The Chinese team completed the genome assembly of Cornus wilsoniana
2023-11-23
(Press-News.org)
Cornus wilsoniana (2n=22) is a common shrub in the northern temperate zone of China. It blooms white flowers in spring and produces purple-black berries in autumn. This tree has a unique mottled bark texture that makes it particularly eye-catching in winter, earning it the common name "ghost dogwood". Due to its peeling bark in winter, it is commonly known as "Guangpi tree" in China. The fruit of C. wilsoniana is rich in oil and can be used to extract edible oil. The oil content of the fruit can reach up to 55% and contains abundant unsaturated fatty acids. Compared to other edible oils, it has hypolipidemic effects. Therefore, the fruit oil of C. wilsoniana can not only serve as a well-balanced dietary oil, but also helps control blood lipids. Meanwhile, owing to its strong stress resistance, it can play a huge role in afforestation, sand-fixation and soil conservation.
In September 2023,Horticulture Research published an article titled "A chromosome-level genome assembly provides insights into Cornus wilsoniana evolution, oil biosynthesis and floral bud development", which was completed by the collaboration between Prof. He Zhenxiang, Prof. Dijun Chen, Prof. Ming Chen and Prof. Liangbo Zhang's group. This study accomplished the chromosome-level genome assembly of C. wilsoniana, laying the foundation for evolutionary analysis and genetic research of key traits in this species.
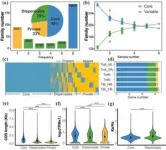
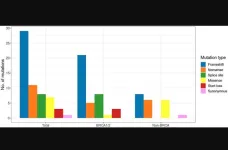
This study obtained the chromosome-level genome sequence of C. wilsoniana using PacBio HiFi and Hi-C sequencing technologies. The genome size is about 843.51 Mb, with a contig N50 of 4.49 Mb and scaffold N50 of 78.00 Mb. A total of 30,474 protein-coding genes were annotated. Comparative genomics analysis identified that the genome of C. wilsoniana has experienced one whole genome triplication event (WGT-γ, 115.86 Mya) and one whole genome duplication event (WGD, 44.90 Mya). The researchers also explored the origin of C. wilsoniana chromosomes and reconstructed its karyotype evolution history. Collinearity analysis revealed that C. wilsoniana shares similar genome structures with C. controversa (2n=20), and they both belong to the genus Cornus in the Cornaceae family, completing divergence about 12.46 Mya. Transcriptomic analysis found that FAD2 gene family members play a key role in regulating the oleic to linoleic acid ratio in C. wilsoniana oil. Additionally, 33 MADS transcription factor genes highly correlated with the flowering process of C. wilsoniana were identified by transcriptomic and metabolomic techniques. The above research provides valuable resources for germplasm innovation and genetic improvement of C. wilsoniana.
###
References
Authors
Zhenxiang He, Haoyu Chao, Xinkai Zhou, Qingyang Ni, Yueming Hu, Ranran Yu, Minghuai Wang, Changzhu Li, Jingzhen Chen, Yunzhu Chen, Yong Chen, Chunyi Cui, Liangbo Zhang, Ming Chen, Dijun Chen
Affiliations
State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, School of Life Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China
About Dijun Chen
Group Leader of Bioinformatics, School of Life Sciences, Nanjing University
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-11-23
Does patient-surgeon gender concordance lead to lower patient mortality? Mostly no, UCLA-led research suggests
New research finds little evidence that post-surgical patient mortality is lower when patient and surgeon are the same gender.
While gender concordance has been shown to improve patient care in other health specialties, evidence has been limited when it comes to concordance between patient and surgeon. This study shows that gender concordance was associated with lower mortality for female patients, but higher mortality for male patients—patient mortality was the lowest for ...
2023-11-23
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have evaluated the possibility of alerting drones equipped with automated external defibrillators (AED) to patients with suspected cardiac arrest. In more than half of the cases, the drones were ahead of the ambulance by an average of three minutes. In cases where the patient was in cardiac arrest, the drone-delivered defibrillator was used in a majority of cases. The results have been published in the journal The Lancet Digital Health.
"The use of an AED is the single most important factor in saving lives. We have been deploying drones equipped with AED since the summer ...
2023-11-23
Death rates after major surgery are similar regardless of whether a male or female surgeon operates on a male or female patient, finds a large US study published by The BMJ today.
The differences seen were small and not clinically meaningful and the researchers say their findings should help improve processes and patterns of care for all patients.
Gender concordance between patients and physicians (when the physician and patient are of the same sex) is generally linked to higher quality care processes and improved patient outcomes through more effective ...
2023-11-23
Receiving at least one dose of a covid-19 vaccine before the first infection is strongly associated with a reduced risk of developing post-covid-19 condition, commonly known as long covid, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The findings, based on data for more than half a million Swedish adults, show that unvaccinated individuals were almost four times as likely to be diagnosed with long covid than those who were vaccinated before first infection.
The researchers stress that causality ...
2023-11-23
Change in clinical practice would have clear benefits for patients undergoing major bowel surgery, according to analysis conducted by researchers from UCL and the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital.
The study, published in The British Journal of Surgery, provides evidence that giving iron intravenously before colorectal surgery improves outcomes for patients, reducing the need for blood transfusion by 33%.
Anaemia is a common problem in patients undergoing bowel surgery due to bleeding from the gut and blood loss during the operation. Anaemia is also associated ...
2023-11-23
Blueberry, a common Vaccinium species with small-sized berries, is known for its delicious taste, balanced sweetness and acidity, and rich nutritional content. It is abundant in various vitamins and antioxidants. However, the limited genetic resources for cultivated blueberries have significantly hindered their development and utilization. Therefore, utilizing wild blueberries' genetic resources for breeding is paramount to enhancing the resilience and quality of cultivated varieties.
Vaccinium duclouxii, native to the southwestern region of China, is an endemic wild blueberry ...
2023-11-22
Chinese and Russian cooperation has grown significantly in the past three decades thanks to joint work on energy trade, politics and official visits, analysis shows.
There was a ‘limited’ Sino–Russian cooperation intensity in 1992–1995, which grew from then until 2007 and then rose. The bilateral relationship grew progressively, with no exponential growth or peaks, according to the study.
There were no or dramatic changes following Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea.
The ...
2023-11-22
A team of investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH), and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have developed a non-invasive genetic test that can screen the blood of pregnant individuals to survey all genes for fetal DNA sequence variants. The team evaluated the test by examining blood samples from 51 pregnant persons, finding that the test was able to capture variants that were inherited from the mother as well as new variants that were not present in the mother and associated with prenatal diagnoses. ...
2023-11-22
“Our study may reveal previously uncharacterized population-specific variants that may increase the risk of BC in the Kazakh population.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on October 4, 2023, entitled, “Determination of genetic predisposition to early breast cancer in women of Kazakh ethnicity.”
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common type of cancer among women in Kazakhstan. To date, little data are available on the spectrum of genetic variation in Kazakh women with BC.
In this new study, researchers Gulnur Zhunussova, Nazgul Omarbayeva, ...
2023-11-22
“Our ultimate goal is to find existing FDA-approved drugs and dietary supplements that can not only increase lifespan but also improve healthspan.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 21, entitled, “Antibiotics that target mitochondria extend lifespan in C. elegans.”
Aging is a continuous degenerative process caused by a progressive decline of cell and tissue functions in an organism. It is induced by the accumulation of damage that affects normal cellular processes, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] The Chinese team completed the genome assembly of Cornus wilsoniana