(Press-News.org) Death rates after major surgery are similar regardless of whether a male or female surgeon operates on a male or female patient, finds a large US study published by The BMJ today.
The differences seen were small and not clinically meaningful and the researchers say their findings should help improve processes and patterns of care for all patients.
Gender concordance between patients and physicians (when the physician and patient are of the same sex) is generally linked to higher quality care processes and improved patient outcomes through more effective communication, reduced (implicit and explicit) sex and gender bias, and better rapport.
But evidence is limited about the effect of patient and surgeon gender concordance on outcomes of patients undergoing a surgical procedure.
To address this, researchers set out to determine whether patient-surgeon gender concordance is associated with death after surgery in the United States.
Their theory was that patients treated by surgeons of the same gender would have a lower postoperative death rate than patients treated by gender discordant surgeons.
They analysed data for almost 3 million Medicare patients aged 65-99 years who underwent one of 14 common major urgent or non-urgent (elective) surgeries between 2016 and 2019 including coronary artery bypass surgery, knee or hip replacement, hysterectomy, liver or lung resection, and thyroidectomy.
Death after surgery was defined as death within 30 days of the operation.
Adjustments were made for patient characteristics (such as age, race and underlying conditions), surgeon characteristics (such as age, years in practice and number of operations performed) and hospital fixed effects (effectively comparing patients within the same hospital).
Of 2,902,756 patients who had surgery, 1,287,845 (44%) had operations done by surgeons of the same gender (1,201,712 (41%) male patient and male surgeon and 86,133 (3%) female patient and female surgeon) and 1,614,911 (56%) were by surgeons of different gender (52,944 (1.8%) male patient and female surgeon and 1,561,967 (54%) female patient and male surgeon).
For urgent and elective procedures combined, the adjusted death rate 30 days after surgery was 2% for male patients treated by male surgeons, 1.7% for male patients treated by female surgeons, 1.5% for female patients treated by male surgeons, and 1.3% for female patients treated by female surgeons.
For elective procedures, female surgeons had slightly lower patient death rates (0.5%) than male surgeons (0.8%), whereas no difference in patient mortality was seen for urgent surgeries.
Several mechanisms could explain this small effect for elective procedures, say the authors. For example, female surgeons may abide by clinical guidelines more than male surgeons, or might have better communication and increased attention to postoperative care than male surgeons, which could affect patient death rates.
What’s more, as elective surgeries allow patients to choose their own surgeon, they are more prone to influence from other factors compared with urgent procedures where patients are assigned to on-call surgeons, they add.
This is an observational study, so can’t establish cause, and the researchers stress that other unmeasured social and cultural factors may have influenced their results. What’s more, they say their findings may not apply to younger populations, patients who receive less common procedures, or patients in other countries.
Nevertheless, they say understanding the underlying mechanisms of this observation “allows the opportunity to improve processes and patterns of care for all patients.”
They add: “Ongoing qualitative and quantitative research will better delineate how surgeon and patient gender, along with race and other aspects of shared identity, affect quality of care and outcomes after surgery.”
END
Death rates after surgery similar regardless of patient-surgeon gender match
Findings should help improve processes and patterns of care for all patients
2023-11-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
COVID vaccination before infection strongly linked to reduced risk of developing long covid
2023-11-23
Receiving at least one dose of a covid-19 vaccine before the first infection is strongly associated with a reduced risk of developing post-covid-19 condition, commonly known as long covid, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The findings, based on data for more than half a million Swedish adults, show that unvaccinated individuals were almost four times as likely to be diagnosed with long covid than those who were vaccinated before first infection.
The researchers stress that causality ...
Iron infusion before bowel surgery reduces need for blood transfusion
2023-11-23
Change in clinical practice would have clear benefits for patients undergoing major bowel surgery, according to analysis conducted by researchers from UCL and the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital.
The study, published in The British Journal of Surgery, provides evidence that giving iron intravenously before colorectal surgery improves outcomes for patients, reducing the need for blood transfusion by 33%.
Anaemia is a common problem in patients undergoing bowel surgery due to bleeding from the gut and blood loss during the operation. Anaemia is also associated ...
