2023-10-25
Rutgers researchers have used neuroimaging to demonstrate that cocaine addiction alters the brain’s system for evaluating how rewarding various outcomes associated with our decisions will feel. This dampens an error signal that guides learning and adaptive behavior.
The observed changes likely propagate a mysterious aspect of some addictive behavior—the tendency to keep doing harmful things that sometimes have no immediate benefit. Those changes also make it harder for long-term users of cocaine to correctly estimate how much benefit they’ll derive from other available actions.
Experts have long hypothesized that cocaine and other addictive ...