(Press-News.org) Ancient people immigrated to Cancun Island and were treated just like locals, according to a study published October 25, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Andrea Cucina of the Autonomous University of Yucatan, Mexico and colleagues.
The Late Postclassic (AD 1200-1500) in the northern Maya lowlands was a period of major changes, including the development of many settlements along the east coast of the Yucatan Peninsula, influenced in part by expanded trade routes. Previous research has found that these settlements were home to many non-local individuals, but it remains unclear whether these people were treated as “foreigners” or if they were integrated into local society.
In this study, Cucina and colleagues analyzed the remains of 50 individuals from two archaeological sites on Cancun Island dating to the Late Postclassic. Investigating strontium isotope signatures in teeth, the team determined that seven of these individuals appear to have been born elsewhere in the Maya lowlands, not local to these sites. However, examination of carbon isotopes (as a proxy for diet) and the construction of the graves of these individuals found no significant difference between locals and non-locals, suggesting that they were all treated similarly in terms of the food they ate and how they were buried.
These results suggest that these non-local individuals had integrated into local culture despite being from other regions. The fact that the non-local people included adults and children suggests that whole families, not just individuals, were in the habit of moving residence. One notable limitation of this study is that these techniques cannot detect “second generation immigrants”, a potentially valuable source of information that will have to be investigated using different methods. Analyzing patterns of mobility in Prehispanic Mesoamerica is essential for a thorough understanding of cultural networks of the time.
The authors add: “In the Postclassic period (AD 1200-1520) the east coast of Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula saw the arrival of foreign people, who were assumed, based on archaeological and architectural records, to come from several locations in central Mexico. However, the current research shows migration from within the Maya cultural region (from what is now Belize, Peten, Guatemala and other parts of the Yucatan Peninsula). Migration for economic, environmental, political or kinship considerations is a familiar part of the human experience, and the current study documents the past movement and integration of individuals, and possibly entire families, into new communities. People may have relocated for similar reasons as they do today—for economic, environmental, political or kinship considerations.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0292022
Citation: Cucina A, Thornton EK, Ortega-Muñoz A (2023) Human mobility on Cancun Island during the Late Postclassic: Intra- and inter-site demographic interactions. PLoS ONE 18(10): e0292022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0292022
Author Countries: México, USA
Funding: This study was granted by the project presented by AC, named: Movilidad demográfica en Meso- y Centroamérica en época prehispánica: análisis isotópico y de morfología dental, with the grant number CB-2017-2018-A1-S-10037 from the National Council of Science and Technology of Mexico (Conacyt, in Spanish, https://conacyt.mx/). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
In Prehispanic Cancun, immigrants were treated just like Maya locals
Families moved residence across Mesoamerica and integrated into new societies
2023-10-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Climate change likely impacted human populations in the Neolithic and Bronze Age
2023-10-25
Human populations in Neolithic Europe fluctuated with changing climates, according to a study published October 25, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ralph Großmann of Kiel University, Germany and colleagues.
The archaeological record is a valuable resource for exploring the relationship between humans and the environment, particularly how each is affected by the other. In this study, researchers examined Central European regions rich in archaeological remains and geologic sources of climate data, using these resources to identify correlations between human population trends and climate change.
The ...
First ever study of wartime deepfakes reveals their impact on news media
2023-10-25
A first ever study of wartime deepfake videos reveals their impact on news media and outlines implications for social media companies, media organisations and governments.
Deepfakes are artificially manipulated audio-visual material. Most deepfake videos involve the production of a fake ‘face’ constructed by Artificial Intelligence, that is merged with an authentic video, in order to create a video of an event that never really took place. Although fake, they can look convincing and are often produced to imitate or mimic an individual.
Researchers at University ...
Anti-anxiety drug may improve brain cancer survival chances
2023-10-25
A new research study shows that cerebrospinal fluid reduces current treatment efficacy in brain cancer and identifies new therapeutic opportunities.
Cerebrospinal fluid, the clear colourless liquid that protects the brain, also may be a factor that makes brain cancers resistant to treatment, Australian researchers led by Associate Professor Cedric Bardy at the South Austraila Health and Medical Research Institute (SAHMRI) and Flinders University reveal in the journal Science Advances.