The first report on telomere-to-telomere gap-free reference genome of wild blueberry (Vaccinium duclouxii)
2023-11-23
Blueberry, a common Vaccinium species with small-sized berries, is known for its delicious taste, balanced sweetness and acidity, and rich nutritional content. It is abundant in various vitamins and antioxidants. However, the limited genetic resources for cultivated blueberries have significantly hindered their development and utilization. Therefore, utilizing wild blueberries' genetic resources for breeding is paramount to enhancing the resilience and quality of cultivated varieties.
Vaccinium duclouxii, native to the southwestern region of China, is an endemic wild blueberry ...
Chinese-Russian cooperation has strengthened significantly in the past 30 years, analysis shows
2023-11-22
Chinese and Russian cooperation has grown significantly in the past three decades thanks to joint work on energy trade, politics and official visits, analysis shows.
There was a ‘limited’ Sino–Russian cooperation intensity in 1992–1995, which grew from then until 2007 and then rose. The bilateral relationship grew progressively, with no exponential growth or peaks, according to the study.
There were no or dramatic changes following Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea.
The ...
Researchers develop new method for prenatal genetic testing
2023-11-22
A team of investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have developed a non-invasive genetic test that can screen the blood of pregnant individuals to survey all genes for fetal DNA sequence variants. The team evaluated the test by examining blood samples from 51 pregnant persons, finding that the test was able to capture variants that were inherited from the mother as well as new variants that were not present in the mother and associated with prenatal diagnoses. ...
Genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in Kazakh women
2023-11-22
“Our study may reveal previously uncharacterized population-specific variants that may increase the risk of BC in the Kazakh population.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on October 4, 2023, entitled, “Determination of genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in women of Kazakh ethnicity.”
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common type of cancer among women in Kazakhstan. To date, little data are available on the spectrum of genetic variation in Kazakh women with BC.
In this new study, researchers Gulnur Zhunussova, Nazgul Omarbayeva, ...
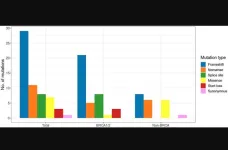
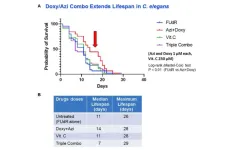
Mitochondria-targeting antibiotics extend lifespan in C. elegans
2023-11-22
“Our ultimate goal is to find existing FDA-approved drugs and dietary supplements that can not only increase lifespan but also improve healthspan.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Antibiotics that target mitochondria extend lifespan in C. elegans.”
Aging is a continuous degenerative process caused by a progressive decline of cell and tissue functions in an organism. It is induced by the accumulation of damage that affects normal cellular processes, ...
Adding a few servings of whole grains linked to slower memory decline in Black people
2023-11-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 22, 2022
MINNEAPOLIS – Black people who eat more foods with whole grains, including some breads and cereals, quinoa, and popcorn, may have a slower rate of memory decline compared to Black people who eat fewer whole grain foods, according to a study published in the November 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The researchers did not see a similar trend in white participants.
The study does not prove that eating more whole grains slows memory decline; it only shows an association.
The study found that among Black ...
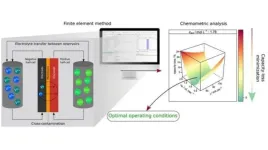
Researchers obtain promising results against capacity loss in vanadium batteries
2023-11-22
An article by researchers at the Center for Development of Functional Materials (CDMF) in Brazil describes a successful strategy to mitigate charge capacity loss in vanadium redox flow batteries, which are used by electric power utilities among other industries and can accumulate large amounts of energy. The article is published in the Chemical Engineering Journal.
CDMF is a Research, Innovation and Dissemination Center (RIDC) funded by FAPESP and hosted by the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in São Paulo state.
The study involved computer ...
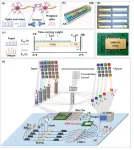
Photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network
2023-11-22
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances, 10.29026/oea.2023.230140 discusses photonic integrated neuro-synaptic core for convolutional spiking neural network.
Brain science and brain-like intelligence are the cutting-edge science and technology that countries all over the world compete to seize. The rapid rise and vigorous development of emerging fields such as artificial intelligence, 5G/6G, big data, autonomous driving, and the Internet of Things has led to the explosive growth of global data. Due to the memory wall effect, the conventional von Neumann architecture performs low energy efficiency. Electronic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Death rates after surgery similar regardless of patient-surgeon gender matchFindings should help improve processes and patterns of care for all patients