Reporting how this occurs, the study in high-profile journal Science Advances shows that a decades-old anti-anxiety drug can improve the effectiveness of chemo-radiotherapy ...
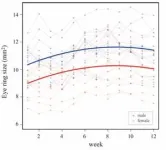
Something in the eyes: Java Sparrows in love show enhanced eye rings
2023-10-25
Pair-bonded Java sparrows show enlarged eye rings to signal breeding readiness.
Birds are known for their elaborate courtship rituals and romantic gestures that are replete with beautiful songs, complex dances, gift-giving practices, preening, and flamboyant plumage. While changes in colorful external attributes during this period has attracted much attention, the role of facial features remains an under-investigated aspect of this behavior.
Associate Professor Masayo Soma and her research group at the Graduate School of Science, Hokkaido University, reported increased swelling in Java sparrows’ eye rings—an area of blushed bare skin around the eyes—upon ...
New atrial fibrillation diagnosis may increase risk of memory decline
2023-10-25
Atrial fibrillation (AF) diagnosis was associated with a 45% increased risk of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) among a cohort of 4.3 million individuals in the UK, according to a new study published in JACC: Advances. These findings suggest that cardiovascular risk factors and multiple comorbidities could further the progression from MCI to dementia in this cohort.
MCI is an early stage of cognitive function decline. In some cases it can be reversed, but it can indicate development of early dementia-associated disease. There has not been sufficient research on the development of MCI in AF patients and the subsequent development of dementia, so the authors of this study sought to ...
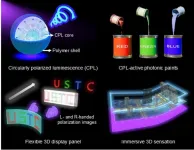
Printable circularly polarized luminescence materials enables flexible, stereoscopic displaying
2023-10-25
Flexible three-dimensional (3D) displays drive innovation in the next-generation display technology, as they allow for the creation of versatile and adaptable displays that can be easily manipulated and customized to fit various viewing scenarios.
Printing circularly polarized luminescence (CPL, generated by the intrinsic chirality of luminescent materials) materials on moving, deformable and free-form surfaces serves to fabricate large-scale and high-performance integral imaging 3D displays: CPL provides a helping hand using its unusual optical rotation characteristics to achieve considerable contrast ratio and wide viewing angle.
Scientists led by Professor ...
Zika infection in pregnant macaques slows fetal growth
2023-10-25
Zika virus infection in pregnant rhesus macaques slows fetal growth and affects how infants and mothers interact in the first month of life, according to a new study from researchers at the California National Primate Research Center at the University of California, Davis. The work, published Oct. 25 in Science Translational Medicine, has implications for both humans exposed to Zika virus and for other viruses that can cross the placenta, including SARS-CoV2, responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Initially I thought this was a story about Zika, but as I looked at the results I think this is also a story about ...
Chloroplasts do more than photosynthesis: They’re also a key player in plant immunity
2023-10-25
Scientists have long known that chloroplasts help plants turn the sun’s energy into food, but a new study, led by plant biologists at the University of California, Davis, shows that they are also essential for plant immunity to viral and bacterial pathogens.
Chloroplasts are generally spherical, but a small percentage of them change their shape and send out tube-like projections called “stromules.” First observed over a century ago, the biological function of stromules has remained ...
Mystery of the Martian core solved
2023-10-25
For four years, NASA’s InSight lander recorded tremors on Mars with its seismometer. Researchers at ETH Zurich collected and analysed the data transmitted to Earth to determine the planet’s internal structure. “Although the mission ended in December 2022, we’ve now discovered something very interesting,” says Amir Khan, a Senior Scientist in the Department of Earth Sciences at ETH Zurich.
An analysis of recorded marsquakes, combined with computer simulations, paint ...
Book examines history of standardized tests in American schools, why they persist
2023-10-25
LAWRENCE — For the past 50 years, standardized tests have been the norm in American schools, a method proponents say determines which schools are not performing and helps hold educators accountable. Yet for the past 20 years, it has become clear that testing has failed to improve education or hold many accountable, according to a University of Kansas researcher whose new book details its history.
“An Age of Accountability: How Standardized Testing Came to Dominate American Schools and Compromise Education” by John Rury, professor emeritus of educational leadership & policy studies at KU, tells the story of how testing became ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] In Prehispanic Cancun, immigrants were treated just like Maya localsFamilies moved residence across Mesoamerica and integrated into new societies